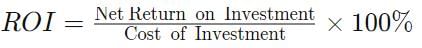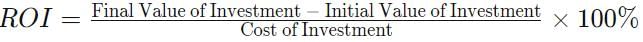Test: Business Arithmetic- 2 - Commerce MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Test: Business Arithmetic- 2
Amul Milk Pvt. Ltd. is conducting campus placement to hire new workforce for their new branch in Patiala, Punjab. The HR team went to a college campus nearby to select around 20 candidates. While conducting the personal interviews of selected 25 candidates, the HR asked one of them to explain what does he understand by the term ‘Production Cycle’. He responded confidently by saying that it is the time period between receiving the raw material and converting them into final finished goods.
Considering the candidate’s response, state whether his statement is true or false.
Considering the candidate’s response, state whether his statement is true or false.
Sohan’s firm has a capital of ₹ 10,00,000; Sales of ₹ 5,00,000; Gross profit of ₹ 2,00,000 and Expenses of ₹ 1,00,000. He has hired a chartered account to work and manage his accounts. The CA, while working on the sales and profits, etc. found that the return on investment for the firm will be 10%. Sohan doubted the calculation of the CA. Keeping in view the above scenario, state whether the CA’s calculation was true or false.
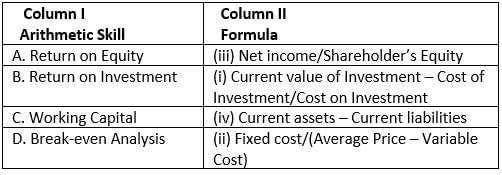
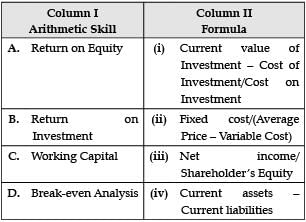
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct formulae in Column 2.

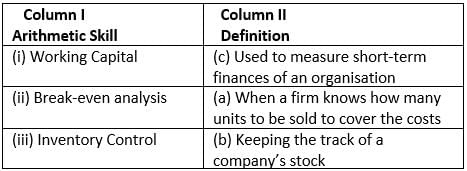
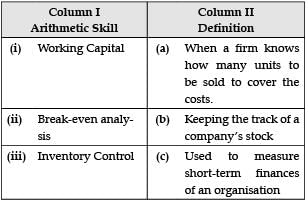
Given are the arithmetic skills in Column 1. Match them with their correct definition in Column 2.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Rent is an example of variable cost.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross margin and gross profit are one and the same.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Sales mix is the proportion in which two or more products are sold.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Working capital is required to meet day-to-day expenses and to facilitate smooth functioning of the business.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Operating Cycle is also referred to as the Cash Community Cycle.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Current liabilities represent short-term source of funds.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. The Cash Conversion Cycle is the length of time between a firm’s purchase of inventory and the receipt of cash from accounts receivable.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Gross working capital is the sum total of all current liabilities of the business.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Longer the operating cycle, working capital quantum is more.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Usage rate is the average rate at which the inventory is drawn over a period.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Low ROI indicates more efficient management and utilization of total funds invested.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Order lead time is an average time that elapses between placing an order and receiving the goods.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. Reorder point = Average daily usage rate × Lead time in days.
State Whether the Following Statements are True or False.
Q. ROE represents the quantity of an item which is most economical to order when fresh supplies are required.
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|