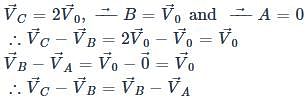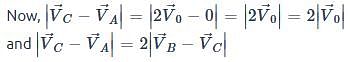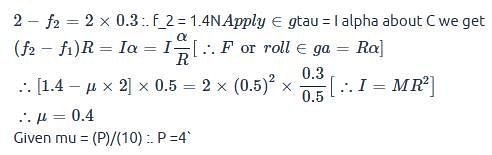JEE Previous Year Questions: Rotational Motion - JEE MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - JEE Previous Year Questions: Rotational Motion
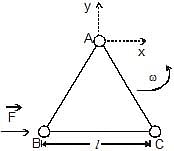
Three particles A, B and C, each of mass m, are connected to each other by three massless rigid rods to form a rigid, equilateral triangular body of side l. This body is placed on a horizontal frictionless table (x-y plane) and is hinged to it at the point A so that it can move without friction about the vertical axis through A (see figure). The body is set into rotational motion on the table about A with a constant angular velocity w.
[JEE'(Scr) 2002]
(a) Find the magnitude of the horizontal force exerted by the hinge on the body
(b) At time T, when the side BC is parallel to the x-axis, a force F is applied on B along BC (as shown). Obtain the x-component and the y-component of the force exterted by the hinge on the body, immediately after time T.
A particle is moving in a horizontal uniform circular motion. The angular momentum of the particle is conserved about the point :
[JEE'(Scr) 2003]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two particles each of mass M are connected by a massless rod of length l. The rod is lying on the smooth surface. If one of the particle is given an impulse MV as shown in the figure then angular velocity of the rod would be
[JEE'(Scr) 2003]

A disc is rolling (without slipping) on a horizontal surface. C is its center and Q and P are two points equidistant from C. Let Vp, VQ and VC be the magnitude of velocities of points P, Q and C respectively, then
[JEE'(Scr) 2004]
A child is standing with folded hands at the centre of a platform rotating about its central axis. The kinetic energy of the system is K. The child now stretches his arms so that the moment of inertia of the system doubles. The kinetic energy of the system now is
[JEE'(Scr) 2004]
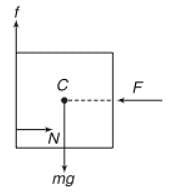
A block of mass m is held fixed against a wall by a applying a hor izontal force F. Which of the following option is incorrect :
[JEE'(Scr) 2005]
A disc has mass 9M. A hole of radius R/3 is cut from it as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of remaining part about an axis passing through the centre `O' of the disc and perpendicular to the plane of the disc is :
[JEE'(Scr) 2005]
A particle moves in circular path with decreasing speed. Which of the following is correct
A solid sphere of mass M, radius R and having moment of inertia about an axis passing through the centre of mass as I, is recast into a disc of thickness t, whose moment of inertia about an axis passing through its edge and perpendicular to its plane remains I. Then, radius of the disc will be
[JEE' 2006]
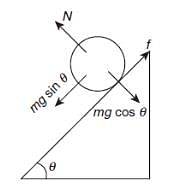
A solid cylinder of mass m and radius r is rolling on a rough inclined plane of inclination q. The coefficient of friction between the cylinder and incline is m. Then
[JEE' 2006]
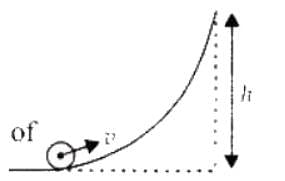
A ball moves over a fixed track as shown in the figure. From A to B the ball rolls without slipping. Surface BC is frictionless. KA, KB and KC are kinetic energies of the ball at A, B and C, respectively. Then
[JEE' 2006]
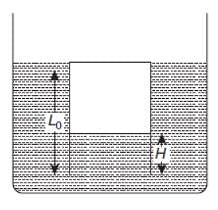
There is a rectangular plate of mass M kg of dimensions (a × b). The plate is held in horizontal position by striking n small balls each of mass m per unit area per unit time. These are striking in the shaded half region of the plate. The balls are colliding elastically with velocity v. What is v ?
[JEE' 2006]
It is given n = 100, M = 3 kg, m = 0.01 kg; b = 2 m, a = 1m; g = 10 m/s2.
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2w using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance x1. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity w by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2. Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
The ratio x1/x2 is
[JEE' 2007]
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2w using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance x1. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity w by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2. Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
When disc B is brought in contact with disc A, they acquire a common angular velocity in time t. The average frictional torque on one disc by the other during this period is
[JEE' 2007]
Two discs A and B are mounted coaxially on a vertical axle. The discs have moments of inertia I and 2I respectively about the common axis. Disc A is imparted an initial angular velocity 2w using the entire potential energy of a spring compressed by a distance x1. Disc B is imparted an angular velocity w by a spring having the same spring constant and compressed by a distance x2. Both the discs rotate in the clockwise direction.
The loss of kinetic energy during the above process is
[JEE' 2007]
A small object of uniform density rolls up a curved surface with an initial velocity v. It reaches up to a maximum height of 3v2 / (4g) with respect to the initial position. The object is
[JEE' 2007]
Statement - 1: If there is no external torque on a body about its center of mass, then the velocity of the center of mass remains constant
because
Statement - 2: The linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant.
[JEE 2007]
Statement - 1: Two cylinders, one hollow (metal) and the other solid (wood) with the same mass and identical dimensions are simultaneously allowed to roll without slipping down an inclined plane from the same height. The hollow cylinder will reach the bottom of the inclined plane first.
Statement - 2: By the principle of conservation of energy, the total kinetic energies of both the cylinders are identical when they reach the bottom of the incline.
[JEE-2008]
If the resultant of all the external forces acting on a system of particles is zero, then from an inertial frame, one can surely say that
[JEE 2009]
A sphere is rolling without slipping on a fixed horizontal plane surface. In the figure A is the point of contact, B is the centre of the sphere and C is its topmost point Then,
[JEE 2009]
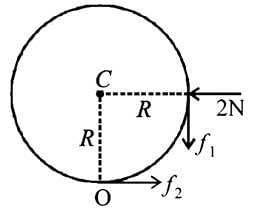
A boy is pushing a ring of mass 2 kg and radius 0.5 m with a stick as shown in the figure. The stick applies a force of 2 N on the ring and rolls it without slipping with an acceleration of 0.3 m/s2. The coefficient of friction between the ground and ring is large enough that rolling always occurs and the coefficient of friction between the stick and the ring is (P/10). The value of P is?
[JEE 2011]
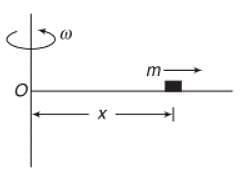
A thin uniform rod, pivoted at O is rotating in the horizontal plane with constant angular speed w, as shown in the figure. At time t = 0, small insect starts from O and moves with constant speed n with respect to the rod towards the other end. it reaches the end of the rod at t = T and stops. The angular speed of the system remains w throughout. The magnitude of the torque on the system about O, as a function of time is best represented by which plot?
[JEE 2012]
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|



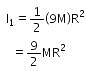

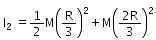
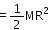



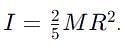
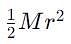
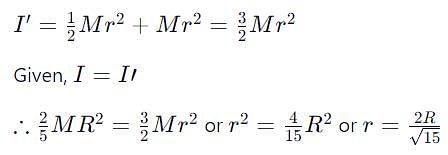
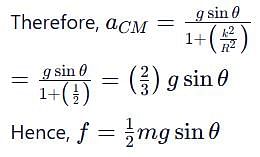
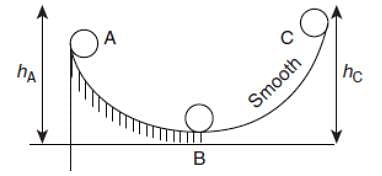
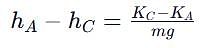

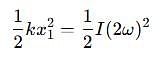
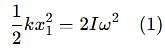
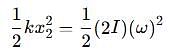
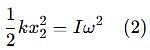
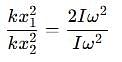
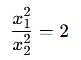
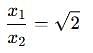
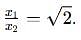
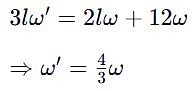
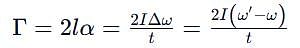
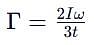
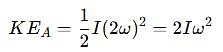
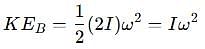
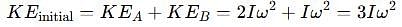
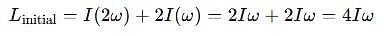
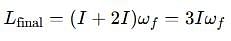
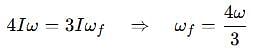
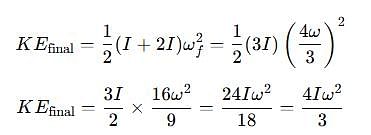
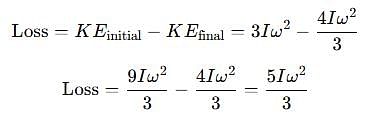
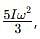 which corresponds to Option B:
which corresponds to Option B: 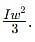
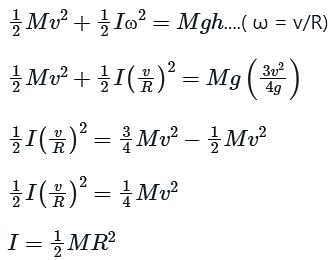
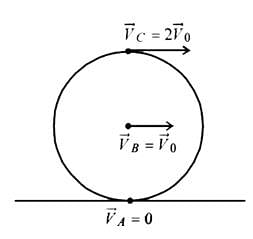
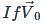 is the velocity of centre of the sphere, then
is the velocity of centre of the sphere, then