Case Based Questions Test: Biological Classification - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Case Based Questions Test: Biological Classification
Basketball and projectile
Using the laws of physics, it is possible to make a successful jump shot in basketball every time. The trajectory of a basketball is always is a parabola when it is launched up into the air, and this is due to the affects of gravity as well as the force put on the ball by the player and its property follows the properties of a projectile.

The ball's velocity changes as it moves through the air, but the velocity of the first half of the path matches with the last half of the path. It may deviate from its path if the ball collides with either the backboard or another player interfering with its path. From the information of the height of the player, the horizontal distance and height of the hoop, the player can easily calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for a sure success. If player’s height is 1.27 meters standing at a distance of 2 meters from the hoop which is at an height of 3.05 meters, he needs an angle of 55° and velocity of the ball 7 m/s to be imparted to make his shot a success. (If he uses a smaller angle has to shoot with a greater velocity.) If he stands 6 meters distance from the hoop, he needs an angle 60° and a velocity 9.5 m/s to be successful. To improve chances of an accurate shot, often a player includes a backspin on the ball as he launches it for a shot. The backspin ensures that the ball enters the hoop, especially if the shot is a "soft shot." Soft shot is when the ball is shot at a low angle and low velocity, the player adds a backspin because if the ball winds up hitting the rim, the spin will help it to enter the hoop. The backspin changes the velocity direction (once it hits the rim) to the opposite direction of the rim rather than bouncing it out.
The trajectory of a basketball is always is a

Basketball and projectile
Using the laws of physics, it is possible to make a successful jump shot in basketball every time. The trajectory of a basketball is always is a parabola when it is launched up into the air, and this is due to the affects of gravity as well as the force put on the ball by the player and its property follows the properties of a projectile.

The ball's velocity changes as it moves through the air, but the velocity of the first half of the path matches with the last half of the path. It may deviate from its path if the ball collides with either the backboard or another player interfering with its path. From the information of the height of the player, the horizontal distance and height of the hoop, the player can easily calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for a sure success. If player’s height is 1.27 meters standing at a distance of 2 meters from the hoop which is at an height of 3.05 meters, he needs an angle of 55° and velocity of the ball 7 m/s to be imparted to make his shot a success. (If he uses a smaller angle has to shoot with a greater velocity.) If he stands 6 meters distance from the hoop, he needs an angle 60° and a velocity 9.5 m/s to be successful. To improve chances of an accurate shot, often a player includes a backspin on the ball as he launches it for a shot. The backspin ensures that the ball enters the hoop, especially if the shot is a "soft shot." Soft shot is when the ball is shot at a low angle and low velocity, the player adds a backspin because if the ball winds up hitting the rim, the spin will help it to enter the hoop. The backspin changes the velocity direction (once it hits the rim) to the opposite direction of the rim rather than bouncing it out.
To calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for an accurate shot the required information are

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Basketball and projectile
Using the laws of physics, it is possible to make a successful jump shot in basketball every time. The trajectory of a basketball is always is a parabola when it is launched up into the air, and this is due to the affects of gravity as well as the force put on the ball by the player and its property follows the properties of a projectile.
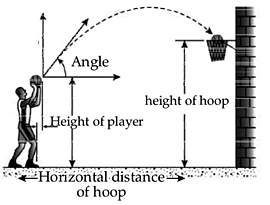
The ball's velocity changes as it moves through the air, but the velocity of the first half of the path matches with the last half of the path. It may deviate from its path if the ball collides with either the backboard or another player interfering with its path. From the information of the height of the player, the horizontal distance and height of the hoop, the player can easily calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for a sure success. If player’s height is 1.27 meters standing at a distance of 2 meters from the hoop which is at an height of 3.05 meters, he needs an angle of 55° and velocity of the ball 7 m/s to be imparted to make his shot a success. (If he uses a smaller angle has to shoot with a greater velocity.) If he stands 6 meters distance from the hoop, he needs an angle 60° and a velocity 9.5 m/s to be successful. To improve chances of an accurate shot, often a player includes a backspin on the ball as he launches it for a shot. The backspin ensures that the ball enters the hoop, especially if the shot is a "soft shot." Soft shot is when the ball is shot at a low angle and low velocity, the player adds a backspin because if the ball winds up hitting the rim, the spin will help it to enter the hoop. The backspin changes the velocity direction (once it hits the rim) to the opposite direction of the rim rather than bouncing it out.
Why backspin applied on basketball while launching it for a shot?

Projectile motion to orbital motion:
If we throw a ball horizontally with a speed 8000 m/s off the surface of the Earth (and there are no obstructions in the way) how far will it travel in the vertical and horizontal directions in 1 second? (Ignore the air resistance)
vx = 8000 m/s
t = 1s
So, horizontally it will move
vyt = 8000 m
Vy = 0
t = 1s
g = 10 m/s2
So, vertically it will move down
1/2 gt2 = 5 m
But the curvature of the Earth changes by 5m in every 8000 m. So, will the ball ever touch the earth? The answer is NO! The ball will continually falls in free fall around the Earth and ultimately it will be orbiting around the Earth!

If v = 8000 m/s the orbit will be circular.
If v is within the range 8000 m/s to 11200 m/s, then the orbit will be elliptical. 11200 m/s is the velocity required to escape the earth. Escape velocity is the velocity of the projectile body that is sufficient for it to escape the gravitational attraction of earth. 42500 m/s is the velocity required to escape the Solar System!
What is the upper limit of the speed for a particle thrown horizontally so that it remains as a projectile?
Projectile motion to orbital motion:
If we throw a ball horizontally with a speed 8000 m/s off the surface of the Earth (and there are no obstructions in the way) how far will it travel in the vertical and horizontal directions in 1 second? (Ignore the air resistance)
vx = 8000 m/s
t = 1s
So, horizontally it will move
vyt = 8000 m
Vy = 0
t = 1s
g = 10 m/s2
So, vertically it will move down
1/2 gt2 = 5 m
But the curvature of the Earth changes by 5m in every 8000 m. So, will the ball ever touch the earth? The answer is NO! The ball will continually falls in free fall around the Earth and ultimately it will be orbiting around the Earth!
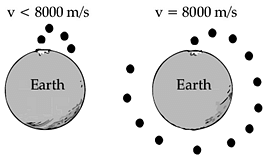
If v = 8000 m/s the orbit will be circular.
If v is within the range 8000 m/s to 11200 m/s, then the orbit will be elliptical. 11200 m/s is the velocity required to escape the earth. Escape velocity is the velocity of the projectile body that is sufficient for it to escape the gravitational attraction of earth. 42500 m/s is the velocity required to escape the Solar System!
When a particle orbits the earth in a circular or elliptical path then the particle
Projectile motion to orbital motion:
If we throw a ball horizontally with a speed 8000 m/s off the surface of the Earth (and there are no obstructions in the way) how far will it travel in the vertical and horizontal directions in 1 second? (Ignore the air resistance)
vx = 8000 m/s
t = 1s
So, horizontally it will move
vyt = 8000 m
Vy = 0
t = 1s
g = 10 m/s2
So, vertically it will move down
1/2 gt2 = 5 m
But the curvature of the Earth changes by 5m in every 8000 m. So, will the ball ever touch the earth? The answer is NO! The ball will continually falls in free fall around the Earth and ultimately it will be orbiting around the Earth!

If v = 8000 m/s the orbit will be circular.
If v is within the range 8000 m/s to 11200 m/s, then the orbit will be elliptical. 11200 m/s is the velocity required to escape the earth. Escape velocity is the velocity of the projectile body that is sufficient for it to escape the gravitational attraction of earth. 42500 m/s is the velocity required to escape the Solar System!
Escape velocity from earth is ............... escape velocity from solar system
Projectile motion to orbital motion:
If we throw a ball horizontally with a speed 8000 m/s off the surface of the Earth (and there are no obstructions in the way) how far will it travel in the vertical and horizontal directions in 1 second? (Ignore the air resistance)
vx = 8000 m/s
t = 1s
So, horizontally it will move
vyt = 8000 m
Vy = 0
t = 1s
g = 10 m/s2
So, vertically it will move down
1/2 gt2 = 5 m
But the curvature of the Earth changes by 5m in every 8000 m. So, will the ball ever touch the earth? The answer is NO! The ball will continually falls in free fall around the Earth and ultimately it will be orbiting around the Earth!

If v = 8000 m/s the orbit will be circular.
If v is within the range 8000 m/s to 11200 m/s, then the orbit will be elliptical. 11200 m/s is the velocity required to escape the earth. Escape velocity is the velocity of the projectile body that is sufficient for it to escape the gravitational attraction of earth. 42500 m/s is the velocity required to escape the Solar System!
What is the value of escape velocity for earth?
Projectile motion to orbital motion:
If we throw a ball horizontally with a speed 8000 m/s off the surface of the Earth (and there are no obstructions in the way) how far will it travel in the vertical and horizontal directions in 1 second? (Ignore the air resistance)
vx = 8000 m/s
t = 1s
So, horizontally it will move
vyt = 8000 m
Vy = 0
t = 1s
g = 10 m/s2
So, vertically it will move down
1/2 gt2 = 5 m
But the curvature of the Earth changes by 5m in every 8000 m. So, will the ball ever touch the earth? The answer is NO! The ball will continually falls in free fall around the Earth and ultimately it will be orbiting around the Earth!
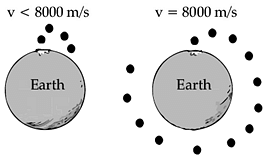
If v = 8000 m/s the orbit will be circular.
If v is within the range 8000 m/s to 11200 m/s, then the orbit will be elliptical. 11200 m/s is the velocity required to escape the earth. Escape velocity is the velocity of the projectile body that is sufficient for it to escape the gravitational attraction of earth. 42500 m/s is the velocity required to escape the Solar System!
Curvature of the Earth changes by………... in every
Basketball and projectile
Using the laws of physics, it is possible to make a successful jump shot in basketball every time. The trajectory of a basketball is always is a parabola when it is launched up into the air, and this is due to the affects of gravity as well as the force put on the ball by the player and its property follows the properties of a projectile.
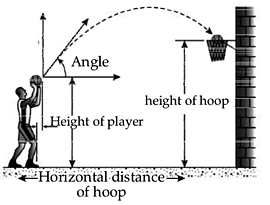
The ball's velocity changes as it moves through the air, but the velocity of the first half of the path matches with the last half of the path. It may deviate from its path if the ball collides with either the backboard or another player interfering with its path. From the information of the height of the player, the horizontal distance and height of the hoop, the player can easily calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for a sure success. If player’s height is 1.27 meters standing at a distance of 2 meters from the hoop which is at an height of 3.05 meters, he needs an angle of 55° and velocity of the ball 7 m/s to be imparted to make his shot a success. (If he uses a smaller angle has to shoot with a greater velocity.) If he stands 6 meters distance from the hoop, he needs an angle 60° and a velocity 9.5 m/s to be successful. To improve chances of an accurate shot, often a player includes a backspin on the ball as he launches it for a shot. The backspin ensures that the ball enters the hoop, especially if the shot is a "soft shot." Soft shot is when the ball is shot at a low angle and low velocity, the player adds a backspin because if the ball winds up hitting the rim, the spin will help it to enter the hoop. The backspin changes the velocity direction (once it hits the rim) to the opposite direction of the rim rather than bouncing it out.
When the basketball deviates from its parabolic path?
Basketball and projectile
Using the laws of physics, it is possible to make a successful jump shot in basketball every time. The trajectory of a basketball is always is a parabola when it is launched up into the air, and this is due to the affects of gravity as well as the force put on the ball by the player and its property follows the properties of a projectile.
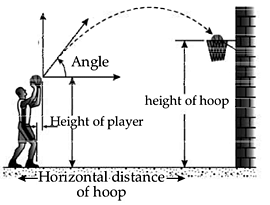
The ball's velocity changes as it moves through the air, but the velocity of the first half of the path matches with the last half of the path. It may deviate from its path if the ball collides with either the backboard or another player interfering with its path. From the information of the height of the player, the horizontal distance and height of the hoop, the player can easily calculate the speed to be imparted to the ball and the angle for a sure success. If player’s height is 1.27 meters standing at a distance of 2 meters from the hoop which is at an height of 3.05 meters, he needs an angle of 55° and velocity of the ball 7 m/s to be imparted to make his shot a success. (If he uses a smaller angle has to shoot with a greater velocity.) If he stands 6 meters distance from the hoop, he needs an angle 60° and a velocity 9.5 m/s to be successful. To improve chances of an accurate shot, often a player includes a backspin on the ball as he launches it for a shot. The backspin ensures that the ball enters the hoop, especially if the shot is a "soft shot." Soft shot is when the ball is shot at a low angle and low velocity, the player adds a backspin because if the ball winds up hitting the rim, the spin will help it to enter the hoop. The backspin changes the velocity direction (once it hits the rim) to the opposite direction of the rim rather than bouncing it out.
Why backspin applied on basketball while launching it for a shot?
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|

















