Assertion & Reason Test: Amines - NEET MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Assertion & Reason Test: Amines
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amines gives poly substituted product.
Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
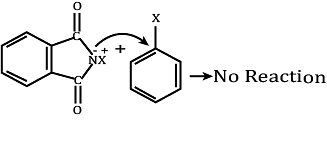
Assertion (A): Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): N, N-Diethylbenzene sulphonamide is insoluble in alkali.
Reason (R): Sulphonyl group attached to nitrogen atom is strong electron withdrawing group.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Nitrating mixture used for carrying out nitration of benzene consists of conc. HNO3+ conc. H2SO4
Reason : In presence of H2SO4, HNO3 acts as a base and produces NO2+ ions.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Reason : –NH2 group of aniline reacts with AlCl3 (Lewis acid) to give acid-base reaction.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Nitration of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason : Acetylation increases the electron-density in the benzene ring.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Acetanilide is less basic than aniline.
Reason : Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density on nitrogen.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Amines are basic in nature.
Reason : Amines have lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Only a small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of nitro compounds with iron scrap and HCl in the presence of steam.
Reason : FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the reaction.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
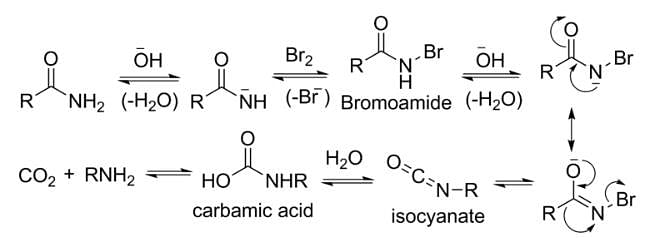
Assertion: Hoffmann's bromamide reaction is given by primary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
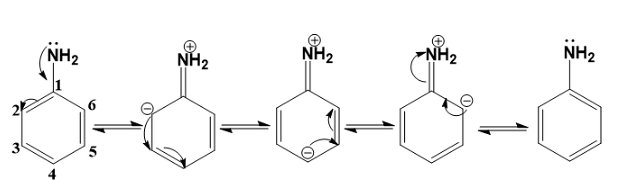
Assertion (A): --NH2 group is o- and p-directing in electrophilic substitution reactions
Reason (R): Aniline cannot undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as..
Assertion (A): Monobromination of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in the increase of electron density at the benzene ring.
|
101 videos|287 docs|123 tests
|