Test: Plant Growth and Development- Growth and Rate of Growth (July 8) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for NEET Preparation - Test: Plant Growth and Development- Growth and Rate of Growth (July 8)
An irreversible or permanent increase in size, mass or volume of a cell, organ or organism is called as ________.
Read the following statements regarding arithmetic growth and select the correct answer.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
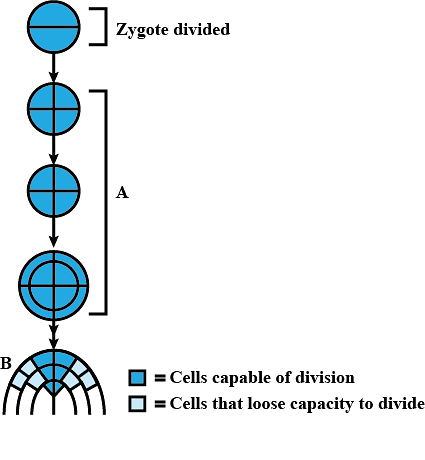
The given figure shows development of an embryo that undergoes two phases A and B. Select the correct option regarding it.

The given figure shows growth of two leaves over the period of one day. If, AG = absolute growth and RGR = relative growth rate, then select the correct option.

Growth in plants is
Vascular cambium and cork cambium are
Cells of tracheary elements (tracheids and vessels) become dead at maturity and lose their protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings. This is an example of
Living differentiated cells which have otherwise lost the capacity to divide, can regain the power of division under certain conditions. This phenomenon is termed as
Different kinds of structures develop in plants in different phases of growth or in response to environment. This ability is called _________.
Auxin synthesis occurs in
|
12 docs|366 tests
|


















