Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 4 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 4
The activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group is ______ as compared to -NH2 group.
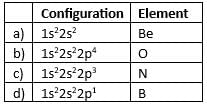
Match list I with list II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following hydrides in increasing order of thermal stability.
A. H2O
B. H2Se
C. H2Po
D. H2Te
E. H2S
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
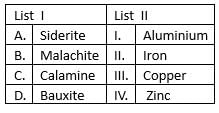
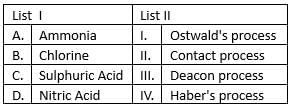
Match list I with list II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which one of the following elements is NOT a Lanthanoid?
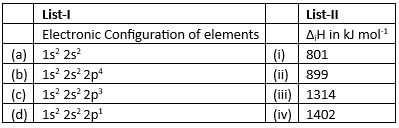
Match List-I with List-II
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which of the following reactions/tests does not help in the distinction between ethylamine and diethylamine?
Which of the following amines, on reaction with benzenesulphonyl chloride, will give a sulphonamide that is insoluble in alkali?
Diethylamine reacts with nitrous acid in the cold to form _______
What is the correct order of magnetic strength among the following elements?
Which gas is produced when ethanamine reacts with nitrous acid?
Benzoic acid is obtained from the oxidation of _______ with alkaline KMnO4 followed by treatment with mineral acid.
Identify the product B in the reaction chain shown.
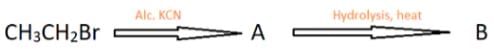
Which of the following elements have a negative value of magnetic susceptibility?
p-Xylene on reaction with acidified potassium dichromate at high temperature gives ________
How can methyl magnesium bromide be converted to propanoic acid?
Benzoic ethanoic anhydride on hydrolysis gives _______
The final product(s) of basic hydrolysis followed by acidification of ethyl butanoate is _______
What is the temperature, above which a ferromagnetic substance shows no ferromagnetism called?
Identify the most suitable reagent for the conversion of ethanal to acetic acid.
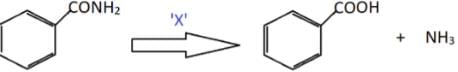
Identify X in the following conversion.Benzamide undergoes oxidation to form benzoic acid
Which of the following pairs do not give the same compound on heating with alkaline potassium permanganate?
Which of the following cannot be converted to benzoic acid on reaction with KMnO4-KOH followed by H3O+?
3-Chlorophenyl magnesium bromide on reaction with dry ice followed by acidification in mineral acid gives _____
|
8 docs|148 tests
|



 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)