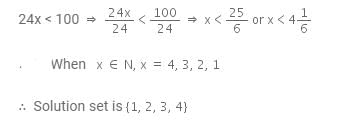Test: Linear Inequalities One Variable - Commerce MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Test: Linear Inequalities One Variable
Find the pairs of consecutive even positive integers both of which should be less than 10 and their sum is greater than 11?
Which of the following is not a linear inequality?
For a student to qualify for a certain course, the average of his marks in the permitted 3 attempts must be more than 60. His first two attempts yielded only 45 and 62 marks respectively. What is the minimum score required in the third attempt to qualify?
Which one of them is the solution for x, when x is integer and 12 x > 30?
Find the value of x which satisfies 5x – 3 < 7, where x is a natural number.
The solution to 5x-3<3x+1, when x is an integer, is
By solving inequality 3(a - 6) < 4 + a, answer will be
A point P lies in the solution region of 3x – 7 > x + 3. So the possible coordinates of P are
The solution of inequality 4x + 3 < 5x + 7 when x is a real number is
Two less than 5 times a number is greater than the third multiple of the number. So the number must be
By solving the inequality 6x - 7 > 5, the answer will be
Find the value of x when x is a natural number and 24x< 100.
|
75 videos|238 docs|91 tests
|