Test: General Organic Chemistry Level - 3 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: General Organic Chemistry Level - 3
Which of the following compounds is/are aromatic?
Which of the following has (have) (4n + 2) π-electrons but not aromatic?
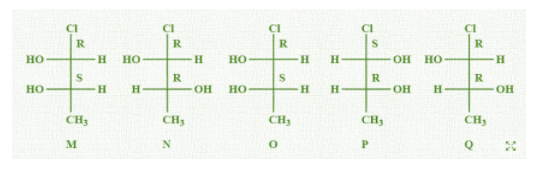
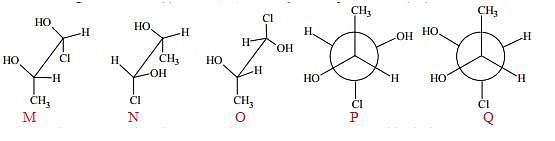
Which of the given statement(s) about N, O, P and Q with respect to M is (are) correct?

A compound does not shows aromaticity when it have:
Select the compounds which is/are anti-aromatic?
Which of the following compounds is expected to undergo faster electrophilic subst itution than unsubstituted benzene?
Which of the following compounds are aromatic?
Which of the following compounds is/are aromatic?
Which of the following compounds are non-aromatic?
Which of the following is/are aromatic?
Which of the following molecules, in pure form, is (are) unstable at room temperature:
Hybridizat ions of the atoms indicated with the asterisk (*) in the fo llowing compounds sequent ially are:
Which of the following species is/are aromatic in nature?
Which of the following species is/are aromatic in nature?
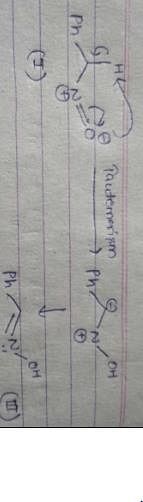
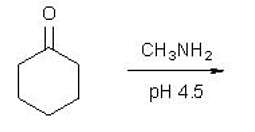
What is the product of the following reaction?
The correct order dipole moments (μ) of the following compounds is:
(1) CH3CH2CH2CHO
(2) CH3CH = CHCHO
(3) CH3CH2CH = CH2
The value of ‘n’ for the following molecule according to Hucke’s rule is
The correct statement describing the relationship between following structures is:
The correct order of acidity among the following structures is:
Arrange the following in the correct order of acidity of the hydrogen indicated in bold
The species/compounds that are aromatic among the following are
The homolytic breaking of the Ca— Cb bond is easiest in:
Which of the following represent the given monde of hydridisation sp2— sp2—sp—sp from left to righ?
Arrange the following free radicals in their stability order:
The correct order of pKa for the following compounds is:
The correct statement (s) about the following compounds is:
Arrange the pKas of the hydroxy groups of methanol, trifluoroacetic acid, phenol and benzyl alcohol in ascending order:
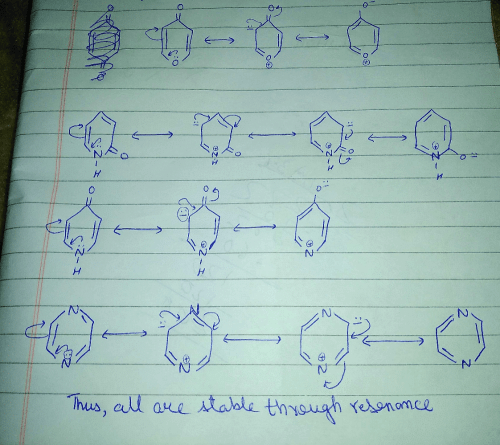
Among the resonance forms given below, the one which contributes most to the stability of azulene is
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|