Test: Stereochemistry Level - 3 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: Stereochemistry Level - 3
Among the following molecules, the one that is chiral is:
The number of Diastereomers possible for the following compound is:
Which one of the following conformations of cyclohexane is chiral:
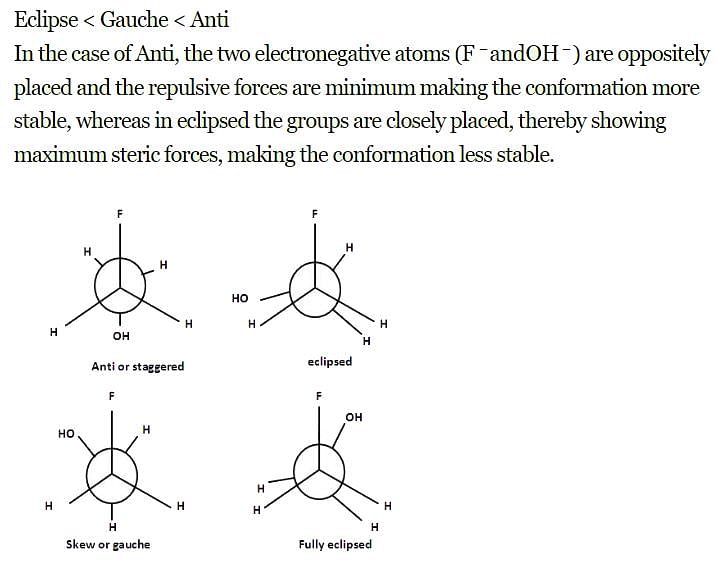
Increasing order of stability among the three main conformations (i.e.. Eclipse, Ami, Gauche) of 2-fluoroethanol is
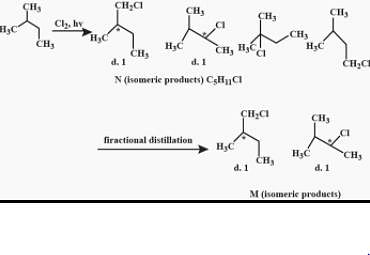
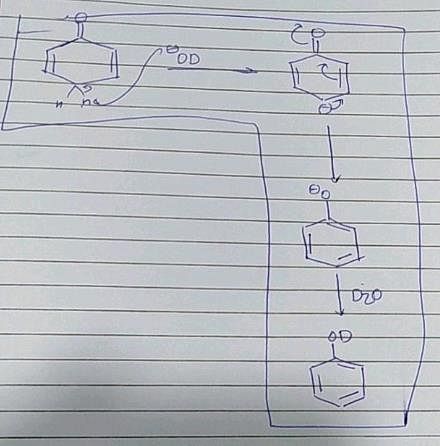
After prolonged treatment of (A) by D2O/DO–, the difference in molecule weights of compounds (A) and (B) is:
The most stable conformation for the following compound is:
The correct order of magnitude of ‘A value’ for the given subst ituents in cyclohexane derivatives is:
The most stable conformation of 2-fluoroethanol is:
The correct statements about conformations X and Y of 2-butanone are:
(I) X is more stable than Y
(II) Y is more stable than X
(III) Methyl groups in X are anti
(IV) Methyl groups in Y are gauche
In the most stable conformation of neomenthol, stereochemical orientation of the three substituents on the cyclohexane ring are:
The [α]D of a 90% optically pure 2-arylpropanoic acid solutions is +135°. On treatment with a base at RT for one hour, [α]D changed to +120°. The optical purity is reduced to 40% after 3 hours. If so, the optically purity of the solution after 1 hour, and its [α]D after 3 hours, respectively, would be:
An optically active compound enriched with R-enantiomer (60% ee) exhibited [α]D + 90°. If the, [α]D value of the sample is -135°, the ratio of R and S enantiomers would be:
Which of the following groups has the highest priority according to the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules?
The correct statement(s) concerning the structures E, F and G is (are)
Which of the following cyclopentane derivative is/are optically active:
Which of the following molecules is (are) chiral:
Identify which of the structures below are meso structures:
Among A-D, the compounds which can't exhibit optical activity are:
The molecule(s) that exist as meso structure(s) is/are:
Amongst the following amino acids, the (S)–enantiomer is represented by:
Which of the following structure is meso–2, 3–butanediol:
Compounds which have different arrangements of atoms in space while having the same atoms bonded to each other are said to have
Which of the following is an alkane which can exhibit optical activity?
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|