Test: Taste (Gustation) and Smell (Olfaction) - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Psychology and Sociology for MCAT - Test: Taste (Gustation) and Smell (Olfaction) - 1
A team of developmental psychologists are testing the taste sensation in children. The researchers want to make sure that the tastants utilized do not interact with charged particles. Which of these tastant combinations should the researcher use?
Which of these papillae categories does not contain taste buds?
Which statement describes a difference between the pathways for taste and the pathways for vision, hearing, and touch?
Which of these is NOT a theory of how odor is coded in the brain?
Many studies have shown auditory processing occurs in sleep. This is the premise behind smoke detectors. A smell researcher is interested in whether smell can be utilized in a similar fashion. The researcher chooses two odors, peppermint and pyridine. Although peppermint and pyridine have different hedonic valence, the trigeminal strength of the two odors was equal.
Why was trigeminal strength controlled in this experiment?
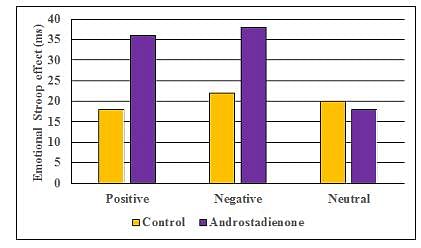
One tool that smell researchers use to investigate the role of pheromones on emotion, motivation, and cognition is called an emotional Stroop test. Similar to the typical Stroop test, a participant will show interference, increased latency, to name the color of the words that have an emotional connotation to the participant. Utilizing this test, smell researchers investigated the effects of ∆4,16-androstadien-3-one (androstadienone) which appears to function as a pheromone in humans. A cotton swab diluted in a strongly fragranced carrier solution before being applied to the upper lip of each participant. The carrier solution alone was administered to the control participants. Both groups were primed with a narrative discussing either a positive or negative emotional experience. The groups were then given a test with either positive or negatively valenced words, based on the narrative type. The effects of both narrative conditions for both groups of participants and the neutral word list are shown in Figure.
What conclusion can be made from the Figure?
Where is the first place in the brain where the olfaction and gustation systems integrate?
Which answer describes the correct pathway that a signal takes from the olfactory mucosa to the frontal lobe of the brain?
Which cranial nerve is primarily responsible for transmitting olfactory (smell) information from the nasal cavity to the brain?
Which part of the brain is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting complex odor information?
|
339 videos|14 docs|42 tests
|


















