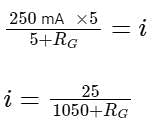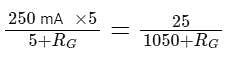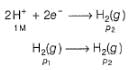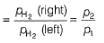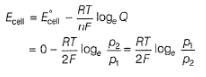JEE Main Part Test - 4 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2025 - JEE Main Part Test - 4
Two point charges 3 × 10-6 C and 8 × 10-6 C repel each other by a force of 6 × 10-3 N. If each of them is given an additional charge of -6 × 10-6 C, then the force between them will be
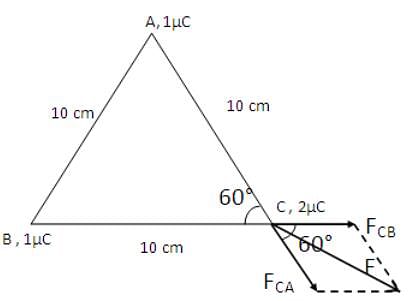
Three charges 1 μC, 1μC and 2 μC are respectively kept at the vertices A, B and C of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 10 cm. The resultant force on the charge at C is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If the inward flux and outward electric flux from a closed surface respectively are 8 × 103 units and 4 × 103 units, then what is the net charge inside the closed surface?
A metallic solid sphere is placed in a uniform electric field as shown. Which path will the lines of force follow?

An electric dipole placed in a non-uniform electric field experiences
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): In a cavity in a conductor, the electric field is zero.
Reason (R): Charges in a conductor reside only at its surface.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : The Coulomb force is the dominating force in the universe.
Reason : The Coulomb force is weaker than the gravitational force.
The potential of the electric field produced by a point charge at any point (x, y, z) is given by V = 3x2 + 5, where x, y and z are in metres and V is in volts. The intensity of the electric field at (–2, 1, 0) is
A capacitor of capacitance C1 is charged by connecting it to a battery. The battery is then removed and this capacitor is connected to a second uncharged capacitor of capacitance C2. If the charge gets distributed equally on the two capacitors, then the ratio of the total energy stored in the capacitors, after connection to the total energy stored in them before connection, is
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct answer according to the instructions given below.
Assertion: A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. The battery is then disconnected. If the distance between the plates is increased, then the energy stored in the capacitor will decrease.
Reason: Work has to be done to increase the separation between the plates of a charged capacitor.
Three point charges of 1 C, 2 C and 3 C are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 1 m. The work done (in joules) in bringing these charges to the vertices of a smaller similar triangle of side 0.5 m is
Three capacitors, each of capacity 4 µF, are to be connected in such a way that the effective capacitance is 6 µF. This can be done by
A 3 μF capacitor is charged to a potential of 300 V and a 2 μF capacitor is charged to a potential of 200 V. The capacitors are then connected in parallel with plates of opposite polarity joined together. What amount of charge will flow when the plates are so connected
An insulator plate is passed through the plates of a capacitor as shown. The current
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion: The electric flux of the electric field ∮ E.dA is zero. The electric field is zero everywhere on the surface.
Reason: The charge inside the surface is zero.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion: On bringing a positively charged rod near the uncharged conductor, the conductor gets attracted towards the rod.
Reason: The electric field lines of the charged rod are perpendicular to the surface of the conductor.
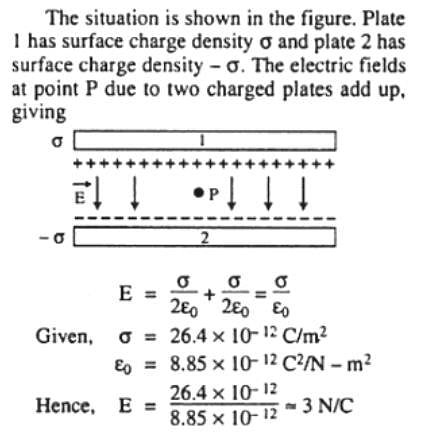
Two parallel, large and thin metal plates have equal surface charge densities (σ = 26.4 x 10-12 C/m2) of opposite signs. The electric field between these plates is
When a conductor is placed in an electric field; its free charge carriers adjust itself in order to oppose the electric field. This happen until
The electric field inside a dielectric decreases, when it is placed in an external electric field. This happens due to ________
The magnetic field inside a toroidal solenoid of radius R is B. If the current through it is doubled and its radius is also doubled keeping the number of turns per unit length the same; magnetic field produced by it will be:
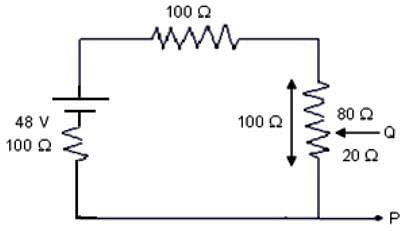
In the given circuit, the potential difference (v) across PQ will be nearest to
(Round off up to 1 decimal place)
If the current flowing in a coil of resistance 90Ω is to be reduced to 90%, what value of resistance (in ohms) should be connected in series with it? (In integer)
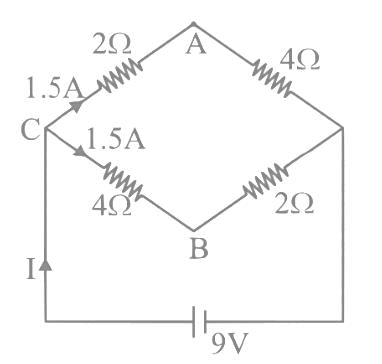
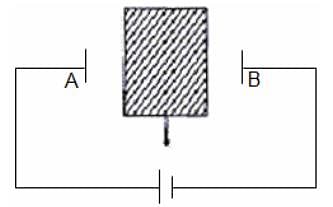
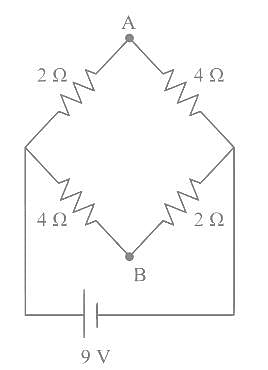
A network of four resistances is connected to 9 V battery, as shown in figure. The magnitude of voltage difference between the points A and B is ___________V.
When a resistance of 5Ω is shunted with a moving coil galvanometer, it shows a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA, however when 1050Ω resistance is connected with it in series, it gives full scale deflection for 25 volt. The resistance of galvanometer is _________ Ω.
For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure p1 and p2
emf is given by
The correct order of thermal stability of the hydrides of group 16 elements is
Which of the following statements regarding ozone are correct?
|
357 docs|148 tests
|
|
357 docs|148 tests
|


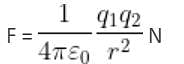
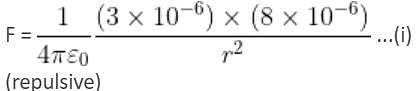
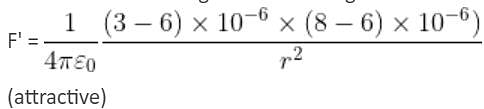
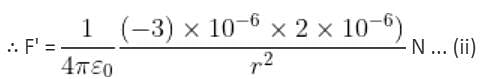
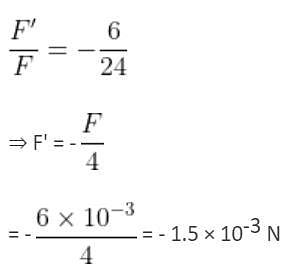
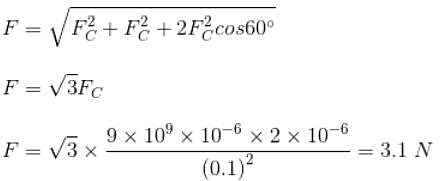
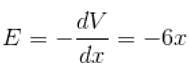
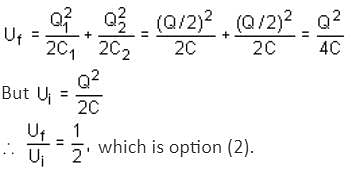
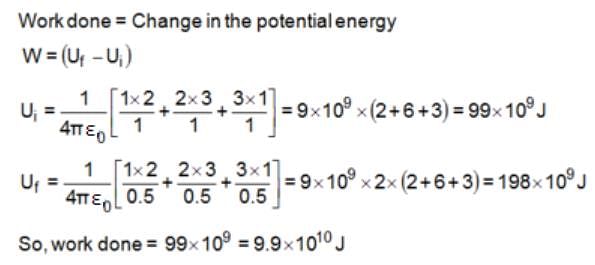

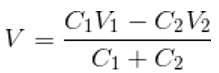

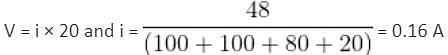
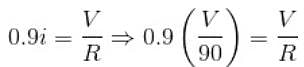


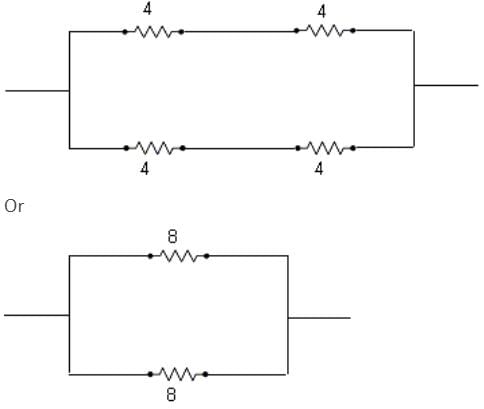
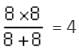 ohms is the equivalent resistance.
ohms is the equivalent resistance.