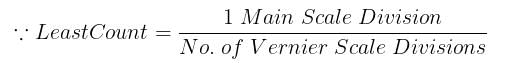Test: Units & Measurement - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 11 - Test: Units & Measurement - 2
If radian correction is not considered in specific heat measurement. The measured value of specific heat will be:
A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in vacuum is unity. What is the distance between the Sun and the Earth in terms of the new unit if light takes 8 min and 20 s to cover this distance?
The length, breadth and thickness of a rectangular sheet of metal are 4.234 m, 1.005 m, and 2.01 cm respectively. Give the volume of the sheet to correct significant figures.
Measurement of a physical quantity is essentially the:
The relative error in a physical quantity raised to the power k is:
The mass of a box measured by a grocer’s balance is 2.300 kg. Two gold pieces of masses 20.15 g and 20.17 g are added to the box. What is the difference in the masses of the pieces to correct significant figures?
Population of a town is reported as 157,900 . Which of the following statements correct?
According to the principle of homogeneity of dimensions:
There are 20 divisions in 4 cm of the main scale. The vernier scale has 10 divisions. The least count of the instrument is:
An object has a length of 0.42 cm. Which of the following statements correct?
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|