Case Based Questions Test: Metals & Non-metals - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Metals & Non-metals - 2
In a thermite reaction, a compound of iron reacts with a metal.
The metal used is:
After completion of this reaction, a metal is obtained in the molten state. Identify the metal:
The correct equation to justify thermite reaction is:
Read the given passage and answer the questions:
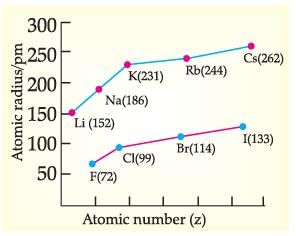
Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ions (cation) is known as electro-positivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
Non-Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electro -negativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
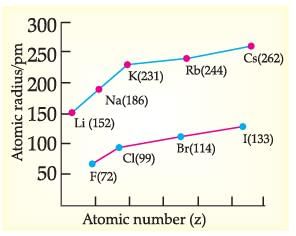
Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of Alkali metals plotted in the graph?
Read the given passage and answer the questions:
Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ions (cation) is known as electro-positivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size. Non-Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electro -negativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
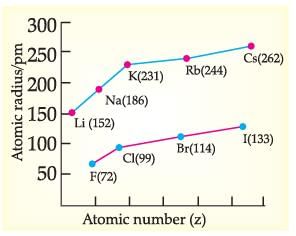
Which of the following has highest electronegativity?
Read the given passage and answer the questions:
Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ions (cation) is known as electro-positivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
Non-Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electro -negativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.

Which of the following reasons correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72pm) has a smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152pm)”?
Read the given passage and answer the questions:
Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ions (cation) is known as electro-positivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size. Non-Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electro -negativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
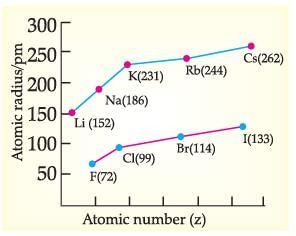
Identify the reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down the group.
Study the given table and answer the questions:
A student took the samples of four metals A, B, C and D and added the following solutions one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows:
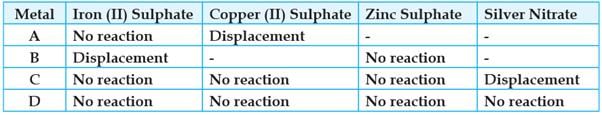
The gas produced when dil. HCl is added to a reactive metal
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Sohan went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was sad but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat.
Which of the following is used for dissolution of gold?
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Sohan went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was sad but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat.
Aqua regia dissolves:
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
During extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals. During the process, the impure metal is made the anode and a thin strip of pure metal is made the cathode. The solution of the metal salt is used as an electrolyte. On passing the current through the electrolyte, the pure metal from the anode dissolves from the electrolyte. An equivalent of pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited on the cathode.
During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets
Read the given passage and answer the questions:
Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ions (cation) is known as electro-positivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size. Non-Metallic Character: The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electro -negativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
Hydrogen is placed along with Alkali metals in the modern periodic table though it shows nonmetallic character:
In a thermite reaction, a compound of iron reacts with a metal.
The correct name for Fe2O3 is:
After completion of this reaction, a metal is obtained in the molten state. Identify the metal:



















