Case Based Questions Test: Carbon & Its compounds - 2 - Year 11 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Carbon & Its compounds - 2
Read the passage and answer the question :
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess the same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
Q. The chemical properties of which of the following compounds is similar to butane ?
Read the passage and answer the question :
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess the same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
Q. Which of the following is not the property of a homologous series ?
Read the passage and answer the question :
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess the same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
Q. What is the difference between two consecutive members in a homologous series in alkanes in terms of molecular mass and number of atoms of elements is:
Read the passage and answer the question :
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess the same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
Q. Which of the following represent the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having the general formula CnH2n + 2 ?
Read the passage and answer the question :
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess the same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
Q. The compound CH3 CH (OH) CH3 belongs to which of the following homologous series ?
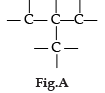
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. Answer the question :
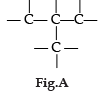
Name the characteristic property of carbon as depicted in the fig. A
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. Answer the question :
Give the number of single bonds present in the Cyclohexane compound.
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. Answer the question :
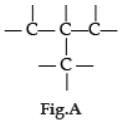
Q. Carbon forms large number of compounds due to :
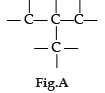
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. Answer the question :
Carbon is :
Carbon has the unique property to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. Answer the question :
Q. Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which 6 carbon atoms are arranged in a ring.
Read the passage and answer the questions :
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
Q. Name the compounds A, B and C.
Read the passage and answer the questions :
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
Q. The general formula for alkene is :
Read the passage and answer the questions :
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
Q. Name the type of reaction.
Read the passage and answer the questions :
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
Q. Choose the correct condition for conversion of ethene to ethane:
Read the passage and answer the questions :
An organic compound A of molecular formula C2H4 on reduction gives another compound B of molecular formula C2H6. B on reaction with chlorine in the presence of sunlight gives C of molecular formula C2H5Cl.
Q. Essential conditions required for the addition reaction to occur :