Test: Chromosomal Inheritance - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biochemistry for MCAT - Test: Chromosomal Inheritance - 1
What of the following provides the best evidence that DNA is the genetic material?
A gene, TALL, has recently been discovered that helps control the height that people will reach and results in taller than average height. Which of the following statements about this gene’s heritability are true?
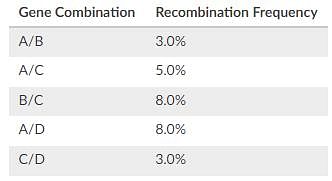
The results of a linkage analysis of genes A, B, C, and D have just come in from the lab. In what order are the alleles found on the chromosome?

A researcher was doing test crosses on mice, but forgot which mice he had bred together. When the litter was born, every mouse had black eyes, and half had brown fur. What was the genotype of the parent mice?
R = red fur; r = brown fur
B = black eyes; b = brown eyes
A set of homologous chromosomes undergoes genetic recombination to create the following results:
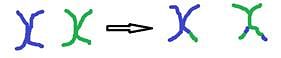
Q. Which of the following is the mostly likely recombination event?
Which of the following statements about synaptonemal complexes is not true?
A color-blind man marries a woman with no family history of color-blindness. What is the likelihood that they have a color-blind daughter?
Which of the following population’s coat/fur/feather color gene is most likely to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder whose carriers have a genetic advantage in surviving malaria. If 42% of the population is malaria resistant, but not anemic, what is frequency of the sickle-cell allele?
Many people have DNA mutations that go unnoticed. What type of mutation is most likely to have no effect on phenotype?
|
138 videos|21 docs|4 tests
|


















