Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 1 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 1
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): An apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction.
Reason (R): There is no fertilisation in apomicts plants and they do not produce any seeds.
Assertion (A): An apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics sexual reproduction.
Reason (R): There is no fertilisation in apomicts plants and they do not produce any seeds.
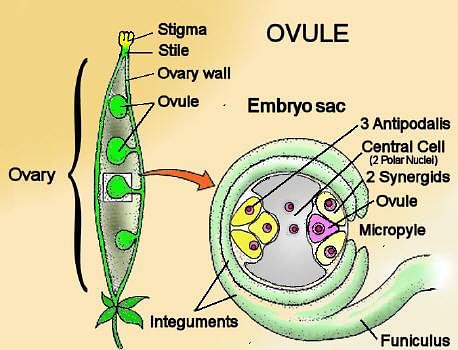
In the given diagram:
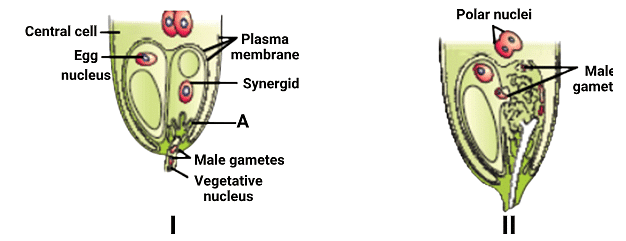
Statement I:I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a synergid under the guidance of A.
Statement II:II shows the discharge of male gametes into a synergid.

Statement I:I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a synergid under the guidance of A.
Statement II:II shows the discharge of male gametes into a synergid.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Endosperm type in which first division of primary endosperm nucleus and few subsequent division are not accompanied by wall formation is called?
Number of nuclei participating in double fertilisation is?
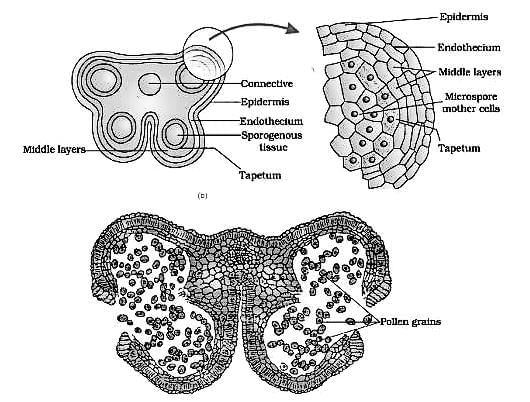
The anther is a four sided structure consisting of four _________ located at the corner.
Inside the ovary, the ovule is attached to the placenta by means of:
While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant?
Pollen grains lose viability within 30 minutes of their release in:-
In most of the angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at _________.
The fruits which develops without fertilization are called as?
Which among the following statement is incorrect with respect to tapetum?
Which of the following is an example of false fruit?
Placenta is located inside the _________.
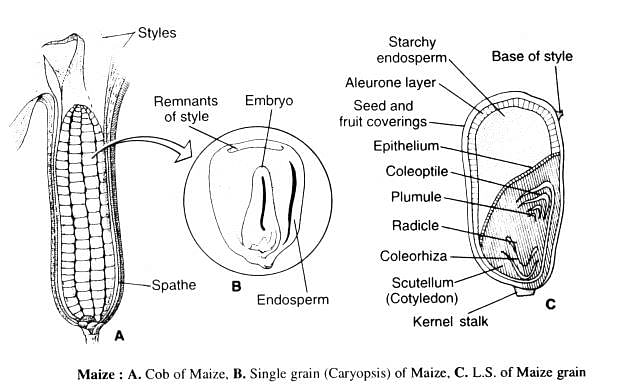
The cotyledon of maize grain is technically called as?
The following is the diagram of T.S. of anther. Identify the parts labelled A, B and C..
A typical angiosperm embryo sac at maturity is _________.
What is the correct sequence of the formation of female gametophyte in angiosperms?
Which of the following plant is not pollinated by water?
A typical anther is
(a) Tetrasporangiate
(b) Tetragonal
(c) Trilobed
(d) Surrounded by four wall layers
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|