Case Based Questions Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Case Based Questions Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Choose the correct statments with regarding the diagram:
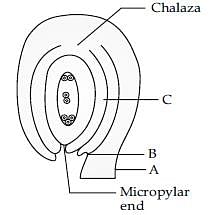
Statement I: A is the Chalazal end.
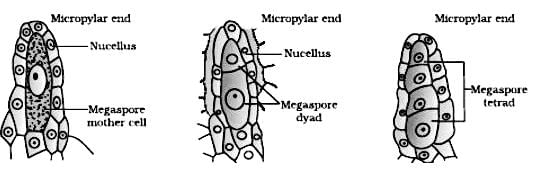
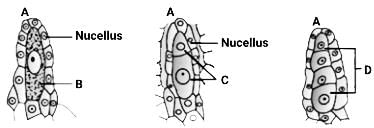
Statement II: B is the microspore mother cell, C is the microspore dyad and D is the microspore tetrad.

Statement I: A is the Chalazal end.
Statement II: B is the microspore mother cell, C is the microspore dyad and D is the microspore tetrad.
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Study the given diagram and answer any of the four questions given below:
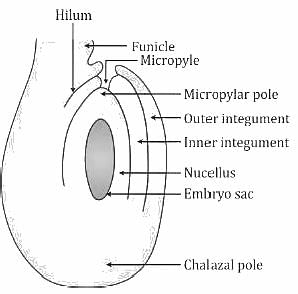
This diagram represent which type of ovule
Study the given diagram and answer any of the four questions given below:

This diagram represent which type of ovule
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
A typical anther is bilobed. It is a tetragonal structure consisting of four microsporangia. These microsporangia form pollen sac which on maturity gets filled with a pollen grains. Pollen grains represent the male gametophytes, their cell wall is very hard. Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies which cause various diseases in human beings.
The prominent pollen grain aperture called germ pore is present in:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
A typical anther is bilobed. It is a tetragonal structure consisting of four microsporangia. These microsporangia form pollen sac which on maturity gets filled with a pollen grains. Pollen grains represent the male gametophytes, their cell wall is very hard. Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies which cause various diseases in human beings.
Which among the following is a major cause of pollen allergy in India?
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Gynoecium, is the female reproductive part of the flower. It may consist of a single or more than one pistil. These pistil may be free or fuse. Each pistils has three parts, stigma, style and ovary. Ovary has an ovarian cavity, which has one or many chambers or locules. The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Megasporangia or ovules arise from the placenta.
In which of the following plants the number of ovules in an ovary is one ?
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Gynoecium, is the female reproductive part of the flower. It may consist of a single or more than one pistil. These pistil may be free or fuse. Each pistils has three parts, stigma, style and ovary. Ovary has an ovarian cavity, which has one or many chambers or locules. The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Megasporangia or ovules arise from the placenta.
Which among the following cell is binucleate in an embryo sac ?
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
A typical anther is bilobed. It is a tetragonal structure consisting of four microsporangia. These microsporangia form pollen sac which on maturity gets filled with a pollen grains. Pollen grains represent the male gametophytes, their cell wall is very hard. Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies which cause various diseases in human beings.
Direction : In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A) : The innermost layer of microsporangium is called tapetum.
Reason (R) : Tapetum nourishes the microspores for thier development into pollen grains.
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
A typical anther is bilobed. It is a tetragonal structure consisting of four microsporangia. These microsporangia form pollen sac which on maturity gets filled with a pollen grains. Pollen grains represent the male gametophytes, their cell wall is very hard. Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies which cause various diseases in human beings.
Select the odd one out with respect to wall layers of microsporangium in flowering plants.
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Gynoecium, is the female reproductive part of the flower. It may consist of a single or more than one pistil. These pistil may be free or fuse. Each pistils has three parts, stigma, style and ovary. Ovary has an ovarian cavity, which has one or many chambers or locules. The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Megasporangia or ovules arise from the placenta.
Flowers with both androecium and gynoecium are called :
At what temperature pollens can be stored for years in liquid nitrogen?
|
78 videos|276 docs|174 tests
|