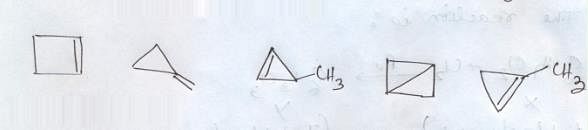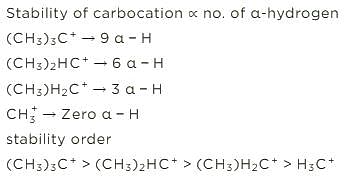Test: General Organic Chemistry Level - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry - Test: General Organic Chemistry Level - 2
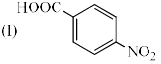
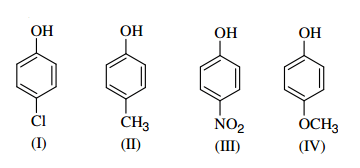
Identify the correct acidic strength order in the following compounds.
The total number of cyclic isomers possible for a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C4H6 is
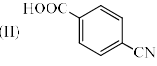
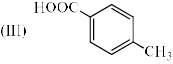
The correct order of acidity of the following compound A-C is:
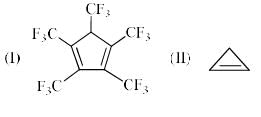
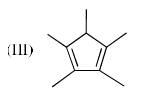
The order of acidity of the protons H in each of the following is:
Imidazole has a pKa = 7 with respect to its conjugate acid. Which N is protonated in this conjugate acid and why?
When CH3Cl undergoes homolytic bond-fission:
For the following compounds, which nitrogen has the least tendency to be protonated?
Increasing order of pKa values (pKa = –log Ka) of H2O, CH3OH and C6H5OH is:
The main sources of arenes among these are:
Which of the following reaction undergoes in the forward direction:
Which among these is the simplest example for polycyclic arenes?
Which among these is not a representative arene compound?
Identify the correct statement which is related to aromatic hydrocarbon
Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity:
Sort the following according to increasing order of the stability of carbocation.
1. (CH3)3C+
2. (CH3)2HC+
3. (CH3)H2C+
4. H3C+
How many compounds become aromatic after deprotonation?
Which of the following is anti-aromatic?
A compound given below shows a large dipole moment. Which of the following resonance structures can be used to adequately explain this observation?
Among the following compounds, which is the correct order of % enol content?
Which of the following compounds have higher enol content?
Which of the following compounds have less enol content?
The order of number of enolizable protons in each of the following:
The amount of enol form present at equilibrium for each of the following is:
Arrange the following compounds in acidic order:
Arrange the following compounds in order of Ca—Cb bond length:
|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|