Test: Soil Mechanics- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Soil Mechanics- 2
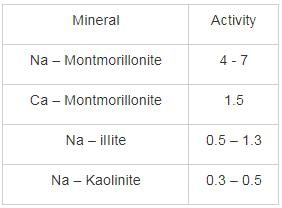
Which one of the following is the most active clay material?
What will be a range of plasticity index for the fine-grained soil below A - line having intermediate compressibility in the plasticity chart.
In an Octahedral unit if Fe2+ is present at the center of the geometry, what will be the net charge present over this unit.
A soil has a liquid limit of 45% and lies above the A-line when plotted on a plasticity chart. The group symbol of the soil as per IS soil classification is
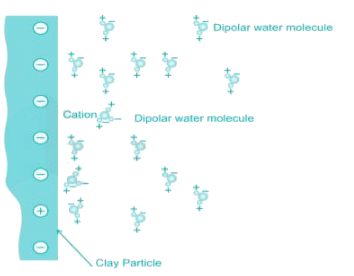
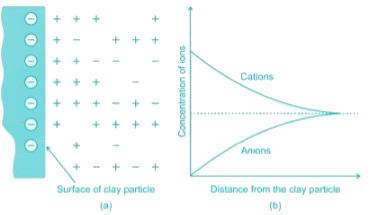
Consider the following statements regarding clay particles.
1. The clay particles carry a net negative charge.
2. The cation concentration increases with the distance from the surface of the particle.
3. When the spacing between the two clay particles is very small, the force of attraction is greater than the force of repulsion.
The correct statements are:
The laboratory test results of the soil sample are given below:
Liquid limit = 37%
Plastic limit = 22%
% passing through 75 μ sieve = 26%
% retained over 4.75 mm IS sieve = 65%
% retained over 0.075 mm but passing through 4.75 mm = 26%
As per IS 1498 – 1970, the soil is classified as:
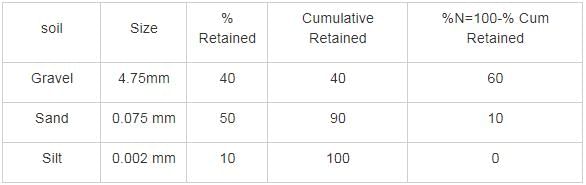
A soil mass contains 40 % gravel, 50 % sand 10 % silt. The soil can be classified as-
Sieve analysis is conducted on two soils A and B. The results of the test are given below:
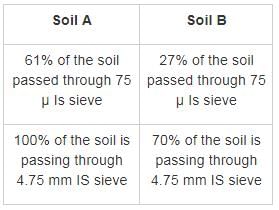
Identify the soil on the basis of the result obtained?
Sieve analysis is conducted on a given sample of soil. The data collected is given below:
(i) % of particles passing through 75 μ IS sieve = 73%
(ii) Liquid limit of the soil = 50
(iii) Plasticity index of the soil = 16
The possible value of Group index for soil is _______
|
31 docs|280 tests
|