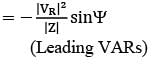Test: Power Systems- 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Power Systems- 1
For a 50 Hz 300 km long transmission line VS = 145∠4.9° kV, IS = 0.164∠-36.9° kA. What is the sending end power?
The ABCD constants of a 3-phase transmission line are
A = D = 0.8 ∠1°
B = 170 ∠85° Ω
C = 0.002 ∠90.4° mho
The sending end voltage is 400 kV. The receiving end voltage under no-load condition is
B = 170 ∠85° Ω
C = 0.002 ∠90.4° mho
If a 250 MVA, 11/400 kV three-phase power transformer has leakage reactance of 0.05 per unit on the base of 250 MVA and the primary voltage of 11kV, then the actual leakage reactance of the transformer referred to the secondary side of 400 kV is
The surge impedance of a 3-phase, 400 kV transmission line is 400 Ω. The surge impedance loading (SIL) is
The 50 Hz generating units operate in parallel with in the same power plant and have the following ratings:
Unit 1: 500 MVA, 0.85 power factor, 20 kV, 3000 rpm,
H1 = 5 MJ/MVA
Unit 2: 200 MVA, 0.9 power factor, 20 kV, 1500 rpm,
H2 = 5 MJ/MVA.
The equivalent inertia constant H in MJ/MVA on 100 MVA base is
If a travelling-wave travelling along a loss-free overhead line does not result in any reflection after it has reached the far end, then the far end of the line is
The active and the reactive power delivered at the receiving end of a short transmission line of impedance Z∠Ψ are respectively given by
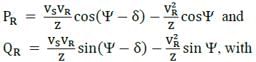
VS and VR being the magnitude of voltage at the sending and receiving ends, δ is the power-angle. At the power-limit condition i.e., for maximum PR
If a 500 MVA, 11 kV three-phase generator at 50 Hz feeds, through a transfer impedance of (0.0 + J 0.605) Ω per phase, an infinite bus also at 11 kV; then the maximum steady state power transfer on the base of 500 MVA and 11 kV is
In a three unit insulator string, voltage across the lowest unit is 17.5 kV and string efficiency is 84.28%. The total voltage across the string will be equal to
Bundled conductors are used for EHV transmission lines primarily for reducing the