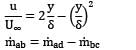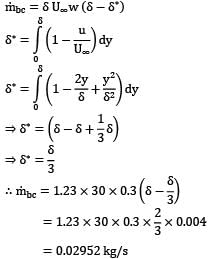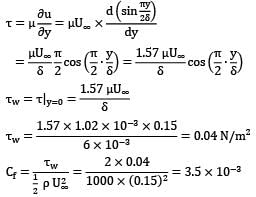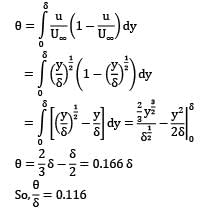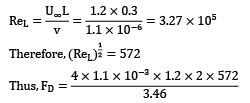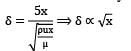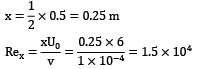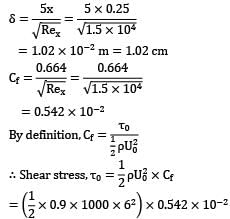Test: Boundary Layer Level - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Boundary Layer Level - 2
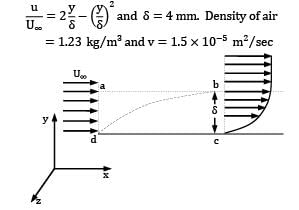
Air is flowing over a thin flat plate which is 1 m long and 0.3 m wide. At the leading edge, the flow is assumed to be uniform and U∞ = 30 m⁄s . The flow condition is independent of z (see Fig.). Using the control volume abcd, calculate the mass flow rate across the surface ab. (in kg/s, upto 3 decimal places). The velocity profile at bc is given by

Water flows over a flat plate at a free stream velocity of 0.15 m/s. There is no pressure gradient and the laminar boundary layer is 6 mm thick. Assume a sinusoidal velocity profile
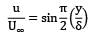
For the flow conditions stated above, calculate the skin friction coefficient. (upto 4 decimal places) [μ = 1.02 × 10−3kg/ms, ρ = 1000 kg/m3]
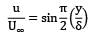
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the ratio of momentum thickness to the boundary layer thickness δ when the layer velocity profile is given by
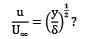
Where u is velocity at height y above surface and U∞ is free stream velocity of flow.
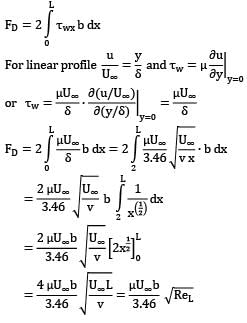
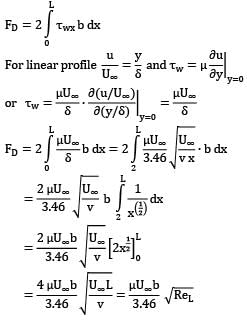
Water at 15°C flows over a flat plate at a speed of 1.2 m/s. The plate is 0.3 m long and 2 m wide. The boundary layer on each surface of the plane is laminar. Assume the velocity profile is approximated by a linear expression
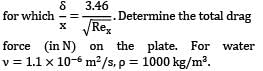
Consider the following statements pertaining to boundary layer on a flat plate
1. The thickness of laminar boundary layer at a distance x from the leading edge varies as x1⁄2
2. The thickness of turbulent boundary layer at a distance x from the leading edge varies as x4⁄5
3. Boundary layer is laminar when Reynolds number is less than 5 × 105
Which of the above statements are correct?
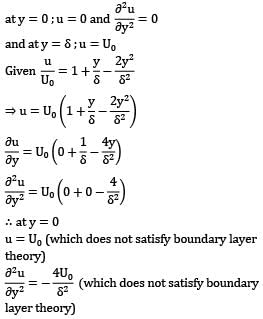
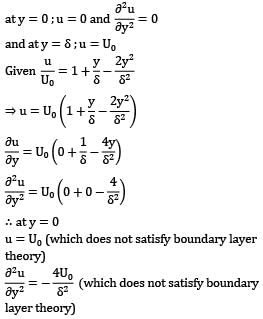
Examine whether or not the following velocity profiles satisfy the essential boundary conditions for velocity distribution in laminar boundary layer on a flat plate
![]()
Where u is the velocity at height y above the surface, U0 is the free stream velocity and δ is the nominal boundary layer thickness.
A plate 0.5 m × 0.2 m has been placed longitudinally in a stream of crude oil which flows with undisturbed velocity of 6 m⁄s.
Given that oil has a specific gravity 0.9 and kinematic viscosity 1 stroke, calculate the boundary layer thickness and shear stress at the middle of plate.
What is the commonly used boundary layer control method to prevent separation?
Which one of the following is correct? For flow of an ideal fluid over a cylinder, from the front stagnation point.
Crude oil at 21°C (ν = 9.3 × 10−6 m2 /s, S = 0.86) with a free-stream velocity of 0.3048 m/s flows past a thin, flat plate that is 1.2192 m wide and 1.8288 m long in a direction parallel to the flow. The flow is laminar. Determine the boundary-layer thickness and the wall shear stress at the trailing edge of the plate.
|
56 videos|104 docs|75 tests
|
|
56 videos|104 docs|75 tests
|