31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Mineral Nutrition - 2 (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Mineral Nutrition - 2 (Old NCERT)
A plant requires magnesium for [2007]
The deficiencies of micronutrients, not only affects growth of plants but also vital functions such as photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect most, both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport: [2005]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A free living nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium which can also form symbiotic association with the water fern Azolla is [2004]
Grey spots of oat are caused by deficiency of [2003]
Boron in green plants assists in [2003]
The major portion of the dry weight of plants comprises of [2003]
Which one of the following mineral elements plays an important role in biological nitrogen fixation ? [2003]
The major role of minor elements inside living organisms is to act as [2003]
Choose the correct match [2002]
Which aquatic fern performs nitrogen fixation? [2001]
Passive absorption of minerals depend on [2001]
Enzyme involved in nitrogen assimilation [2001]
A pair of insectivorous plants is [1999]
Which of the following is a free living aerobic nonphotosynthetic nitrogen-fixer? [1997]
Which of the following is not caused by deficiency of mineral nutrition? [1997]
Which one of the following is not an essential element for plants ? [1996]
Which one of the following is a micronutrient for plants? [1996]
Which of the following can fix atmospheric nitrogen ? [1995]
The association between blue-green algae and fungi occurs in [1995]
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic relationship between roots of higher plants and [1995]
Which one is an essential mineral, not constituent of any enzyme but stimulates the activity of many enzymes [1989]
Phosphorus and nitrogen ions generally get depleted in soil because they usually occur as[1989]
Minerals absorbed by roots move to the leaf through [1988]
The plants growing in magnesium-deficient soil, but sprayed with urea would show: [1987]
Which one of the following roles is not characteristic of an essential element? [1986]


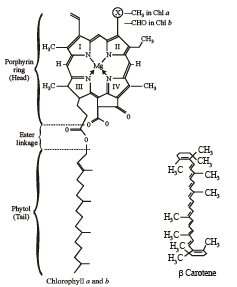
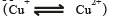 Maintenance of carbohydrate / nitrogen balance, chlorophyll synthesis.
Maintenance of carbohydrate / nitrogen balance, chlorophyll synthesis.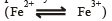 development of chloroplasts, chlorophyll and other pigments, protein synthesis.
development of chloroplasts, chlorophyll and other pigments, protein synthesis.














