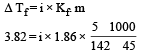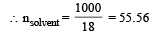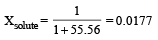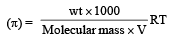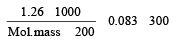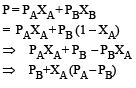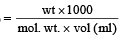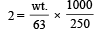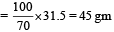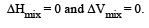31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Solutions - 1 - NEET MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Solutions - 1
During osmosis, flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane [2006]
A solution containing 10 g per dm 3 of urea (molecular mass = 60 g mol–1) is isotonic with a 5% solution of a non-volatile solute. The molecular mass of this nonvolatile solute is [2006]
1.00 g of a non-electrolyte solute (molar mass 250 g mol–1) was dissolved in 51.2 g of benzene. If the freezing point depression constant, Kf of benzene is 5.12 K kg mol–1, the freezing point of benzene will be lowered by [2006]
0.5 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid (HX) is 20% ionised. If Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol– 1,the lowering in freezing point of the solution is
A 0. 00 20 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound Co(NH3)5(NO2)Cl freezes at – 0.00732 °C. Number of moles of ions which 1 mol of ionic compound produces on being dissolved in water will be (Kf = – 1.86°C/m)
An aqueous solution is 1.00 molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase? [2010]
A solution of sucrose (molar mass = 342 g mol–1) has been prepared by dissolving 68.5 g of sucrose in 1000 g of water. The freezing point of the solution obtained will be ( f for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1). [2010]
2 5. 3 g of sodium carbonate, Na2 CO3 is dissolved in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. If sodium carbonate dissociates completely, molar concentration of sodium ions, Na+ and carbonate ions, CO32– are respectively (Molar mass of Na2CO3 = 106 g mol–1) [2010]
The freezing point depression constant for water is – 1.86ºC m–1. If 5.00 g Na2SO4 is dissolved in 45.0 g H2O, the freezing point is changed by – 3.82ºC. Calculate the van’t Hoff factor for Na2SO4. [2011]
The van’t Hoff factor i for a compound which undergoes dissociation in one solvent and association in other solvent is respectively : [2011]
Mole fraction of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution is : [2011]
A 0.1 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid is 30% ionized. If Kf for water is 1.86°C/m, the freezing point of the solution will be : [2011 M]
200 mL of an aqueous solution of a protein contains its 1.26 g. The osmotic pressure of this solution at 300 K is found to be 2.57 × 10–3 bar.The molar mass of protein will be (R = 0.083 L bar mol–1 K–1) [2011 M]
PA and PB are the vapour pressure of pure liquid components, A and B, respectively of an ideal binary solution. If XA represents the mole fraction of component A, the total pressure of the solution will be. [2012]
Vapour pressure of chloroform (CHCl3) and dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) at 25ºC are 200 mm Hg and 415 mm Hg respectively. Vapour pressure of the solution obtained by mixing 25.5 g of CHCl3 and 40 g of CH2Cl2 at the same temperature will be : (Molecular mass of CHCl3 = 119.5 u and molecular mass of CH2Cl2 = 85 u). [2012 M]
How many grams of concentrated nitric acid solution should be used to prepare 250 mL of 2.0M HNO3 ? The concentrated acid is 70% HNO3 [NEET 2013]
Which condition is not satisfied by an ideal solution? [NEET Kar. 2013]




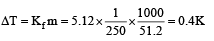
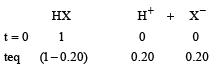
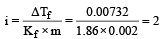
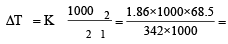 0.372
0.372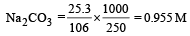
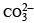 = 0.955 M
= 0.955 M