31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Transport in Plants - 1 (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Transport in Plants - 1 (Old NCERT)
Match List - I with List-II. [2021]

Choose the correct answer from the options given below.


Choose the correct answer from the options given below.

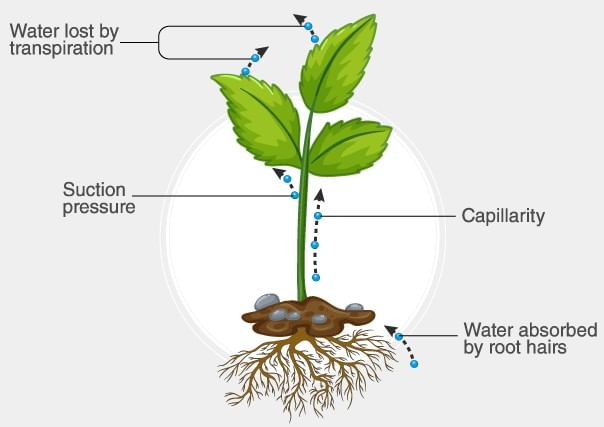
The process responsible for facilitating loss of water in liquid form from the tip of grass blades at night and in early morning is: [2020]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Xylem translocates [2019]
Due to low atmospheric pressure, the rate of transpiration will
Which of the following criteria does not pertain to facilitated transport? [NEET 2013]
Guttation is the result of : [2011M]
Guard cells help in: [2009]
Carbohydrates are commonly found as starch in plant storage organs. Which of the following five properties of starch (a-e) make it useful as a storage material? [2008] (A) Easily translocated (B) Chemically non-reactive (C) Easily digested by animals (D) Osmotically inactive (E) Synthesized during photosynthesis The useful properties are
The rupture and fractionation do not usually occur in the water column in vessel/tracheids during the ascent of sap because of [2008]
Which one of the following statements is correct? [2007]
Two cells A and B are contiguous. Cell A has osmotic pressure 10 atm, turgor pressure 7 atm and diffusion pressure deficit 3 atm. Cell B has osmotic pressure 8 atm, turgor pressure 3 atm and diffusion pressure deficit 5 atm. The result will [2007]
The translocation of organic solutes in sieve tube members is supported by [2006]
Sulphur is an important nutrient for optimum growth and productivity in [2006]
Potometer works on the principle of [2005]
The ability of the Venus fly trap to capture insects is due to: [2005]
Dough kept overnight in warm weather becomes soft and spongy because of [2004]
Stomata of a plant open due to [2003]
When water moves through a semi permeable membrane then which of the following pressure develops? [2001]
Which of the following plant is found to have minimum transpiration [2001]
Movement of ions or molecules in a direction opposite to that of prevailing electrochemical gradient is known as [2000]
Water potential of actively absorbing cells is [1999]
If a cell A with DPD 4 bars is connected to cell B, C, D whose OP and TP are respectively 4 and 4, 10 and 5 and 7 and 3 bars, the flow of water will be [1998]
The water potential and osmotic potential of pure water are [1998]
Water potential in the leaf tissue is positive (+) during [1997]
Suppose an aquatic plant is placed in a test tube containing distilled water and the tube is stoppered. The tube is left outdoors for 24 hours and the pH value of the water is then measured at regular intervals. Which of the following is the most probable result? [1997]