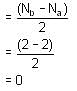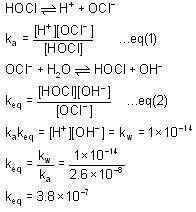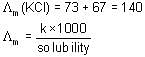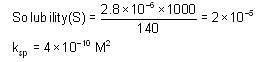BITSAT Chemistry Test - 6 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BITSAT Chemistry Test - 6
In the conversion of Br2 to BrO-3 the oxidation number of Br changes from
In the reaction, SO2 + 2H2S → 3S + 2H2O the substance that oxidised is,
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How do you account for the following observations ?
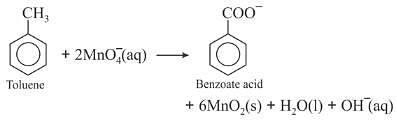
Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why ? Write a balance redox equation for the reaction.
What will be the ratio of number of moles of cerric ammonium sulphate required per mole of ferrous ammonium sulphate to the number of moles of KMnO4 required per mole of ferrous ammonium sulphate?(Cerric ammonium sulphate and potassium permanganate are used as oxidising agents in acidic medium for oxidation of ferrous ammonium sulphate to ferric sulpahte.)
A mixture of 0.02 mole mole of KBrO3 and 0.01 mole of KBr was treated with excess of KI and acidified. The volume of 0.1 M Na2S2O3 solution required to consume the liberated iodine will be:
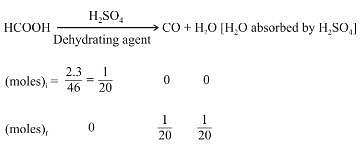
A mixture of 2.3 g formic acid and 4.5 g oxalic acid is treated with concentrate H2SO4 . The evolved gaseous mixture is passed through KOH pellets. What will be the weight in grams of the remaining product at STP?
An aqueous solution of 6.3 g of oxalic acid dihydrate(molar mass = 126.07 g/mol) is made up to 250 mL. The volume of 0.1 N NaOH required to completely neutralize 10 mL of this solution is -
20 ml of 0.2 M NaOH (aq) solution is mixed with 35 ml of 0.1 M NaOH (aq) solution and the resultant solution is diluted to 100 ml . 40 ml of this diluted solution reacted with 10% impure sample of oxalic acid (H2C2O4). The weight of the impure sample is
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze in a cold climate. Mass of ethylene glycol which should be added to 4 kg of water to prevent it from freezing at −6° will be (Kf for water1.86 K kg mol−1 , and molar mass of ethylene glycol=62 g mol−1 )
Depression in freezing point of 0.322 molal aqueous solution of glucose will be
Liquids A and B form an ideal solution. Vapour pressure of pure A and B are 7 x 103 and 12 x 103 Pa respectively. Find the vapour composition of A and B if mole fraction of 'A' in liquid solution is 0.4.
The freezing point of an aqueous solution is - 0.186°C. The Ebullioscopic constant of the solvent is Kb = 0.52°C kg mol-1 and Cryoscopic constant of the solvent is Kf = 1.86°C kg mol-1. find the increase in boiling point.
The following salts were dissolved in water to get an aqueous solution of mentioned concentration. Which one of the following will have maximum freezing point?
Two elements, A and B, form compounds having molecular formulae AB2 and AB4 when dissolved in 20g of C6H6, 1.0g AB2 lowers the freezing point by 2.3K whereas 1.0g of AB4 lowers it by 1.3K. The molal depression freezing point constant for benzene is 5.1 kg mol-1. The atomic masses of A and B (in g mol-1) respectively are (assume AB2 and AB4 are non-ionisable)
The freezing point (in°C) of solution having 0.1 g of K3 [Fe (CN)6] (molecular weight 329)in 100 g of water (Kf = 1.86 K kg mol- 1) is
A 5.25% solution of a substance is isotonic with 1.5% solution of urea (molar mass = 60 g mol-1) in the same solvent. If the densities of both the solutions are assumed to be equal to 1.0 g cm-3, molar mass of the substance will be:
When 0.2g of acetic acid is added to 20g of benzene, then the freezing point of benzene decreases by 0.45°C. If acetic acid associates to form a dimer in benzene, then find the percentage association of acetic acid in benzene.
(Kf for benzene=5.12 K kg mol−1)
The required energy for photoelectric effect for few metals is as listed below:
Li - 2.4 eV; Mg - 3.7 eV; Ag - 4.3 eV; Fe - 4.7 eV
If light of wavelength of 400 nm falls on these metals, which of these metals will show photoelectric effect?
Electron emits radiation with a wavelength of 4900 x10-10 m from a certain electronic state and is lying in the Balmer series in the spectrum of hydrogen atom. Find the electronic state of the electron. Take approximate value and RH = 1.097 x 107m-1.
The t1/2 values for the decomposition of CH3CHO at constant temperature and at initial pressure of 340 mm and 170 mm of Hg were 410 and 820 s, respectively. The order of the reaction is
For the given reaction the first order rate constant for the decomposition of Ammonium Nitrite is 2.60x 10-5 s-1 at 700 K. What will be the value of rate constant of the reaction at 900 K when the energy of activation is 150 kJ mol-1?
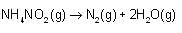
Which of the following equations is/are correct for energy of electron in nth orbit?
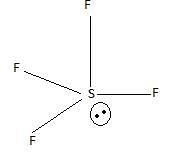
Which of the following has/have bond order zero and show(s) diamagnetic behaviour?
I. Ne2
II. He2
III. N2
IV. O2
One mole of gas is heated at constant volume and temperature is raised from 298 to 308K. The heat supplied to the gas is 200 J. Which of the following is correct?
The ka for HOCl Is 2.6 x 10-8.
What will be the value of equilibrium constant for the given reaction?
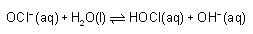
(Take kw = 1 x 10-14)
At 300 K, the conductivity of saturated solution of KCl in water is 2.8 x 10-6 Scm-1. Its solubility product at 300 K (given λ∞(K+) = 73 S cm2 mol-1, λ∞(Cl-) = 67 Scm2 mol-1) is


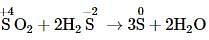
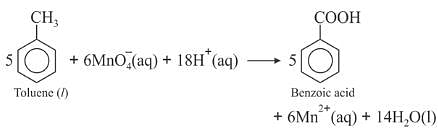
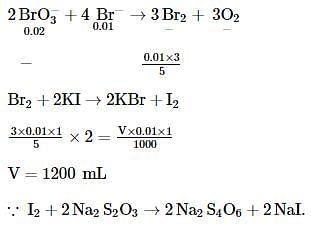
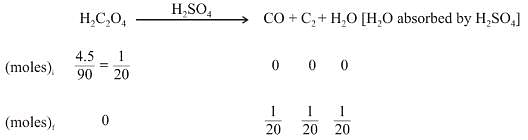
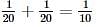 Left mass of CO = moles × molar mass
Left mass of CO = moles × molar mass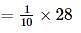
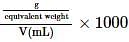
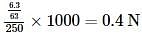
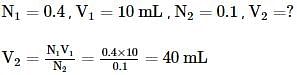
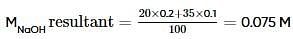
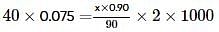
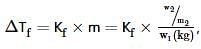
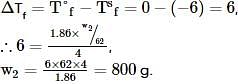
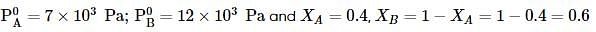
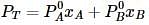
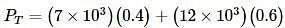
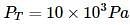
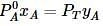
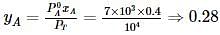
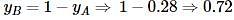
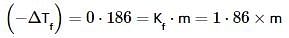
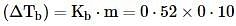
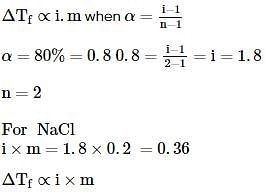
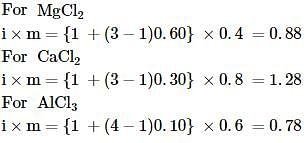
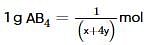
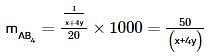
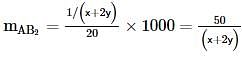
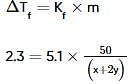
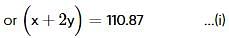
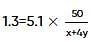
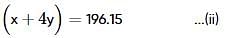
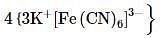
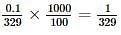
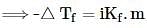
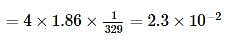
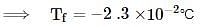
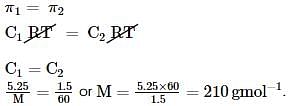
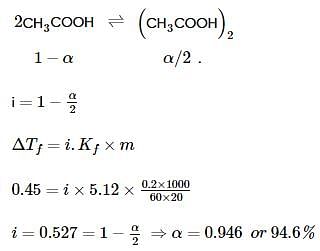
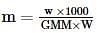 where, w = weight of the solute, W = weight of the solvent and GMM =
where, w = weight of the solute, W = weight of the solvent and GMM =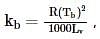
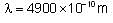
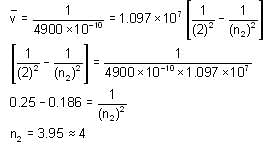
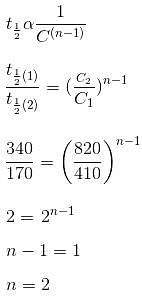
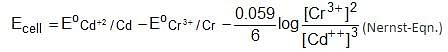
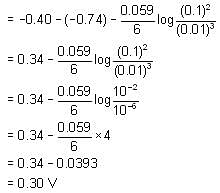
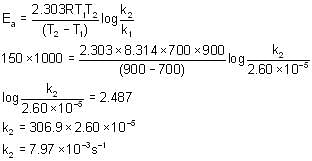
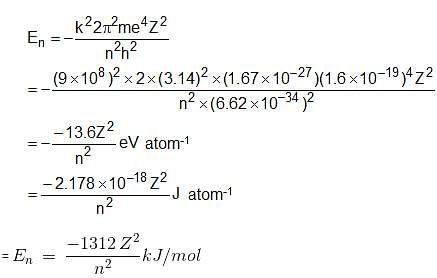
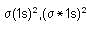 is the MO configuration.
is the MO configuration.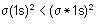 Bond order
Bond order