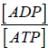Bioenergetics MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 - Bioenergetics MCQ
In which of the following conditions the Gibbs free energy change shall be negative when the
Gibbs free energy change does not depend on which of the following factors?
Which of the following information is not derived from first law of thermodynamics
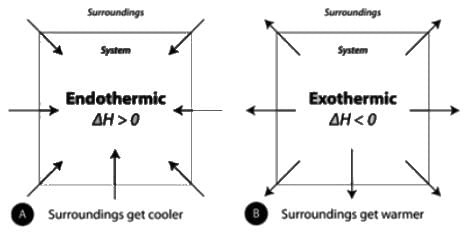
If the value of ΔH and ΔS are positive, which of the following statements will be true.
Which of the following complex of electron transport chain is not involved in proton pumping across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Which of the following options consist of combination of inhibitors which inhibit the same target.
In which of the following conditions the Gibbs free energy change can be negative
Arrange the following electron carries of electron transport chain in ascending order of redox potential. FMN, cytochrome c, cytochrome a3 and O2
Which of the following molecules produces highest energy on breakdown of its high energy bond
Which of the following is not true for energy currency of the cell
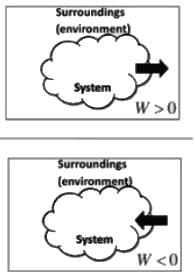
Which of the following is true about the sign convention of work done and heat
Which one of the following statements about cytochromes P450 is/are CORRECT?
The chemiosmotic theory of Peter Mitchell proposes a mechanism for the tight coupling of electron transport via the respiratory chain to the process of oxidative phosphorylation.Which of the following options is predicted by the theory?
The value of standard reduction potential is –30 mV for an oxidation reaction involving 2 electrons. The standard Gibbs free energy (in kilojoule) for this reaction is _________ (F = 96500 Joule/mol). (Answer upto one decimal place)
The Gibbs free energy change for conversion of compound X to Compound Y is 20 kJ mol–1 and it is a non spontaneous reaction.
Also hydrolysis of ATP is a coupled reaction and provides –30 kJ/mol energy on hydrolysis.
From the information given above, the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction
Compound X + ATP —> Compound Y + ADP is__________ (in kJ mol-1) (answer in integer)
If the ratio of ATP: ADP is 105 :1, the Gibbs free energy change of hydrolysis of ATP at 37°C will be _____ (kilo Joule). Given that standard Gibbs free energy change is –30 kJ/ mol. (Answer in integer)
|
7 docs|34 tests
|