Biology: CUET Mock Test - 10 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Biology: CUET Mock Test - 10
According to the law of dominance, what are the discrete units that control the characters?
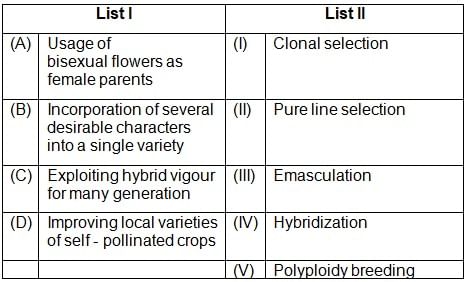
Match the following columns and select the correct option.
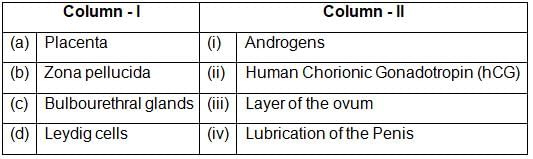

Match the Column I and II and select the correct match from the options given below :
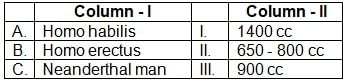
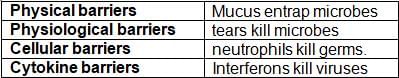
Match the following list I (barrier) with list II (function).
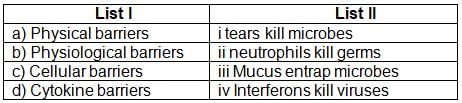
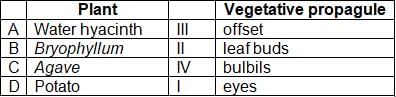
Match the following columns.
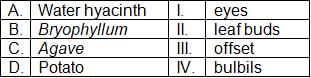
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The male gamete in plants is the pollen grain.
(B) The female gamete in plants is the egg cell.
(C) The ovule develops into a fruit after fertilization.
(D) The ovary in plants becomes the seed after fertilization.
(E) Pollinators like bees help in cross-pollination.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Pollination is necessary for fertilization to occur.
(B) Plants cannot reproduce sexually without pollinators.
(C) Some plants are capable of both self-pollination and cross-pollination.
(D) The male part of a flower is called the pistil.
(E) Fertilization results in the formation of the embryo.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a population?
Which of the following is an example of a population attribute?
What factor is critical in understanding population growth and stability?
What is one key factor that influences life history variation in species?
Which strategy do species like salmon adopt regarding reproduction?
Why do some organisms produce a small number of large offspring?
What reproductive strategy involves producing many small offspring?
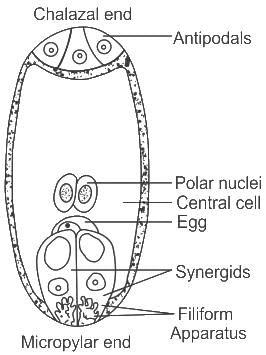
Which of the following statement is /are correct about reproduction in a plant?
(a) Pollen grain consists of vegetative cells and a generative cell.
(b) Embryo sac is 8-nucleate is 7-celled.
(c) Endosperm is diploid.
(d) Dicot seeds consist of two cotyledons.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Certain mass of living material at each trophic level is called as standing crop.
(B) The crop that can withstand adverse conditions is called standing crop
(C) The amount of nutrients in soil is called Biomass
(D) Only Biotic components make an Ecosystem
(E) Most of Phytoplanktons are member of algae
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following species :
- Quagga
- Thylacine
- Steller’s Sea Cow
- Snow leopard
Which of the above species are extinct?
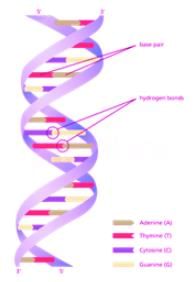
Considered the following statements and choose the INCORRECT one-
A. According to Chargaff’s Rule, the amount of guanine is equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine.
B. DNA is made up of one nucleotide chain.
C. In RNA, the Uracil is found in place of thymine.
D. Adenine and guanine base pair are pyrimidines.
Which of the following is not a statement of the principle of dominance?
What generation of Mendelian cross has a phenotypic ratio of 3:1?
The ratio of genotypes observed in progeny after a cross has been performed is called ________
What is represented in the boxes of the Punnett square?
What is the generation of plants produced by the crossing of true-breeding plants called?
What should be the phenotype of the F1 progeny produced by a cross between tall and dwarf true-breeding garden pea plants?