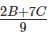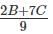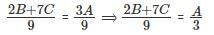CAT Previous Year Questions : Mixtures & Alligations (June 18) - CAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for CAT Preparation - CAT Previous Year Questions : Mixtures & Alligations (June 18)
A mixture P is formed by removing a certain amount of coffee from a coffee jar and replacing the same amount with cocoa powder. The same amount is again removed from mixture P and replaced with same amount of cocoa powder to form a new mixture Q. If the ratio of coffee and cocoa in the mixture Q is 16 : 9, then the ratio of cocoa in mixture P to that in mixture Q is
[2023]
A mixture contains lemon juice and sugar syrup in equal proportion. If a new mixture is created by adding this mixture and sugar syrup in the ratio 1 : 3, then the ratio of lemon juice and sugar syrup in the new mixture is
[2022]
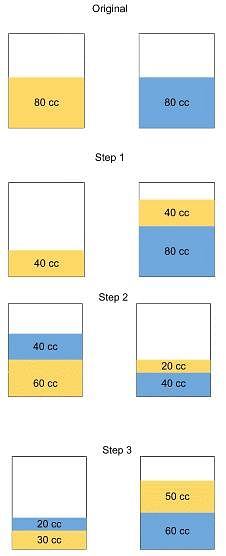
There are two containers of the same volume, first container half-filled with sugar syrup and the second container half-filled with milk. Half the content of the first container is transferred to the second container, and then the half of this mixture is transferred back to the first container. Next, half the content of the first container is transferred back to the second container. Then the ratio of sugar syrup and milk in the second container is
[2022]
A chemist mixes two liquids 1 and 2. One litre of liquid 1 weighs 1 kg and one litre of liquid 2 weighs 800 gm. If half litre of the mixture weighs 480 gm, then the percentage of liquid 1 in the mixture, in terms of volume, is
[2019]
The strength of a salt solution is p% if 100 ml of the solution contains p grams of salt. Each of three vessels A, B, C contains 500 ml of salt solution of strengths 10%, 22%, and 32%, respectively. Now, 100 ml of the solution in vessel A is transferred to vessel B. Then, 100 ml of the solution in vessel B is transferred to vessel C. Finally, 100 ml of the solution in vessel C is transferred to vessel A. The strength, in percentage, of the resulting solution in vessel A is
[2019]
A trader sells 10 litres of a mixture of paints A and B, where the amount of B in the mixture does not exceed that of A. The cost of paint A per litre is Rs. 8 more than that of paint B. If the trader sells the entire mixture for Rs. 264 and makes a profit of 10%, then the highest possible cost of paint B, in Rs. per litre, is
[2018]
A wholesaler bought walnuts and peanuts, the price of walnut per kg being thrice that of peanut per kg. He then sold 8 kg of peanuts at a profit of 10% and 16 kg of walnuts at a profit of 20% to a shopkeeper. However, the shopkeeper lost 5 kg of walnuts and 3 kg of peanuts in transit. He then mixed the remaining nuts and sold the mixture at Rs. 166 per kg, thus making an overall profit of 25%. At what price, in Rs. per kg, did the wholesaler buy the walnuts?
[2018]
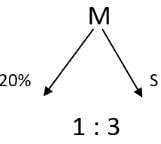
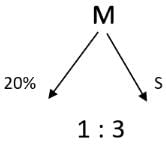
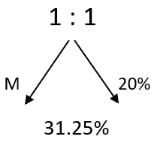
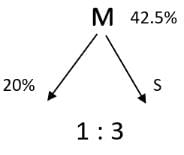
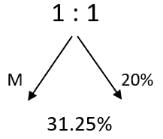
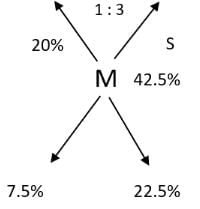
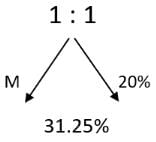
A 20% ethanol solution is mixed with another ethanol solution, say, S of unknown concentration in the proportion 1:3 by volume. This mixture is then mixed with an equal volume of 20% ethanol solution. If the resultant mixture is a 31.25% ethanol solution, then the unknown concentration of S is
[2018]
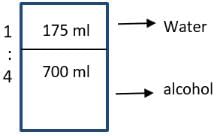
A jar contains a mixture of 175 ml water and 700 ml alcohol. Gopal takes out 10% of the mixture and substitutes it by water of the same amount. The process is repeated once again. The percentage of water in the mixture is now
[2018]
The strength of a salt solution is p% if 100 ml of the solution contains p grams of salt. If three salt solutions A, B, C are mixed in the proportion 1 : 2 : 3, then the resulting solution has strength 20%. If instead the proportion is 3 : 2 : 1, then the resulting solution has strength 30%. A fourth solution, D, is produced by mixing B and C in the ratio 2 : 7. The ratio of the strength of D to that of A is
[2018]
|
152 docs|327 tests
|


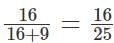 at the end of the two replacements.
at the end of the two replacements.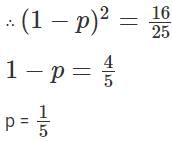
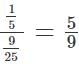
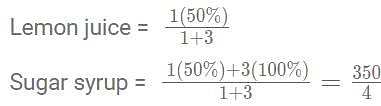

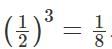

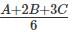 = 0.2 ⇒ A + 2B + 3C = 1.2 ...(1)
= 0.2 ⇒ A + 2B + 3C = 1.2 ...(1) = 0.3 ⇒ 3A +2B + C = 1.8 ...(2)
= 0.3 ⇒ 3A +2B + C = 1.8 ...(2)