CPU 6 - Acid Amides (Carboxylic Acids And Acid Derivatives) - Class 12 MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - CPU 6 - Acid Amides (Carboxylic Acids And Acid Derivatives)
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
What is formed as the major organic product in the reaction ?
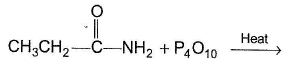
What is formed as the major organic product of the reaction?
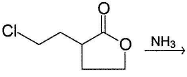
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which is most reactive in base catalysed hydrolysis reaction?
Which reaction given below produces a secondary amide?
Which reaction gives a polymeric amide?
Which reaction gjyen below gives a lactum as the major organic product?
What is the major product of the reaction?
Which of the following reactions does not give ethanamide?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-14) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which reagent given below can bring about the following transformation?
Which is/are the expected product in the following sequence of reaction?
Consider the following Hofmann’s degradation reaction,
Q.
The expected product(s) is/are
Which reaction(s) below gives primary amine?
In the reaction given below, the intermediates formed is/are
Consider the following hydrolysis reaction of a pure enantiomer of amide,
Q.
The correct statement regarding the above hydrolysis reaction is/are
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Hofmann’s bromamide degradation is used to convert a primary amide into primary amine. The proposed mechanism of reaction are :
Q.
Which is the most important intermediate formed in the slow, rate determining step?
Hofmann’s bromamide degradation is used to convert a primary amide into primary amine. The proposed mechanism of reaction are :
Q.
In the following reaction,
Formation of the above shown products and not any cross-products eliminates completely which step of the reaction mechanism?
Hofmann’s bromamide degradation is used to convert a primary amide into primary amine. The proposed mechanism of reaction are :
Q.
If a pure enantiomer of amide given below is used
What can be predicted regarding product?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-21) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
How many amide isomers exist for C4H9ON that do not form amine on treatment with Br2-NaOH ?
How many amide isomers exist for C5H11ON that on treatment with NaOH/Br2 give amines ?
Nylon-6 is formed by the acid catalysed hydrolysis of a cyclic amide. How many carbon atoms are present in this cyclic amide ?
How many total amide isomers exist for C3H7ON?

















