Chemical Bonding - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Bonding
Arrange the following species in their stability order:
(I) H2+ (II) He2+ (III) He22+
Arrange the following compounds in their C—F bond length:
(I) CH3F (II) CH2F2 (III) CHF3
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following alkalimetal halide has the lowest lattice energy:
Out of SiCl4, TiCl4, PO43–, SO42–, CrO42–, CCl4, SF4 isostructural are:
Arrange the following species in increasing order of stability.
Li2, Li2+, Li2–
In valence-bond calculations, contributions of various resonance structures an used to calculate the total energy of a molecule. Given below are four resonance structures of the cyanate ion. Which one contributes least to the total energy:
Find out the correct increasing order of hardness of the following compounds:
LiCl, SrO, BaO, CaO, CaF2
Consider ψA and ψB are the wave-function of atoms A and B respectively, then the charge density for anti-bonding molecular orbital can be given as:
If one assumes linear structure instead of bent structure of water, then which of the following properties cannot be explained?
Identify the correct order of solubility of Na2S, CuS, and ZnS in aqueous medium:
Polarization is the distortion of the shape of an anion by an adjacently placed cation. Which of the following statement is correct:
The correct increasing order of melting points of the following is:
If the dipole moment of HCl is 1.08 D and the bond distance is 1.27 Å, the partial charge on hydrogen and chlorine, respectively are:
The AsF3 molecule is trigonal pyramidal. The hybrid orbitals used by the As atoms for bonding are:
Assuming 2s-2p mixing is not operative, the paramagnetic species among the following is:
Which one of the following pairs of species have the same bond order?
Which type of interaction results in molecular orbitals with the same number of nodal planes:
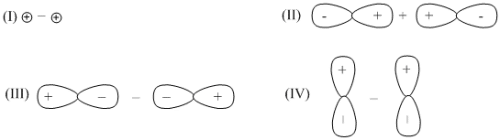
For the oxidation state(s) of sulphur atoms in S2O, consider the following
(I) –2 and +4 (II) 0 and +2 (III) +4 and 0
The correct answer(s) is/are
The reason for the chemical inertness of gaseous nitrogen at room temperature is best given by its:


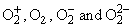 respectively are:
respectively are: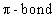 of ethene is located in:
of ethene is located in: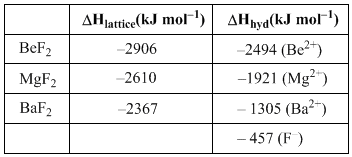
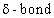 is formed via the overlap of:
is formed via the overlap of:














