Chemical Equation MCQ - 1 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Equation MCQ - 1 (Advanced)
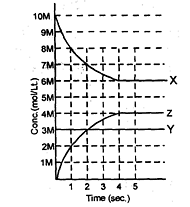
X,Y and Z react in the 1 : 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio. The concentration of X, Y and Z where found to vary with time as shown in the figure below
Q.
Which of the following equilibrium reaction represents the correct variation of concentration with time.
X,Y and Z react in the 1 : 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio. The concentration of X, Y and Z where found to vary with time as shown in the figure below

Q.
Value of the equilibrium constant (Kc) for the equilibrium represented in above sketch will be.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
X,Y and Z react in the 1 : 1 : 1 stoichiometric ratio. The concentration of X, Y and Z where found to vary with time as shown in the figure below

Q.
If above equilibrium is established in a 2L container by taking reactants in sufficient amount then how many moles of component Y must have reacted to establish the equilibrium.
For certain substances such as ammonium chloride, nitrogen peroxide, phosphorus pentachloride, etc. the measured densities are found to be less than those calculated from their molecular formula. The observed densities decrease towards a limit as the temperature is raised. This is due to the splitting of the molecules into simpler ones. The process is reversible and is called thermal dissociation.
Examples :
With increase in the number of molecules, the volume increases (pressure remaining constant) and, in consequence, the density decreases. As the temperature rises, more and more dissociation takes place, and when practically complete dissociation occursthe density reaches its lowest limit.The extent of issociation, ice., the fraction of the total number of molecules which suffers dissociation is called the degree of dissociation. Gas density measurements can be used to determine the degree of dissociation. Let us take by general case where one molecule of a substance A splits up into n molecule of B on heating; i.e.,
t = 0 a
t = teq a — x nx
Total no. of moles
Observed molecular weight or molar mass of the mixture
Q.
A sample of mixture of A(g), B(g) and C(g) under equilibrium has a mean molecular weight (observed) is 80.
The equilibrium is
Find the degree of dissociation α for A(g).
For certain substances such as ammonium chloride, nitrogen peroxide, phosphorus pentachloride, etc. the measured densities are found to be less than those calculated from their molecular formula. The observed densities decrease towards a limit as the temperature is raised. This is due to the splitting of the molecules into simpler ones. The process is reversible and is called thermal dissociation.
Examples :
With increase in the number of molecules, the volume increases (pressure remaining constant) and, in consequence, the density decreases. As the temperature rises, more and more dissociation takes place, and when practically complete dissociation occursthe density reaches its lowest limit.The extent of issociation, ice., the fraction of the total number of molecules which suffers dissociation is called the degree of dissociation. Gas density measurements can be used to determine the degree of dissociation. Let us take by general case where one molecule of a substance A splits up into n molecule of B on heating; i.e.,
t = 0 a
t = teq a — x nx
Total no. of moles
Observed molecular weight or molar mass of the mixture
Q.
If the total mass of the mixture in the above case is 300 gm, the moles at C(g) present are.
For certain substances such as ammonium chloride, nitrogen peroxide, phosphorus pentachloride, etc. the measured densities are found to be less than those calculated from their molecular formula. The observed densities decrease towards a limit as the temperature is raised. This is due to the splitting of the molecules into simpler ones. The process is reversible and is called thermal dissociation.
Examples :
With increase in the number of molecules, the volume increases (pressure remaining constant) and, in consequence, the density decreases. As the temperature rises, more and more dissociation takes place, and when practically complete dissociation occursthe density reaches its lowest limit.The extent of issociation, ice., the fraction of the total number of molecules which suffers dissociation is called the degree of dissociation. Gas density measurements can be used to determine the degree of dissociation. Let us take by general case where one molecule of a substance A splits up into n molecule of B on heating; i.e.,
t = 0 a
t = teq a — x nx
Total no. of moles
Observed molecular weight or molar mass of the mixture
Q.
The K for the reaction is 640 mm at 775 K. The percentage dissociation of N2O4 at equilibrium pressure of 160 mm is :
For certain substances such as ammonium chloride, nitrogen peroxide, phosphorus pentachloride, etc. the measured densities are found to be less than those calculated from their molecular formula. The observed densities decrease towards a limit as the temperature is raised. This is due to the splitting of the molecules into simpler ones. The process is reversible and is called thermal dissociation.
Examples :
With increase in the number of molecules, the volume increases (pressure remaining constant) and, in consequence, the density decreases. As the temperature rises, more and more dissociation takes place, and when practically complete dissociation occursthe density reaches its lowest limit.The extent of issociation, ice., the fraction of the total number of molecules which suffers dissociation is called the degree of dissociation. Gas density measurements can be used to determine the degree of dissociation. Let us take by general case where one molecule of a substance A splits up into n molecule of B on heating; i.e.,
t = 0 a
t = teq a — x nx
Total no. of moles
Observed molecular weight or molar mass of the mixture
Q.
x (degree of dissociation) varies with D/d in the above reaction according to :
For certain substances such as ammonium chloride, nitrogen peroxide, phosphorus pentachloride, etc. the measured densities are found to be less than those calculated from their molecular formula. The observed densities decrease towards a limit as the temperature is raised. This is due to the splitting of the molecules into simpler ones. The process is reversible and is called thermal dissociation.
Examples :
With increase in the number of molecules, the volume increases (pressure remaining constant) and, in consequence, the density decreases. As the temperature rises, more and more dissociation takes place, and when practically complete dissociation occursthe density reaches its lowest limit.The extent of issociation, ice., the fraction of the total number of molecules which suffers dissociation is called the degree of dissociation. Gas density measurements can be used to determine the degree of dissociation. Let us take by general case where one molecule of a substance A splits up into n molecule of B on heating; i.e.,
t = 0 a
t = teq a — x nx
Total no. of moles
Observed molecular weight or molar mass of the mixture
Q.
The equation is correctly matched for :
Match the following (multiple)
Left column : Represents an equilibrium situratton through a chemical equation and below each equation a stimulus is given which may or may not
disturb the equilibrium situration.
Right coloumn : Represents the responses immediately after the disturbance is created.
With R1 : Rate of forward reaction.
Rb Rate of backward reaction.
Q : Reaction quotient
K : Equilibrium constant

















