Chemical Kinetics & Thermodynamics (26-12-2017) - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemical Kinetics & Thermodynamics (26-12-2017)
The equation of state for a gas is given by PV = nRT + αV, where n is the number of moles and α is a positive constant. The initial temperature and pressure of one mole of the gas contained in a cylinder are T0 and P0 respectively. The work done by the gas when its temperature doubles isobarically will be:
The standard enthalpy of formation of NH3 is –46.0 kJ/mol. If the enthalpy of formation of H2 from its atoms is –436 kJ/mol and that of N2 is –712 kJ/mol, the average bond enthalpy of N—H bond in NH3 is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For a given first order reaction, the reactant reduces to 1/4th its initial value in 10 min. The rate constant of the reaction is:
For the reaction shown below,
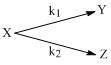
The value of k1 is 1 × 10–4 s–1. If the reaction starts from X, the ratio of the concentrations of Y and Z at any given time during the course of the reaction is found to be 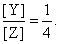 The value of k2 is:
The value of k2 is:
For a first order gas phase reaction,
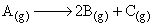
P0 be initial pressure of A and Pt be the total pressure at time ‘t’. Integrated rate equation is:
The value of the rate constant for the gas phase reaction, 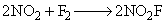 is 38 dm3 mol–1 s–1 at 300 K. The order of the reaction is:
is 38 dm3 mol–1 s–1 at 300 K. The order of the reaction is:
A reaction follows second order rate law, 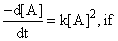
The specific rate constant of decomposition of a compound is represented by
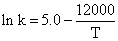 The activation energy of decomposition for this compound at 300 K is:
The activation energy of decomposition for this compound at 300 K is:
The fluorescence life time of a molecule in solution is 10 ns. If the fluorescence quantum yield is 0.1, the rate constant of fluorescence decay is:
For the reaction, P + Q + R → S, experiment data for the measured initial rates is given below:
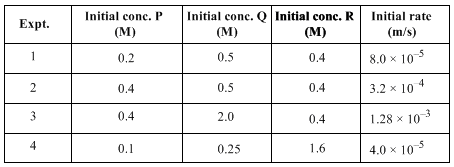
The order of the reaction with respect to P, Q and R respectively, is:
Sucrose is converted to a mixture of glucose and fructose in a pseudo first order process under alkaline conditions. The reaction has a half-life of 28.4 min. The time required for the reduction of a 8.0 mM sample of sucrose to 1.0 mM is:
The reaction, 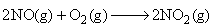 proceeds via the following steps:
proceeds via the following steps:
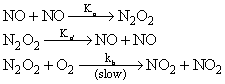
The rate of this reaction is equal to
1 g of 90Sr gets converted to 0.953 g after 2 yr. The half-life of 90Sr, and the amount of 90Sr remaining after 5 yr are:
Consider an exothermic reaction 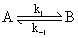
As the temperature increases
A reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate B in a unimolecular reaction
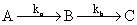
The integrated rate law for this reaction is:
If ka >> kb, then concentration versus time plot for the reaction is:
Noncatalytic oxidation of the aromatic hydrocarbons is slow at which temperature?
The half-life of a first order reaction varies with temperature according to:
The molar entropy of crystalline CO at absolute zero is:
Among the following, the system that would require the least amount of thermal energy to bring its temperature to 80°C is:
The plot that describes a Carnot cycle is:
The rate of evaporation of a liquid is always faster at a higher temperature because:
For the process,
1 Ar (300 K, 1 bar) → 1Ar (200 K, 10 bar) assuming ideal gas behaviour, the change in molar entropy is:
For the reaction, 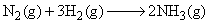
Compute the entropy change (in J/K/mol) for the process and comment on the sign of the property.
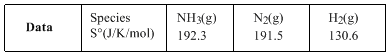
For the reaction,
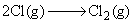
The thermodynamic properties
A radioactive isotope having a half-life of 3 days was received after 12 days. It was found that there were 3 g of the isotope in the container. The initial weight of the isotope when packed was:
Among the following, the most stable isotope to radioactive decay is:
Activity of a radioactive substance is A1 at time t1 and A2 at time t2 (t2 > t1). The activity ratio 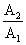 is
is
(λ = decay constant)
A radioactive sample consists of two distinct species having equal number of atoms initially. The mean life of one species is t and that of the other is 5t. The decay products in both cases are stable. A plot is made of the total number of radioactive nuclei as a function of time. What of the following figures best represents the form of this plot:


















