Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 1 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 1
Consider the 1M aqueous solution of the following compounds and arrange them in the increasing order of elevation in the boiling points.
A. C6H12O6
B. NaCl
C. MgCl2
D. AlCl3
E. Al2(SO4)3
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 5g of NaOH in 450 mL solution
Among the following statements related to ionic conductance, choose the correct statements.
A. Ionic conductance depends on the nature of electrolyte
B. Ionic conductance is due to the movements of electrons
C. Ionic conductance is also called electronic conductance
D. Ionic conductance depends on temperature
E. Ionic conductance also depends on the nature of solvent
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
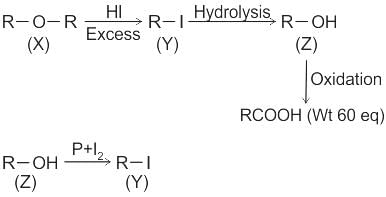
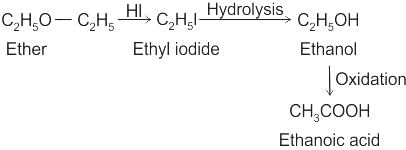
Compound (X) on treatment with an excess of CI2 in presence of light gives
Which one of the following is the correct IUPAC name of K3[ Fe (CN)5NO]?
What role do ammonia molecules play in the coordination compounds studied by Werner?
Based on Werner's theory, what does the term "secondary valence" refer to?
What was the method Werner used to distinguish between different cobalt(III) chloride complexes?
Consider the following statements regarding molarity:
(A) Molarity is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
(B) Molarity is independent of temperature.
(C) Molarity can be used to express the concentration of solid solutions.
(D) Molarity changes with temperature because the volume of the solution changes with temperature.
Choose the correct statements:
The standard electrode potential for the reaction:Cu²⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu (s)is +0.34 V. What will be the cell potential (E°) for a cell where copper is the anode and zinc is the cathode, given that the standard electrode potential for the zinc half-reaction is -0.76 V?
Which of the following oxides is amphoteric in nature?
The rate constant of a reaction is 0.01s-1, how much time does it take for 2.4 mol L-1 concentration of reactant reduced to 0.3 mol L-1?
What time does it take for reactants to reduce to 3/4 of initial concentration if the rate constant is 7.5 x 10-3 s-1?
Which of the following is the correct expression for the temperature coefficient (n)?
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?
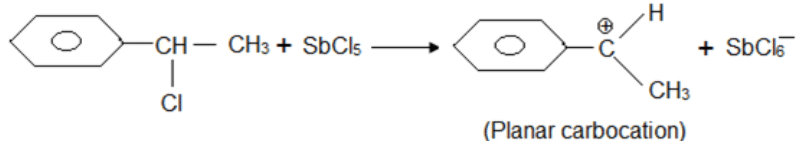
A solution of (–)-1-chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5, due to the formation of
Which of the following is not a secondary pollutant
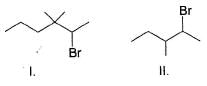
What is the increasing order of reactivity of the following in an E2 reaction with ethanolic KOH solution?
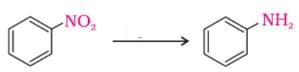
The following reaction takes place in the presence of
The functional group, which is found in amino acid is -
[AIEEE-2002]
Complete hydrolysis of cellulose gives –
[AIEEE-2003]




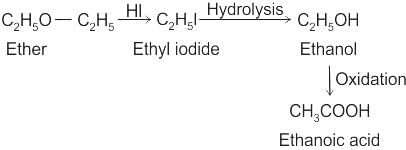
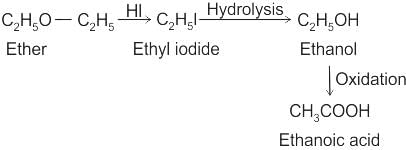
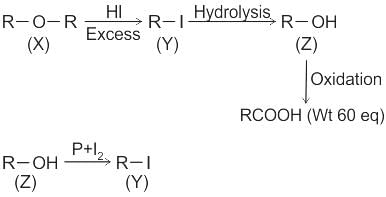
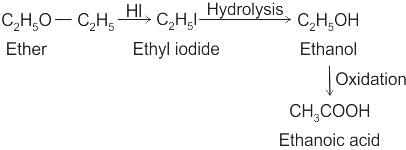
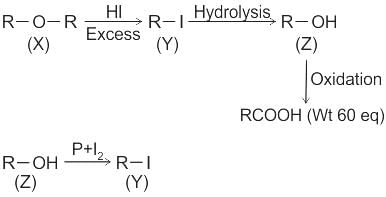
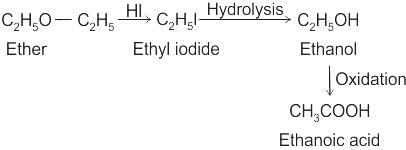
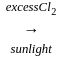 CCl3CCl2 - O - CCl2CCl3
CCl3CCl2 - O - CCl2CCl3