Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 8 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 8
Which of the following is not an oxo-acid of nitrogen?
Which of the following compound would undergo Aldol condensation?
Among the following statements choose the correct statements
A. Analgesics reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion.
B. Tranquilizers are neurological inactive drugs.
C. Morphine is the example of non- narcotic analgesics.
D. Disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects whereas antiseptics are applied to the living tissues.
E. Same substance can act as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant by varying the concentration.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
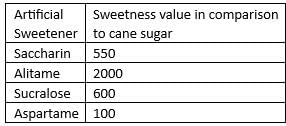
Out of the following artificial sweetening agents, which one has highest sweetness value in comparison to cane sugar?
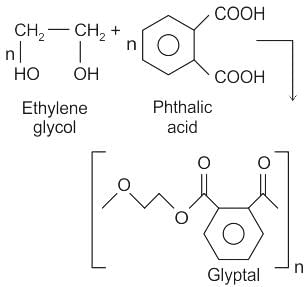
Among the following polymers, which one is the copolymer?
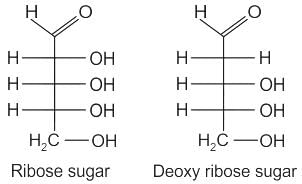
RNA and DNA are chiral molecules, their chirality is due to
The two DNA strands are composed of simpler monomeric units called Nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of nitrogen-containing nucleobases. Consider the following,
1. Cytosine
2. Guanine
3. Adenine
4. Thymine
5. Uracil
Which of the above nucleobase is present in DNA?
Polymerization is a type of reaction in which ________.
Which one of the following statement is NOT correct for detergents?
What is the key characteristic that differentiates phenols from alcohols?
Which of the following is an example of a polyhydric alcohol?
What property makes phenols more acidic than alcohols?
What type of alcohol is formed when a Grignard reagent reacts with an aldehyde?
Which reaction is used to prepare phenols from haloarenes?
What is the major difference between the preparation methods of ethanol and methanol?
Which enzyme is responsible for the fermentation process that produces ethanol?
What happens if air gets into the fermentation mixture?
Consider the following statements:
(A) Transition metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
(B) Transition metals form a wide range of complex compounds, many of which are important in industrial catalysis.
(C) The first transition series elements show a gradual change in properties as we move across the period.
(D) The properties of d-block elements are influenced by the energy gap between the 3d and 4s orbitals.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Consider the following statements:
(A) The first transition series elements only have two electrons in their outermost s-orbitals.
(B) Transition metals like iron and copper are used in the manufacture of steel due to their high strength.
(C) All transition metals have an oxidation state of +2 in their compounds.
(D) Transition metals show multiple oxidation states because of the involvement of d-electrons in bonding.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Which of the following reactions best represents lab scale preparation of nitric acid?
What is the catalyst used in the industrial manufacture of nitric acid?
How many moles of nitric acid is required to convert 1 mole of sulfur to sulfuric acid?
What product(s) is/are formed when aluminum metal is treated with concentrated nitric acid?
What is the nitric acid – water composition by mass, respectively, for the components to form an azeotrope?
What is the name of the industrial process to manufacture nitric acid?
Which of the following is true regarding nitric acid?