Computer Science: CUET Mock Test - 4 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 - Computer Science: CUET Mock Test - 4
Which of the following words cannot be a variable in python language?
Identify the SQL query which displays the data of table Stulibrary in ascending order of student ID.
The primary key of Stulibrary table is / are:
Which of the following SQL query will fetch ID of those issued books which have not been returned?
The alternate key for Student table will be ________.
Which of the following SQL queries will display dates on which number of issued books is greater than 5?
Srishti writes a program to find an element in the array A[5] with the following elements in order: 8 30 40 45 70. She runs the program to find a number X. X is found in the first iteration of binary search. What is the value of X?
Which statement about IPv6 addresses is true?
Consider the following statements regarding statistical data analysis:
Statement I: In a skewed distribution, the median is always found between the mean and the mode.
Statement II: The range of a dataset is defined as the difference between its maximum and minimum values.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below based on the truthfulness of the above statements:
Two statements are given below:
Statement I: A ring topology is a type of network topology in which all devices are connected to a single cable.
Statement II: A bus topology is a type of network topology in which all devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
What is the purpose of the rewind() function?
Directions: Match the contents under List I with those under List II.
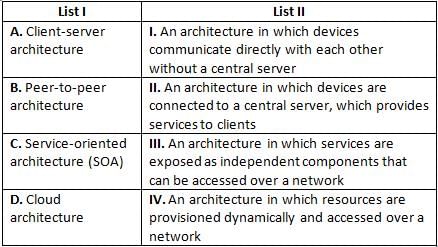
What will the following statement do?
FILE *fp1;
char Tch;
fp1=fopen("TCY.c","r");
while((Tch=getc(fp1)) != EOF)
printf("%c",Tch);
This method returns an integer that specifies the current position of the file object.
What is the output of the following program:
print((1, 2) + (3, 4))
Which of the following is an application of stack?
____ command helps to add new data to the database.
Which of the following best describes a white hat hacker?
Millions of computer science students have taken a course on algorithms and data structures, typically the second course after the initial one introducing programming. One of the basic data structures in such a course is the stack. The stack has a special place in the emergence of computing as a science, as argued by Michael Mahoney, the pioneer of the history of the theory of computing. The stack can be used in many computer applications; a few are given below:
(a) In recursive function
(b) When function is called
(c) Expression conversion such as – Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Postfix to Infix, Prefix to Infix
In stack, insertion operation is known as push, whereas deletion operation is known as pop.
Code – 1
def push(Country,N):
Country._________(len(Country),N)) #Statement 1
#Function Calling
Country=[]
C=['Indian', 'USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Sri Lanka']
for i in range(0,len(C),________): #Statement 2
push(Country,C[i])
print(Country)
Required Output:
['Indian', 'UK', 'Sri Lanka']
Code - 2
def pop(Country):
if ______________: #Statement 3
return "Under flow"
else:
return Country.________() #Statement 4
#Function Calling
for i in range(len(Country)+1):
print(_______________) #Statement 5
Required Output:
Sri Lanka
UK
India
Under flow
Fill the statement based on the given question:
Q. Identify the suitable code for the blank of Statement 1.
Millions of computer science students have taken a course on algorithms and data structures, typically the second course after the initial one introducing programming. One of the basic data structures in such a course is the stack. The stack has a special place in the emergence of computing as a science, as argued by Michael Mahoney, the pioneer of the history of the theory of computing. The stack can be used in many computer applications; a few are given below:
(a) In recursive function
(b) When function is called
(c) Expression conversion such as – Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Postfix to Infix, Prefix to Infix
In stack, insertion operation is known as push, whereas deletion operation is known as pop.
Code – 1
def push(Country,N):
Country._________(len(Country),N)) #Statement 1
#Function Calling
Country=[]
C=['Indian', 'USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Sri Lanka']
for i in range(0,len(C),________): #Statement 2
push(Country,C[i])
print(Country)
Required Output:
['Indian', 'UK', 'Sri Lanka']
Code - 2
def pop(Country):
if ______________: #Statement 3
return "Under flow"
else:
return Country.________() #Statement 4
#Function Calling
for i in range(len(Country)+1):
print(_______________) #Statement 5
Required Output:
Sri Lanka
UK
India
Under flow
Fill the statement based on the given question:
Q. Fill Statement 3, to check if the stack is empty.
Millions of computer science students have taken a course on algorithms and data structures, typically the second course after the initial one introducing programming. One of the basic data structures in such a course is the stack. The stack has a special place in the emergence of computing as a science, as argued by Michael Mahoney, the pioneer of the history of the theory of computing. The stack can be used in many computer applications; a few are given below:
(a) In recursive function
(b) When function is called
(c) Expression conversion such as – Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Postfix to Infix, Prefix to Infix
In stack, insertion operation is known as push, whereas deletion operation is known as pop.
Code – 1
def push(Country,N):
Country._________(len(Country),N)) #Statement 1
#Function Calling
Country=[]
C=['Indian', 'USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Sri Lanka']
for i in range(0,len(C),________): #Statement 2
push(Country,C[i])
print(Country)
Required Output:
['Indian', 'UK', 'Sri Lanka']
Code - 2
def pop(Country):
if ______________: #Statement 3
return "Under flow"
else:
return Country.________() #Statement 4
#Function Calling
for i in range(len(Country)+1):
print(_______________) #Statement 5
Required Output:
Sri Lanka
UK
India
Under flow
Fill the statement based on the given question:
Q. Fill Statement 5, to call the pop function.
Millions of computer science students have taken a course on algorithms and data structures, typically the second course after the initial one introducing programming. One of the basic data structures in such a course is the stack. The stack has a special place in the emergence of computing as a science, as argued by Michael Mahoney, the pioneer of the history of the theory of computing. The stack can be used in many computer applications; a few are given below:
(a) In recursive function
(b) When function is called
(c) Expression conversion such as – Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Postfix to Infix, Prefix to Infix
In stack, insertion operation is known as push, whereas deletion operation is known as pop.
Code – 1
def push(Country,N):
Country._________(len(Country),N)) #Statement 1
#Function Calling
Country=[]
C=['Indian', 'USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Sri Lanka']
for i in range(0,len(C),________): #Statement 2
push(Country,C[i])
print(Country)
Required Output:
['Indian', 'UK', 'Sri Lanka']
Code - 2
def pop(Country):
if ______________: #Statement 3
return "Under flow"
else:
return Country.________() #Statement 4
#Function Calling
for i in range(len(Country)+1):
print(_______________) #Statement 5
Required Output:
Sri Lanka
UK
India
Under flow
Fill the statement based on the given question:
Q. Fill Statement 2, to insert the alternate element from Country list.
Millions of computer science students have taken a course on algorithms and data structures, typically the second course after the initial one introducing programming. One of the basic data structures in such a course is the stack. The stack has a special place in the emergence of computing as a science, as argued by Michael Mahoney, the pioneer of the history of the theory of computing. The stack can be used in many computer applications; a few are given below:
(a) In recursive function
(b) When function is called
(c) Expression conversion such as – Infix to Postfix, Infix to Prefix, Postfix to Infix, Prefix to Infix
In stack, insertion operation is known as push, whereas deletion operation is known as pop.
Code – 1
def push(Country,N):
Country._________(len(Country),N)) #Statement 1
#Function Calling
Country=[]
C=['Indian', 'USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Sri Lanka']
for i in range(0,len(C),________): #Statement 2
push(Country,C[i])
print(Country)
Required Output:
['Indian', 'UK', 'Sri Lanka']
Code - 2
def pop(Country):
if ______________: #Statement 3
return "Under flow"
else:
return Country.________() #Statement 4
#Function Calling
for i in range(len(Country)+1):
print(_______________) #Statement 5
Required Output:
Sri Lanka
UK
India
Under flow
Fill the statement based on the given question:
Q. Fill Statement 4, to delete an element from the stack.
Which of the following File open modes is used for opens the file in read,write and binary mode?
How many swaps are required to sort the list L2 using selection sort?
L2: [54, 23, 12, 44, 18, 22, 14]
In python, to support enqueue and dequeue operations which operations are used?
Which of the following statement are true?
Statement 1: dump() method is used to write the objects in a binary file.
Statement 2: load() method is used to read data from a binary file.
Which method is called before calling POP() method in the program.
What is the output for the given python program?
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/0;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
|
39 docs|145 tests
|




















