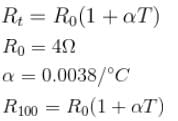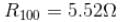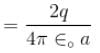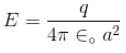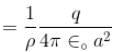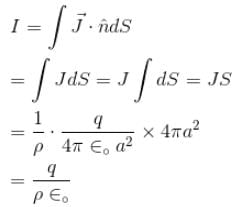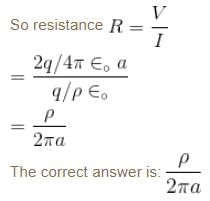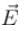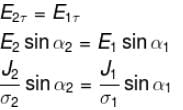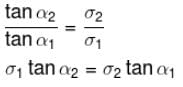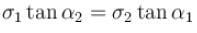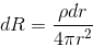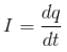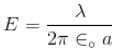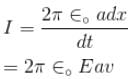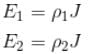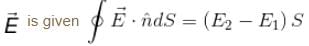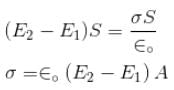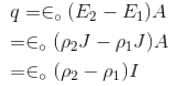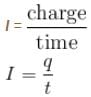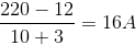Current Electricity MCQ Level - 3 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Basic Physics for IIT JAM - Current Electricity MCQ Level - 3
The resistance of platinium wire at 0°C is 4Ω What will be the resistance of the wire at 100°C. If the temperature coefficient of resistance of platinium is 0.0038/°C
Two metal ball of the same radius a are located in homogeneous poorly conducting medium with resistivity ρ.The resistance of the medium between the ball provided that the separation between them is much greater than the radius of the ball.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In case of insulator as the temperature decrease resistivity
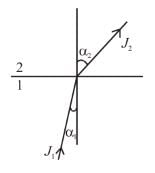
The law of refraction of direct current lines at the boundary between two conducting media having σ1 and σ2 are the conductivity of media 1 and 2 and α1 and α2 are the angle between the current lines and normal of the boundary surface as shown in figure.
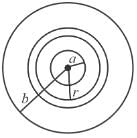
A metal ball of radius a is surrounded by a thin concentric metal shell of radius b. The space between these electrodes is filled up with a poorly conducting homogeneous medium of resistivity ρ. The resistance of the interelectrode gap. assume b → ∞
A long cylinder with uniformly charged surface an cross-section radius a moves with a constant velocity v along its axis. An electric field strength at the surface of the cylinder is equal to E. So current caused by mechanical transfer of a charge.
What is the drift velocity of an electron in a copper conductor having area 10 × 10–6 m2 and 10 × 1028 electron/m3
Two cylindrical conductor with equal cross-sections and different resistivity ρ1 and ρ2 are put end to end. The charge at the boundary of the conductor if a current I flows from conductor 1 to conductor 2
A current of 1A flows through a copper wire. How many electron pass through any cross-section of the wire in 1.6 seconds. (Charge on electron in 1.6 × 10–19C)
A battery of 6 cells, each of emf 2V and internal resistance 0.5Ω is being charged by a 220V supplying an external resistance of 10Ω is series. The potential difference across the battery is :
|
210 videos|156 docs|94 tests
|