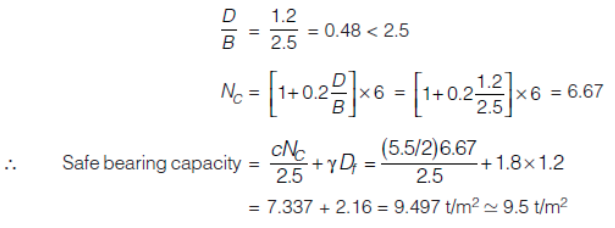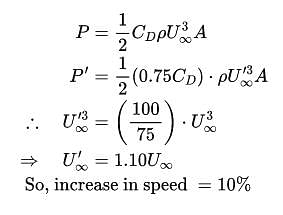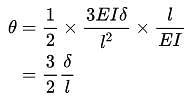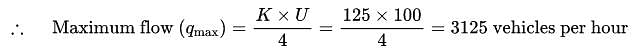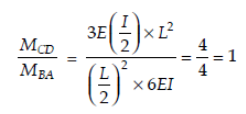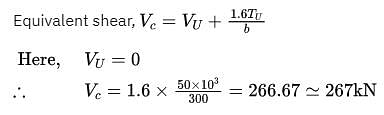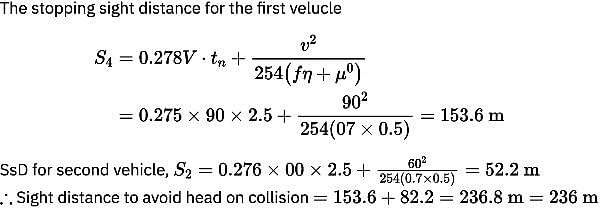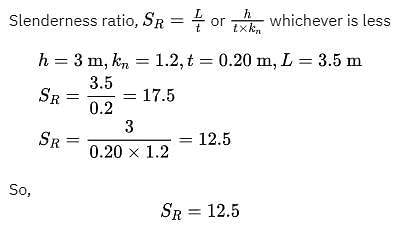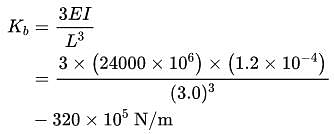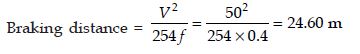ESE (CE) Paper II Mock Test - 5 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series for IES/ESE (CE) - ESE (CE) Paper II Mock Test - 5
Consider the following structure:

The horizontal shear in column ‘NQ’ is [Use portal method]

In PERT, slack is computed as the difference between which are of the following?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the anchorage value of a standard hook of a reinforcement bar of diameter D?
Two bars one of material A and the other of material B of same length are tightly secured between two unyielding walls. Coefficient of the thermal expansion of bar A is more than that of B. When temperature rises then the stresses induced are
Which of the following losses occur in pre-tensioned prestressed concrete?
1. Elastic deformation of concrete
2. Relaxation of steel
3. Friction
4. Anchorage slip
Contact pressure beneath a rigid footing resting on a cohesive soil is
A square footing of 2.5 m × 2.5 m size has been founded at 1.2 m below the ground level in a cohesive soil having a bulk density of 1.8 t /m3 and an unconfined compressive strength of 5.5 t /m2. Determine the safe bearing capacity of the footing for a factor of safety of 2.5. Use Skempton’s theory.
In the following questions two statements are given. Read them carefully and choose from the options given below:
a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
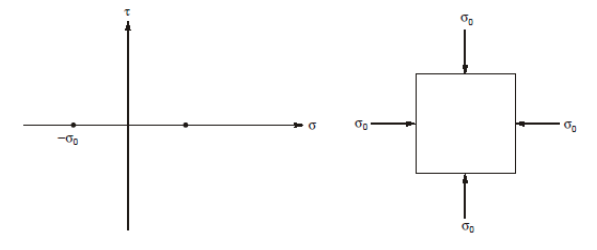
Assertion (A): Mohr’s circle of an element subjected to hydrostatic loading, reduces into a point.
Reason (R): In hydrostatic loading, shear stress is zero and principal stresses are equal and alike.
Improved stream lining produces 25% reduction in the drag coefficient of a torpedo. When it is travelling fully submerged and assuming the driving power to remain the same, the increase in speed will be
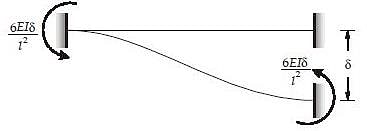
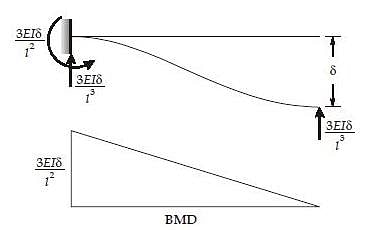
If the hinged end of a propped cantilever beam of span L settles by an amount then the rotation of the hinged end will be
Consider the following statements:
- The moisture content in a properly seasoned timber will be in the rage of 10 - 12%.
- The sapwood contains most of the moisture and dries more rapidly than the heartwood.
Which of the above statements is(are) CORRECT?
Traffic flow equation for a section of road is U = 100 – 0.8 K, where ‘U’ is speed (in kmph) and ‘K’ is density (in vehicles per km). The maximum expected flow is
The amount of irrigation water required to meet the evapo-transpiration needs of a crop for its full growth is called
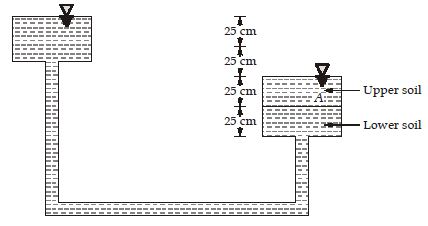
Two different granular soils are placed in a permeameter tube and flow is allowed to take place under a constant total head. The total head and pressure head at point A in centimeters, are respectively
The arithmetical check for the computation of RL by “Rise and Fall” method is given by
A beaker filled with water is falling freely under the influence of gravity. Point B is on the free surface of water and point C is vertically below B near the bottom of the beaker. If PB is the pressure at the point B and PC the pressure of point C, then which one of the following is correct?
A column ABCD of rectangular section is subjected to an eccentric load at Z as shown in the given figure.
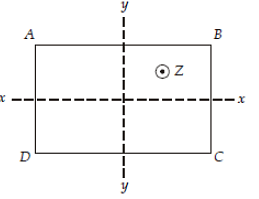
Under the compressive load, the direct stress is 400 t/m2 and maximum bending stresses are
σxx = +1200 t/m2 and σyy = +800 t/m2.
The stress at corner A will be
When subjected to a torque, a circular shaft undergoes a twist of 1° in a length of 1200 mm, and the maximum shear stress induced is 80 N/mm2. The modulus of rigidity of material of shaft is 0.8 × 105 N/mm2. The radius of shaft is
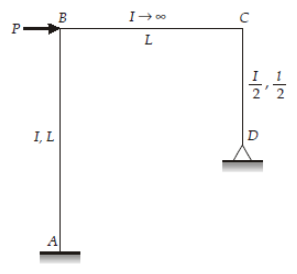
In the portal frame shown below the ratio of moments MCD to MBA induced in the column due to side sway is
Consider the following statements:
- One year strength of continuously moist cured concrete is 40% higher than that of 28 days strength.
- Moist curing for the first seven to fourteen days results in a compressive strength of 70 to 80% of that of 28 days moisture curing.
- Curing of concrete by steam under pressure results in early gain of compressive strength of concrete.
Which of the above statements is(are) CORRECT?
If a beam of cross–section 300 mm × 600 mm is subjected to a torsional moment of 50 kNm, then the equivalent shear force is:
If the atomic radius of aluminum is 0.143 nm; then the volume of its unit cell in cubic meter is given by
The two cars are approaching from the opposite directions at a speed of 90 km/hr and 60 km/hr. If the coefficient of friction is 0.7 and brake efficiency is 50% then the minimum sight distance required to avoid head on collision of two vehicles is ___________. [Take reaction time as 2.5 sec]
If the actual thickness of brick masonry wall is 20 cm, its effective length is 3.50 m, its effective height is 3 m and its code specified stiffening coefficient is 1.2, then, for design considerations, the slenderness ratio of the wall will be taken as
The natural frequency of the structural system as shown in figure will be :
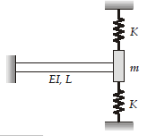
Where, L = 3.0 m, E = 24000 MPa, I = 1.2 x 10-4 m4, K = 40 kN/m, m = 10 kN. [Take g = 10 m/s2]
A beam of uniform strength refers to which one of the following?
In any project network, the execution of various activities can be expedited if necessary by
The coefficient of friction in the longitudinal direction of highway is estimated as 0.4. The braking distance for a car moving at a speed of 50 km/hr is
The maximum bending moment in purlin of span ‘L’ and total load ‘W’ is