Electrochemistry & Conductance Test (19-12-2016) - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Electrochemistry & Conductance Test (19-12-2016)
The ionic strength of a solution containing 0.008 M AlCl3 and 0.005 M KCl is:
The standard reduction potential for the following two reactions are given:
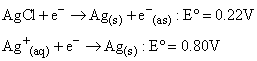
The solubility product of AgCl under standard condition will be:
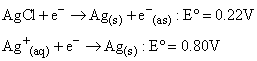
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The standard E°red value of A, B and C are +0.68 V, –2.54 V, –0.50 V respectively. The order of their reducing power is:
E1, E2 and E3 are the e.m.f.s. of the following three galvanic cells respectively:
(i) Zn(s)/Zn2+ (0.1M) || Cu2+ (1M)/Cu(s).
(ii) Zn(s)/Zn2+ (1M) || Cu2+ (1M)/Cu(s).
(iii) Zn(s)/Zn2+ (1M) || Cu2+ (0.1M)/Cu(s).
Which one of the following is true?
The temperature coefficient of a galvanic cell is +5.0 × 10–5 vk–1. During the discharge of the cell, the cell temperature:
The cell reaction involving quinhydrone electrode is:
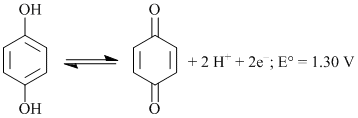
What will be the electrode potential at pH = 3:
The specific conductivity of a saturated solution of silver chloride is 2.30 × 10–6 mho cm–1 at 25°C. The solubility of silver chloride at 25°C if 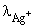 = 61.9 mho cm2 mol–1 and
= 61.9 mho cm2 mol–1 and 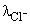 = 76.3 mho cm2 mol–1:
= 76.3 mho cm2 mol–1:
The molar conductance at infinite dilution of aluminium sulphate is 858 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1. Given the molar ionic conductance of sulphate ions as 160 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1, the molar ionic conductance of Al3+ ion is:
Two students use same stock solution of ZnSO4 and a solution of CuSO4. The emf of one cell is 0.03 V higher than that of other. The concentration of CuSO4 in the cell with higher emf value is 0.5 M. Find out the concentration of CuSO4 in the other cell: 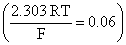
During electrolysis of H2SO4(aq) with high charge density, H2S2O8 formed as by product. In such electrolysis 22.4 L H2(g) and 8.4 L O2(g) liberated at 1 atm and 273 K at electrode. The moles of H2S2O8 formed is:
Given
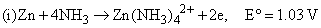
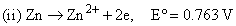
the formation constant of the complex Zn(NH3)42+ is approximately:
What is the standard electrode potential for the electrode, MnO–4 /MnO2 in an acid solution:
Calculate the liquid function potential at 25°C between two solutions of HCl having mean ionic activities of 0.01 and 0.001, respectively. The transference number of H+ ion (ft) in HCl may be taken as 0.83.
Molar conductance 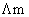 is plotted agains C1/2 (mol / lit–1) for three electrolytes (NaCl, HCl, NH4OH)
is plotted agains C1/2 (mol / lit–1) for three electrolytes (NaCl, HCl, NH4OH)
which of the following is correct?
Given the standard oxidation potentials,
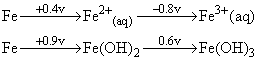
it is easier to oxidise Fe2+ to Fe3+ in:
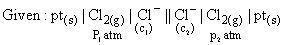
Identify in which of following condition working of cell takes place:
Ag | Ag+, KI || AgI | Ag emf is E, then Ksp of AgI is given as:
During the electrolysis of AgNO3 (using Pt electrodes) concentration around cathode as well as anode falls from 4M to 3M. What will happen if this happened with Ag electrodes:
Rusting on the surface of iron involves:
The ratio of 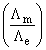 for Ca3(PO4)2 will be equal to:
for Ca3(PO4)2 will be equal to:
The amount of electricity which releases 2.626 g of Au from a gold salt is same as that which dissolves 1.26 g of Cu from copper anode during electrolysis of CuSO4 solution. Oxidation number of gold in the gold salt is:
A cell contains two hydrogen electrodes. The negative electrode is in contact with a solution of 10-6 M H+ ions. The emf of the cell is 0.118 V at 250C. Concentration of H+ ion at the +ve electrode is 10-xM. Value of x is:
In an electrolysis of an aqueous solution of NaOH, 2.8 L of oxygen gas at STP was liberated at anode. The volume of hydrogen gas at STP liberated at cathode is x times the volume of oxygen gas at anode value of x is:
A 0.05 N solution of a salt occupying a volume between two platinum electrode separated by a distance of 1.72 cm and having an area of 4.5 cm2 has a resistance of 250 ohm. The equivalent conductance of the solution ( in ohm–1 cm2) eq–1, is:
For the cell reaction, at 25°C Mg|Mg2+(aq)||Ag+(aq)|Ag
maximum work that can be obtained by operating the cell is (in J)
Given: E°mg2+/mg = –2.37 volt and E°Ag+/Ag = +0.80 volt:
The EMF of the concentration cell with transference, viz.,
Pt ; H2 (1atm), HCl 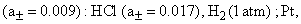
Is 0.028 V at 25°C. The EMF of the corresponding cell without transference is 0.017 V. The transference number of the H+ ion is:
Emf of the cell (1 atm) | H+ (aq.) || AgCl|Ag is 0.27 V and 0.26 V at 250C and 350C. Heat of reaction occurring inside the cell at 250C is.
While determining the pH of a solution, the quinhydrone electrode, H+ , Q. QH2 was used in conjuction with a saturated calomel electrode, as represented below:
Hg, Hg2Cl2 (s) ; KCl (sat, soln.) || H+ (unknown); Q, QH2, Pt
The EMF of the cell was found to be 0.26 volt at 25°C. Calculate the pH of the solution at this temperature. Ecalomel = + 0.24 volt at 25°C and 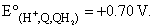
I2(s)|I–(0.1m) half-cell is connnected to H+(aq)|H2(1atm) pt half-cell and its cell potential is found to be 0.7714 V. If 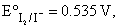 the pH of H+/H2 half-cell will be:
the pH of H+/H2 half-cell will be:

















