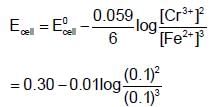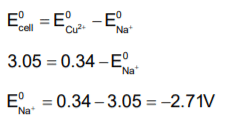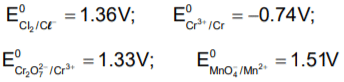Electrochemistry - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Electrochemistry
The amount of electricity required to produce one mole of copper from copper sulphate solution will be:
Which of the following condition is correct for operation of electrolytic cell?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
On passing one faraday of electricity through a dilute solution of an acid, the volume of hydrogen obtained at NTP is:
When electricity is passed through a solution of AICI3, 13.5 g of AI is discharged. The amount of charge passed is:
The specific conductance of a 0.01 M solution of KCI is 0.0014 ohm-1 at 250C. Its equivalent conductance is:
The equivalent conductivity of 0.1 N CH3COOH at 250C is 80 and at infinite dilution 400 ohm-1. The degree of dissociation of CH3COOH is:
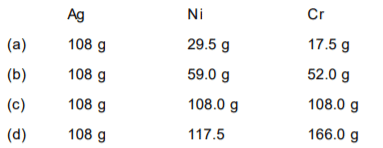
One faraday of charge was passed through the electrolytic cells placed in series containing solution of Ag+, Ni2+ and Cr3+ respectively. The amount of Ag (At. mass 108), Ni (At. mass 59) and Cr (At mass 52) deposited will be:
At 250C, the , molar conductance at infinite dilution for the strong electrolytes NaOH, NaCI and BaCI2 are 248 x 10-4, 126 x 10-4 and 280 x 10-4 S m2 mol-1 respectively. 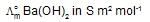
If a spoon of copper metal is placed in a solution of ferrous sulphate :
Which of the following represent the potential of silver wire dipped into 0.1 M AgNO3 solution at 250C ?
If the solution of the CuSO4 in which copper rod is immersed is diluted to 10 times, the electrode potential :
Given, standard electrode potential;The standard electrode potential

The standard electrode potential 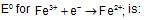
The standard emf for the cell reaction,
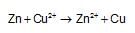
is 1.10 volt at 250C. The emf for the cell reaction when  solution are used at 250C
solution are used at 250C
Statements:
(i) Unit of specific conductivity is ohm-1 cm-1
(ii) Specific conductivity of strong electrolytes decreases on dilution.
(iii) The amount of an ion discharged during electrolysis does not depend upon resistance.
(iv) The unit of electrochemical equivalence is g/coulomb.
The emf of the cell in which the following reaction, 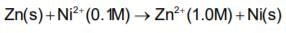 occurs, is formed to 0.5105 V at 298 K. The standard emf of the cell is:
occurs, is formed to 0.5105 V at 298 K. The standard emf of the cell is:
In the electrochemical reaction. 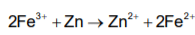 increasing the concentration of Fe2+:
increasing the concentration of Fe2+:
When 9.65 coulomb of electricity is passed through a solution of silver nitrate (Atomic mass of Ag=108 g mol-1), the amount of silver deposited is:
A current is passed through two voltameters connected in series. The first voltameter contains XSO4(aq.) while the second voltameter conatins Y2SO4(aq.). The relative atomic masses of X and Y are in the ratio 2:1. The ratio of the mass of X liberated to the mass of Y liberated is:
In which of the following cells will the emf be independent of the acitvity of the chloride ions?
The emf of the cell, 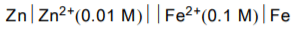 at 298 K is 0.2905 V then the value of equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is:
at 298 K is 0.2905 V then the value of equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is:
The standard electrode potential of Ag+/ Ag is + 0.80 V and of Cu2+ / Cu is + 0.34 V. These electrodes are connected through a salt bridge and if:
The reduction potential of hydrogen half-cell will be negative if:
The emf of a cell containing sodium/ copper electrodes is 3.05 V, if the electrode potential copper electrode is +0.34 V, the electrode potential of sodium is:


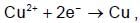 no. of electrons used is equal to no. of Faradays.
no. of electrons used is equal to no. of Faradays.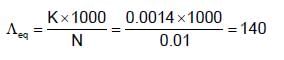
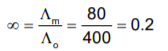
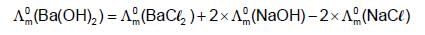
 ion is positive while Fe2+ ion is negative) When copper metal is placed in ferrous sulphate solution nothing happens, as they do not react
ion is positive while Fe2+ ion is negative) When copper metal is placed in ferrous sulphate solution nothing happens, as they do not react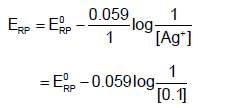
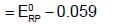
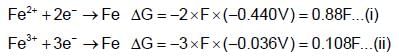
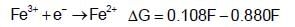
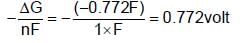
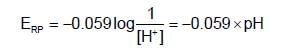
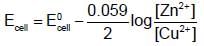
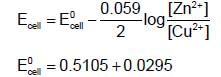
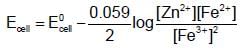
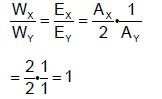
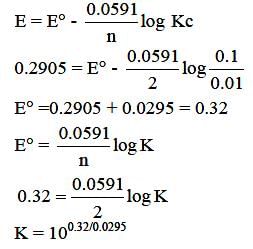
 acts as anode & high
acts as anode & high  as cathode, so,as to get +ve value of
as cathode, so,as to get +ve value of 
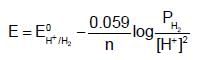
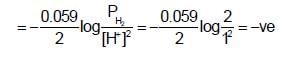
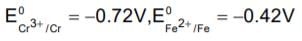 The potential for the cell,
The potential for the cell,  :
: