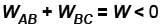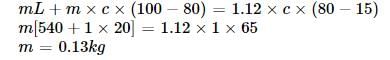First Law Of Thermodynamic MCQ Level - 1 (Part - 1) - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - First Law Of Thermodynamic MCQ Level - 1 (Part - 1)
A vessel contains 1 mole of O2 gas (molar mass 32) at a temperature T. The pressure of the gas is p. An identical vessels containing one mole of the gas (molar mass 4) at a temperature 2T has a pressure of
A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
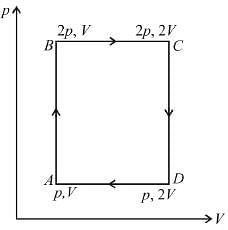
An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round that cycle ABCDA as shown in the p-V diagram (see figure). The work done during the cycle is

In a given process of an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. The for the gas
Select one:
70 cal of heat are required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at constant pressure from 30ºC to 35°C. The amount of heat required (in calorie) to raise the temperature of the same gas through the same range (30°C to 35°C) at constant volume is
An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT pressure remaining constant. The quantity 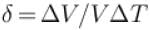 varies with temperature as
varies with temperature as
Select one:
When an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant pressure, the fraction of the heat energy supplied which increases the internal energy of the gas is
Select one:
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume V1 to V2 in three different ways, the work done by the gas is W1 if the process is purely isothermal, W2 if purely isobaric and W3 if purely adiabatic, then
An ideal gas expands isothermally from a volume V1 to V2 and then compressed to original volumes V1 adiabatically. Initial pressure is p1 and final pressure is p3. The total work done is W. Then,
Select one:
Steam at 100°C is passed into 1.1 kg of water contained in a calorimeter of water equivalent 0.02 kg at 15°C till the temperature of the calorimeter and its contents rises to 80°C. The mass of the steam condensed (in kg) is
Select one:



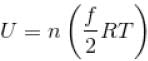
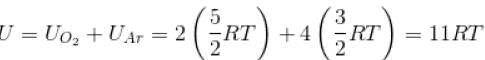
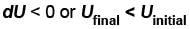 or temperature will decrease
or temperature will decrease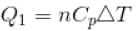

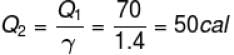
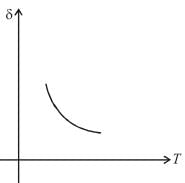
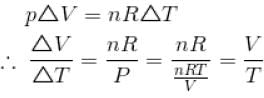

 graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.
graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.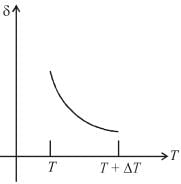
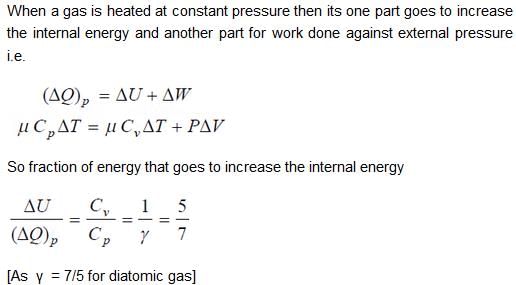
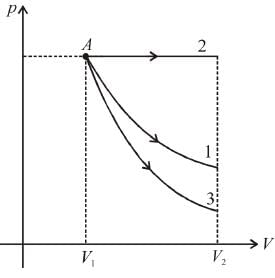
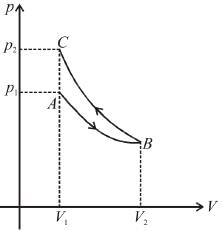
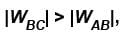 as area under p–V graph gives the work done.
as area under p–V graph gives the work done.