Genetics MCQ 1 - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2025 - Genetics MCQ 1
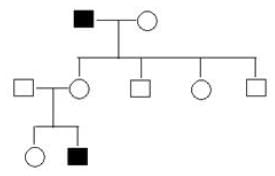
Pigmentation in moth is maternally affected where a+ is the allele for pigmentation. A mother with genotype a+ /a and a father with genotype aa will produce a progeny which is
A disease is inherited to the next generation only through the mother. The inheritance will be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two albino individuals marry and start a family. Their first child is normal in pigmentation. Is infidelity suspected and why/why not?
In a polygenic trait, 4 gene pairs were involved. How many phenotypic classes would you expect in the F2 generation?
In humans, which of the following is a primary determinant of maleness?
Two siblings who inherit 50% of the genome from the mother and 50% from the father show lot of phenotypic differences. Which one of the following events during gametogenesis of the parents will maximally contribute to the difference?
In Limnaea peregra, shell coiling is due to maternal effect. If the female parent is dextral (dd) and the male parent is sinistral (dd), the progeny would be
Blood group type A antigen is a complex oligosaccharide which differs from H antigen present in type O individuals by the presence of terminal
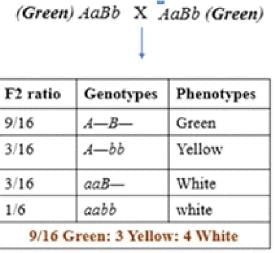
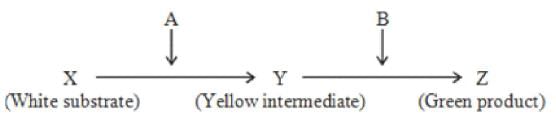
Following is a hypothetical biochemical pathway responsible for pigmentation of leaves. The pathway is controlled by two independently assorting genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ encoding enzymes as shown below. Mutant alleles ‘a’ and ‘b’ code for non-functional proteins
What is the expected progeny after selfing a plant with the genotypes AaBb?
Which of the following can result in Down Syndrome in an individual?
In which case will the heterozygous individual (Aa) have a phenotype different from the homozygous dominant individual (aa)?
Compensation loop is formed when homologues of a chromosome pair. During which of the following events would a compensation loop form?
In a cross between two F1 heterozygous tall plants, the F2 progeny consisted of tall and dwarf plants in the ratio 3 : 1. The probability that out of 7 plants chosen at random, 4 would be tall and 3 would be dwarf ______________ (answer upto 3 decimal points)
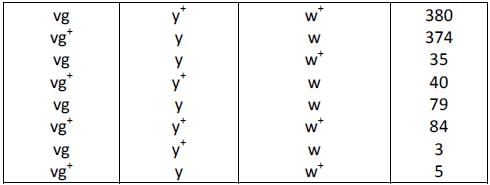
In a Drosophila, three recessive mutations can lead to white eyes, yellow body and vestigial wings. A heterozygous fly is crossed with a fly recessive for all these mutations. Using the following data, the distance between the gene for wing shape and eye color would be ________cM. (Answer upto one point after decimal)
In a population of insects, the color brown (B) is dominant over the color white (b). 4% of all insects are white. The frequency of heterozygous individuals would be _________ (Answer upto two point after decimal)
A population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. If the frequency of a recessive allele for a certain hereditary trait is 0.30. In the next generation percentage of individuals expected to show the dominant trait would be_____%. (Answer in integer)