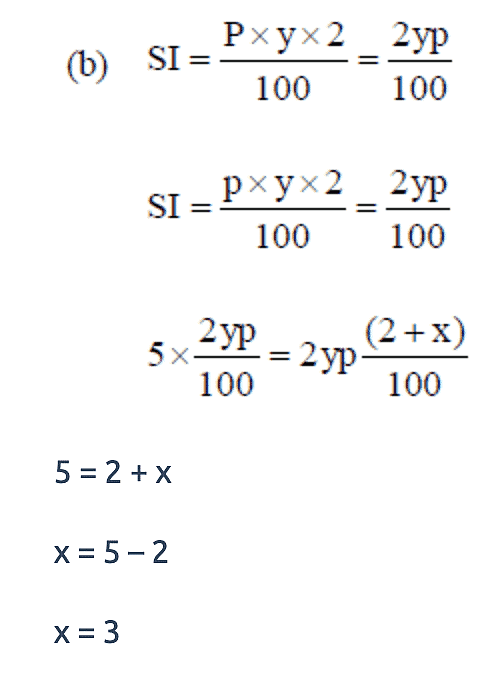HPPSC HPAS Prelims Paper 2 Mock Test - 2 - HPPSC HPAS (Himachal Pardesh) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test HPPSC HPAS Mock Test Series 2024 - HPPSC HPAS Prelims Paper 2 Mock Test - 2
What is a primary cause of urban flooding in India according to recent studies?
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), what is a likely future trend regarding monsoon rainfalls in South Asia?
What is the main objective of the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) Scheme launched by the Government of India?
Which of the following is a significant challenge associated with India's reliance on coal for energy needs?
What innovative approach is included in nature-based solutions to combat urban flooding?
What historical significance does Savitribai Phule hold in Indian society?
What is the primary aim of the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) launched by the Government of India?
Which of the following is NOT one of the five core themes of the Aspirational Districts Programme?
What role does NITI Aayog play in the Aspirational Districts Programme?
Which of the following is a significant challenge faced by the Aspirational Districts Programme?
Which of the following statements regarding the representation of women in the Indian judiciary is TRUE?
An amount is lent at y% p.a. simple interest for two years. Instead, had it been lent at 2y% p.a. simple interest for y more years, then the interest would have been five times the earlier interest. Find the value of y.
Passage 2
Focus should be on raising land productivity and water use efficiency. State specific strategies are needed. Dry areas need to focus on livestock. Most importantly, markets must be reformed. An important beginning has been made by granting statutory status to warehouse receipts. However, the real benefits from this measure can accrue only when the appropriate warehouse infrastructure and supporting backward linkages have been created and a nationwide trading platform has been put in place. Consideration should be given to extending infrastructure status to a wider range of agricultural market facilities in the same manner as for warehouses. States must modify the Essential Commodities Act (ECA) and the APMC Act (perhaps exclude horticulture and perishables entirely from the ambit of APMC), rebuild the extension system, increase the involvement of the private sector in marketing, and also facilitate leasing in/out of land by farmers. State agricultural universities and extension networks are in a bad shape and need strengthening.
MGNREGS has helped generate employment and income in rural areas but it can do much more to increase land productivity, particularly in rainfed areas. In addition, MGNREGS has transformed rural labour relations, which is bound to affect the production decisions of farmers, both in terms of crops as well as technologies. The agricultural support systems must facilitate this transition, which requires greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Q. Consider the following statements:
1. Currently the land productivity is quite low.
2. Appropriate warehouse infrastructure is potentially beneficial.
As per the above passage, which of the given statements is/are valid?
Passage 2
Focus should be on raising land productivity and water use efficiency. State specific strategies are needed. Dry areas need to focus on livestock. Most importantly, markets must be reformed. An important beginning has been made by granting statutory status to warehouse receipts. However, the real benefits from this measure can accrue only when the appropriate warehouse infrastructure and supporting backward linkages have been created and a nationwide trading platform has been put in place. Consideration should be given to extending infrastructure status to a wider range of agricultural market facilities in the same manner as for warehouses. States must modify the Essential Commodities Act (ECA) and the APMC Act (perhaps exclude horticulture and perishables entirely from the ambit of APMC), rebuild the extension system, increase the involvement of the private sector in marketing, and also facilitate leasing in/out of land by farmers. State agricultural universities and extension networks are in a bad shape and need strengthening.
MGNREGS has helped generate employment and income in rural areas but it can do much more to increase land productivity, particularly in rainfed areas. In addition, MGNREGS has transformed rural labour relations, which is bound to affect the production decisions of farmers, both in terms of crops as well as technologies. The agricultural support systems must facilitate this transition, which requires greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Q. Consider the following assumptions:
1. State agricultural universities have a room for improvement.
2. The current problem can be solved through market reforms alone.
With reference to the passage, which of the following assumptions is/are valid?
Passage 2
Focus should be on raising land productivity and water use efficiency. State specific strategies are needed. Dry areas need to focus on livestock. Most importantly, markets must be reformed. An important beginning has been made by granting statutory status to warehouse receipts. However, the real benefits from this measure can accrue only when the appropriate warehouse infrastructure and supporting backward linkages have been created and a nationwide trading platform has been put in place. Consideration should be given to extending infrastructure status to a wider range of agricultural market facilities in the same manner as for warehouses. States must modify the Essential Commodities Act (ECA) and the APMC Act (perhaps exclude horticulture and perishables entirely from the ambit of APMC), rebuild the extension system, increase the involvement of the private sector in marketing, and also facilitate leasing in/out of land by farmers. State agricultural universities and extension networks are in a bad shape and need strengthening.
MGNREGS has helped generate employment and income in rural areas but it can do much more to increase land productivity, particularly in rainfed areas. In addition, MGNREGS has transformed rural labour relations, which is bound to affect the production decisions of farmers, both in terms of crops as well as technologies. The agricultural support systems must facilitate this transition, which requires greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Q. Consider the following statements:
1. MGNREGS has not done much to increase land productivity
2. Transformation of rural labour relations influences production decisions of farmers With reference to the passage, which of the following statements is/are valid?
Directions for the following (one) item:
Read the following passage and answer the item that follow. Your answer to this item should be based on the passage only.
The impact of environmental disasters is immense but unequal. Houses in poorer areas will often be less stable, storm barriers may be weaker, sanitation is often a problem, emergency services will be poorly resourced - and preventing disease outbreaks may be hindered by the poor state of public health services.
Q. Which among the following is the most logical and essential message conveyed by the above passage?
Three taps A, B and C can fill a tank in 12, 15 and 20 hours respectively. If A is opened all the time and B and C are opened one hour each alternatively , the tank will be full in :
If a pipe A can fill a tank 3 times faster than pipe B. If both the pipes can fill the tank in 32 minutes, then the slower pipe alone will be able to fill the tank in?
A, B and C together earn Rs.300 per day, while A and C together earn Rs.188 and B and C together earn Rs.152. The daily earning of C is?
A alone can do a piece of work in 6 days and B alone in 8 days. A and B undertook to do it for Rs.3200. With the help of C, they completed the work in 3 days. How much is to be paid to C?
A and B together can complete a work in 12 days. A alone can complete it in 20 days. If B does the work only for half a day daily, then in how many days A and B together will complete the work?
Directions for the following (one) item:
Read the following passage and answer the item that follow. Your answer to this item should be based on the passage only.
As the planet warms, we need to be able to predict what populations will be at risk for infectious diseases because prevention is always superior to reaction. The researchers are now working on a map to pin point future changes in the distribution of vector-borne diseases.
Q. Which among the following is the most critical and rational inference that can be drawn from the above passage?
A, B and C can do a piece of work in 11 days, 20 days and 55 days respectively, working alone. How soon can the work be done if A is assisted by B on odd days and C on even days?
9 kids can finish a bit of work in 360 days. 18 men can finish the same work of piece in 72 days and 12 ladies can finish it in 162 days. In how long can 4 men, 12 ladies and 10 kids together finish the bit of work?
4 men and 6 women complete a piece of work in 8 days while 3 men and 7 women complete it in 10 days. In how many days 10 women can finish the work?
A works twice as fast as B. If two can together complete a bit of work in 12 days, then B alone can do it in:
In one minute 3/7 of a tank is filled. How much time will it take to fill the remaining part of the tank?
Read the information given below carefully and answer the following question.
The whole biosphere, like the individual organisms that live inside it, exists in a chemically dynamic state. In this homeostatic system, a great number of organic compounds are synthesized, transformed, and decomposed continuously; together, these processes constitute the major parts of the carbon cycle. For the smooth operation of this cycle, degradation is just as important as synthesis: the green plants produce great quantities of polymers, such as cellulose, and innumerable other compounds like alkaloids, terpenes, and flavonoids, that green plants cannot use as sources of energy during respiration. The release of the carbon in these compounds for recycling depends almost entirely on the action of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria and certain types of fungi. Some bacteria and fungi possess the unique and extremely important biochemical asset of being able to catalyse the oxidation of numerous inert products, thereby initiating reaction sequences that produce carbon dioxide and so return much carbon to a form that actively enters into life cycles once again.
Q. The passage contains information that would answer which of the following questions about the carbon cycle?
1. What are some of the compounds that are broken down in the carbon cycle?
2. Why are some compounds that are involved in the carbon cycle less reactive than others? 3. What role do bacteria and fungi play in the carbon cycle?
Read the information given below carefully and answer the following question.
The whole biosphere, like the individual organisms that live inside it, exists in a chemically dynamic state. In this homeostatic system, a great number of organic compounds are synthesized, transformed, and decomposed continuously; together, these processes constitute the major parts of the carbon cycle. For the smooth operation of this cycle, degradation is just as important as synthesis: the green plants produce great quantities of polymers, such as cellulose, and innumerable other compounds like alkaloids, terpenes, and flavonoids, that green plants cannot use as sources of energy during respiration. The release of the carbon in these compounds for recycling depends almost entirely on the action of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria and certain types of fungi. Some bacteria and fungi possess the unique and extremely important biochemical asset of being able to catalyse the oxidation of numerous inert products, thereby initiating reaction sequences that produce carbon dioxide and so return much carbon to a form that actively enters into life cycles once again.
Q. The author implies that which of the following is the primary reason that degradation is as important as synthesis to the smooth operation of the carbon cycle?
Based on the following bar graph. (Number of Industrial Townships in 1978 is 160000)
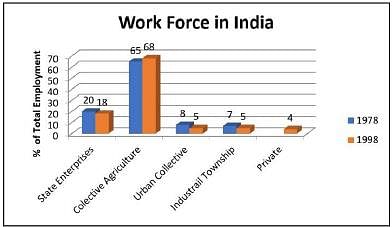
Which was the first year when people were employed in private enterprises?