History: CUET Mock Test - 6 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - History: CUET Mock Test - 6
Some aspects of the Harappan civilisation are as yet what?
Which of the following type of tax was collected during the Delhi Sultanate?
Who was the ruler of the Delhi Sultanate when it faced the Mongol onslaught?
Mark the year in which the first revenue settlement in Bombay Deccan took place?
Match List - I with List - II.
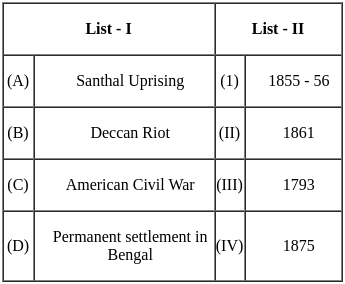
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Animal bones found at Harappan sites indicate that these animals were _________.
How were roads and streets laid out in the lower town?
What was often in a room that could be reached from the outside and perhaps used by passers-by?
What has been found in burials of both men and women?
Chemical analyses have shown that both Omani copper and Harappan artifacts have traces of what?
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement I: archaeological material is interpreted and how some aspects of the civilisation are as yet unknown and may even remain so.
Statement II: Archaeologists use the term “culture” for a group of objects, distinctive in style, that are not usually found together within a specific geographical area and period of time.
Statement III: see what we know about the Harappan civilisation and how we know it.
Which of the above Statement(s) is/are correct:
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement I: know a great deal about the lives of the people who lived in the region from what they left behind – their houses, pots, ornaments, tools, and seals – in other words, from archaeological evidence.
Statement II: The Harappan civilization is not sometimes called the Mature Harappan culture to distinguish it from them.
Statement III: The Indus valley civilisation is also called the Harappan culture.
Which of the above Statement(s) is/are correct:
What is an example of a Harappan artifact found in the Khatri region of Rajasthan?
Which routes along the Indus and its tributaries, as well as coastal routes, were probably used?
What were the hollowed-out spaces of burial pits lined with?
What was the center of cooking and weaving activities, especially during hot and dry weather?
|
8 docs|148 tests
|


















