Indian Air Force Agniveer Other than Science Subject Mock Test - 5 - Indian Air Force Agniveer Vayu MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Indian Air Force Agniveer Other than Science Subject Mock Test - 5
In the following questions four alternatives are given for the idiom/phrase italicised and underlined in the sentence. Choose the alternative which best expresses the meaning of idiom/phrase.
Q. The party stalwarts have advised the President to take it lying down for a while.
The year 1973… (1)… a watershed in the economic….(2)…..of young male high school graduates in the United States. In the twenty four years…(3).. to this date, the medium income of 25 to 34 year old males, ….(4)… highest level of educational attainment was a high school diploma, ……(5)…. from $14,483 to $24,482 (in constant 1987 dollars.) This increase was the ….(6)… of the rapid growth of the U.S. economy..(7)… this period. As the expression goes, the rapidly growing economy was like a rising tide that…(8)… all boats. This rapid…(9)… in income permitted several generations of young high-school educated men to enjoy a higher standard of living….(10)…their fathers had.
Q. Find the word most appropriate for Blank No. 10
Praise for Johnny Starstruck and his entourage are common, although statisticsshow Americans still associate his name with the ritualistic murders.
If seriously mentally ill people do not receive medication, they can grow unable tosupport themselves, become irrational, and perhaps even threatening the safetyof themselves or others.
If sentence (3), 'In most economic systems, the prices of the majority of goods and services do not change over short periods of time' is the first sentence, what is the order of other sentences after rearrangement?
1. In some, it is of course possible for an individual to bargain over prices, because they are not fixed in advance.
2. When planning his expenditure, he must therefore accept these fixed prices.
3. In most economic systems, the prices of the majority of goods and services do not change over short periods of time.
4. A consumer will go on buying bananas for as long as he continues to be satisfied.
5. If he buys more, he shows that his satisfaction is still greater than his dislike of losing money.
6. In general terms, however, the individual cannot change the prices of the commodities he wants.
Directions: Rearrange the following six sentences (1), (2), (3), (4), (5) and (6) in the proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph and then answer the question given below.
1. Officials of the Russian-American Company reasoned that a permanent settlement along the more temperate shores of California could serve both as a source of food and a base for exploiting the abundant sea otters in the region.
2. The Russians had begun their expansion into the North American continent in 1741 with a massive scientific expedition to Alaska.
3. By the early 19th century, the semi-governmental Russian-American Company was actively competing with British and American fur-trading interests as far south as the shores of Spanish-controlled California.
4. As a growing empire with a long Pacific coastline, Russia was in many ways well positioned to play a leading role in the settlement and development of the West.
5. Returning with news of abundant sea otters, the explorers inspired Russian investment in the Alaskan fur trade and some permanent settlement.
6. Russia's Alaskan colonists found it difficult to produce their own food because of the short growing season of the far north.
Q. Which of following is the FOURTH sentence after rearrangement?
The active voice sentence "The dog chased the cat" can be changed to passive voice as:
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Development is about expanding the capabilities of the disadvantaged, thereby improving their overall quality of life. Based on this understanding, Maharashtra, one of India’s richest States, is a classic case of a lack of development which is seen in its unacceptably high level of malnutrition among children in the tribal belts. While the State’s per capita income has doubled since 2004, its nutritional status has not made commensurate progress.
Poor nutrition security disproportionately affects the poorest segment of the population. According to NFHS 2015-16, every second tribal child suffers from growth restricting malnutrition due to chronic hunger. In 2005, child malnutrition claimed as many as 718 lives in Maharashtra’s Palghar district alone. Even after a decade of double digit economic growth (2004-05 to 2014-15), Palghar’s malnutrition status has barely improved.
In September 2016, the National Human Rights Commission issued notice to the Maharashtra government over reports of 600 children dying due to malnutrition in Palghar. The government responded, promising to properly implement schemes such as Jaccha Baccha and Integrated Child Development Services to check malnutrition. Our independent survey conducted in Vikramgad block of the district last year found that 57%, 21% and 53% of children in this block were stunted, wasted and underweight, respectively; 27% were severely stunted. Our data challenges what Maharashtra’s Women and Child Development Minister said in the Legislative Council in March — that “malnutrition in Palghar had come down in the past few months, owing to various interventions made by the government.”
Stunting is caused by an insufficient intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. It is generally accepted that recovery from growth retardation after two years is only possible if the affected child is put on a diet that is adequate in nutrient requirements. A critical aspect of nutrient adequacy is diet diversity, calculated by different groupings of foods consumed with the reference period ranging from one to 15 days. We calculated a 24-hour dietary diversity score by counting the number of food groups the child received in the last 24 hours. The eight food groups include: cereals, roots and tubers; legumes and nuts; dairy products; flesh foods; eggs; fish; dark green leafy vegetables; and other fruits and vegetables.
In most households it was rice and dal which was cooked most often and eaten thrice a day. These were even served at teatime to the children if they felt hungry. There was no milk, milk product or fruit in their daily diets. Even the adults drank black tea as milk was unaffordable. Only 17% of the children achieved a minimum level of diet diversity — they received four or more of the eight food groups. This low dietary diversity is a proxy indicator for the household’s food security too as the children ate the same food cooked for adult members.
Q. As per the passage, which of the following is/are needed for an adequate meal?
I. Macro and micro nutrients
II. Multiple food groups
III. High level of Intermittent fasting
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Development is about expanding the capabilities of the disadvantaged, thereby improving their overall quality of life. Based on this understanding, Maharashtra, one of India’s richest States, is a classic case of a lack of development which is seen in its unacceptably high level of malnutrition among children in the tribal belts. While the State’s per capita income has doubled since 2004, its nutritional status has not made commensurate progress.
Poor nutrition security disproportionately affects the poorest segment of the population. According to NFHS 2015-16, every second tribal child suffers from growth restricting malnutrition due to chronic hunger. In 2005, child malnutrition claimed as many as 718 lives in Maharashtra’s Palghar district alone. Even after a decade of double digit economic growth (2004-05 to 2014-15), Palghar’s malnutrition status has barely improved.
In September 2016, the National Human Rights Commission issued notice to the Maharashtra government over reports of 600 children dying due to malnutrition in Palghar. The government responded, promising to properly implement schemes such as Jaccha Baccha and Integrated Child Development Services to check malnutrition. Our independent survey conducted in Vikramgad block of the district last year found that 57%, 21% and 53% of children in this block were stunted, wasted and underweight, respectively; 27% were severely stunted. Our data challenges what Maharashtra’s Women and Child Development Minister said in the Legislative Council in March — that “malnutrition in Palghar had come down in the past few months, owing to various interventions made by the government.”
Stunting is caused by an insufficient intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. It is generally accepted that recovery from growth retardation after two years is only possible if the affected child is put on a diet that is adequate in nutrient requirements. A critical aspect of nutrient adequacy is diet diversity, calculated by different groupings of foods consumed with the reference period ranging from one to 15 days. We calculated a 24-hour dietary diversity score by counting the number of food groups the child received in the last 24 hours. The eight food groups include: cereals, roots and tubers; legumes and nuts; dairy products; flesh foods; eggs; fish; dark green leafy vegetables; and other fruits and vegetables.
In most households it was rice and dal which was cooked most often and eaten thrice a day. These were even served at teatime to the children if they felt hungry. There was no milk, milk product or fruit in their daily diets. Even the adults drank black tea as milk was unaffordable. Only 17% of the children achieved a minimum level of diet diversity — they received four or more of the eight food groups. This low dietary diversity is a proxy indicator for the household’s food security too as the children ate the same food cooked for adult members.
Q. What is ironical about the situation mentioned in paragraph 1?
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Development is about expanding the capabilities of the disadvantaged, thereby improving their overall quality of life. Based on this understanding, Maharashtra, one of India’s richest States, is a classic case of a lack of development which is seen in its unacceptably high level of malnutrition among children in the tribal belts. While the State’s per capita income has doubled since 2004, its nutritional status has not made commensurate progress.
Poor nutrition security disproportionately affects the poorest segment of the population. According to NFHS 2015-16, every second tribal child suffers from growth restricting malnutrition due to chronic hunger. In 2005, child malnutrition claimed as many as 718 lives in Maharashtra’s Palghar district alone. Even after a decade of double digit economic growth (2004-05 to 2014-15), Palghar’s malnutrition status has barely improved.
In September 2016, the National Human Rights Commission issued notice to the Maharashtra government over reports of 600 children dying due to malnutrition in Palghar. The government responded, promising to properly implement schemes such as Jaccha Baccha and Integrated Child Development Services to check malnutrition. Our independent survey conducted in Vikramgad block of the district last year found that 57%, 21% and 53% of children in this block were stunted, wasted and underweight, respectively; 27% were severely stunted. Our data challenges what Maharashtra’s Women and Child Development Minister said in the Legislative Council in March — that “malnutrition in Palghar had come down in the past few months, owing to various interventions made by the government.”
Stunting is caused by an insufficient intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. It is generally accepted that recovery from growth retardation after two years is only possible if the affected child is put on a diet that is adequate in nutrient requirements. A critical aspect of nutrient adequacy is diet diversity, calculated by different groupings of foods consumed with the reference period ranging from one to 15 days. We calculated a 24-hour dietary diversity score by counting the number of food groups the child received in the last 24 hours. The eight food groups include: cereals, roots and tubers; legumes and nuts; dairy products; flesh foods; eggs; fish; dark green leafy vegetables; and other fruits and vegetables.
In most households it was rice and dal which was cooked most often and eaten thrice a day. These were even served at teatime to the children if they felt hungry. There was no milk, milk product or fruit in their daily diets. Even the adults drank black tea as milk was unaffordable. Only 17% of the children achieved a minimum level of diet diversity — they received four or more of the eight food groups. This low dietary diversity is a proxy indicator for the household’s food security too as the children ate the same food cooked for adult members.
Q. Which of the following strengthen the claim that the nutrition indicators fare poorly in India?
I. Stunting declined from 46.3% in 2005 to 34.4% in 2016.
II. As per an NHFS survey, wasting rates have increased from 16.5% to 25.6% over a period of 10 years.
III. The underweight rate (36%) has remained static in the last 10 years.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
Development is about expanding the capabilities of the disadvantaged, thereby improving their overall quality of life. Based on this understanding, Maharashtra, one of India’s richest States, is a classic case of a lack of development which is seen in its unacceptably high level of malnutrition among children in the tribal belts. While the State’s per capita income has doubled since 2004, its nutritional status has not made commensurate progress.
Poor nutrition security disproportionately affects the poorest segment of the population. According to NFHS 2015-16, every second tribal child suffers from growth restricting malnutrition due to chronic hunger. In 2005, child malnutrition claimed as many as 718 lives in Maharashtra’s Palghar district alone. Even after a decade of double digit economic growth (2004-05 to 2014-15), Palghar’s malnutrition status has barely improved.
In September 2016, the National Human Rights Commission issued notice to the Maharashtra government over reports of 600 children dying due to malnutrition in Palghar. The government responded, promising to properly implement schemes such as Jaccha Baccha and Integrated Child Development Services to check malnutrition. Our independent survey conducted in Vikramgad block of the district last year found that 57%, 21% and 53% of children in this block were stunted, wasted and underweight, respectively; 27% were severely stunted. Our data challenges what Maharashtra’s Women and Child Development Minister said in the Legislative Council in March — that “malnutrition in Palghar had come down in the past few months, owing to various interventions made by the government.”
Stunting is caused by an insufficient intake of macro- and micro-nutrients. It is generally accepted that recovery from growth retardation after two years is only possible if the affected child is put on a diet that is adequate in nutrient requirements. A critical aspect of nutrient adequacy is diet diversity, calculated by different groupings of foods consumed with the reference period ranging from one to 15 days. We calculated a 24-hour dietary diversity score by counting the number of food groups the child received in the last 24 hours. The eight food groups include: cereals, roots and tubers; legumes and nuts; dairy products; flesh foods; eggs; fish; dark green leafy vegetables; and other fruits and vegetables.
In most households it was rice and dal which was cooked most often and eaten thrice a day. These were even served at teatime to the children if they felt hungry. There was no milk, milk product or fruit in their daily diets. Even the adults drank black tea as milk was unaffordable. Only 17% of the children achieved a minimum level of diet diversity — they received four or more of the eight food groups. This low dietary diversity is a proxy indicator for the household’s food security too as the children ate the same food cooked for adult members.
Q. What could possibly be a/some possible reason/s for such extreme food insecurity among tribal households as has been shown in the passage?
I. Loss of their traditional dependence on forest livelihood.
II. Weak implementation of public nutrition schemes.
III. A worsening agriculture situation.
Directions: Out of the given alternatives, choose the one which can be substituted for the given words/sentence.
A person who is womanish in his habits
Who was the Viceroy of India when the Rowlatt Act was passed?
Find the rate of interest if the amount after 2 years of simple interest on a capital of Rs. 1200 is Rs. 1440.
?, 6, 10.5, 23, 60
Find the 4-digit smallest number which when divided by 12, 15, 25, 30 leaves no remainder?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
ZRYQ : KCJB :: PWOV : ?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions two statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered (1) and (2). You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
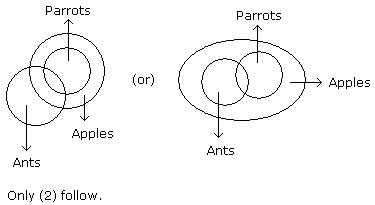
Question -
Statements: Some ants are parrots. All the parrots are apples.
Conclusions:
- All the apples are parrots.
- Some ants are apples.
Directions to Solve
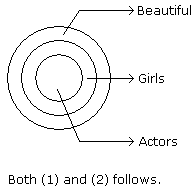
In each of the following questions two statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered (1) and (2). You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Question -
Statements: All the actors are girls. All the girls are beautiful.
Conclusions:
- All the actors are beautiful.
- Some girls are actors.
If A + B means A is the brother of B; A - B means A is the sister of B and A x B means A is the father of B. Which of the following means that C is the son of M?
Find the one which does not belong to that group ?
In human body, Vitamin A is stored in the
The Thar Express goes to –
Which of the following trends were seen in the Indian economy after the 1991 economic reforms?
1. The growth rate steadily increased.
2. Agriculture and allied sector continuously show a positive growth rate.
3. Share of the public sector in total investment increased.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A dishonest milkman mixes 20 litres of water with 80 litres of milk. After selling one-fourth of this mixture, he adds water to replenish the quantity that he had sold. What is the current proportion of water to milk?
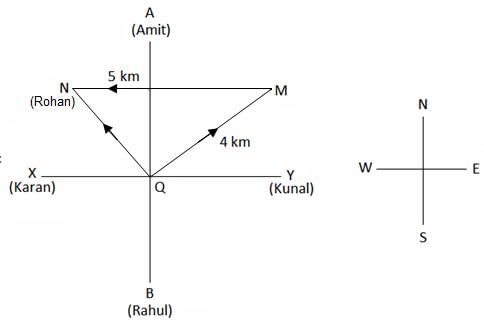
Directions: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
There are two axes AB and XY such that A is in north, B is in south, X is in west and Y is in east. Q is the point of intersection of both the axes. At A, B, X and Y, there are houses of 4 friends - Amit, Rahul, Karan and Kunal, respectively. Another friend Rohan is standing at the point 'Q' facing north-east direction. He then walks 4 km in the same direction which he is facing and reaches 'M'. Then he turns 135° anticlockwise and walks 5 km straight and reaches 'N'. Amit starts walking towards south from his house and reaches point Q. After reaching Q, Rohan tells Amit to meet him at N; so Amit travels the shortest distance possible to reach N in the end where he meets Rohan.
Q. Point 'M' is in which direction with respect to Rahul's house?
What is the objective of the NCC Integrated Software launched by Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh?
Direction : Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
Q: In a certain code RAIN is written as TCKP. How is CLOUD written in that code?
Direction : Study the following question carefully and choose the right answer.
Q: If in a code language ‘PUTREFY’ is written as ‘XPQSTRL’ and ‘NAVIGATE’ is written as ‘GYMOWYQT’ how is ‘AVIARY’ written in that language?