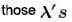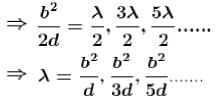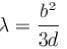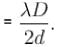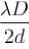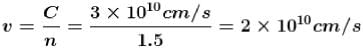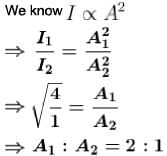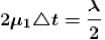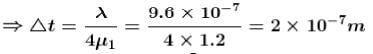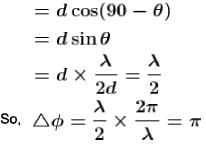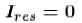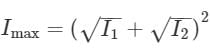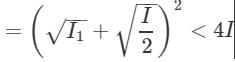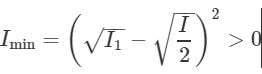OneTime: Interference MCQ Level -2 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - OneTime: Interference MCQ Level -2
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities l and 4I are superposed the maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are :
White light is used to illuminate the two slits in a young’s double slit experiment. The separation between the slit is b and the screen is at a distance d (>> b ) from the slits. At a point on the screen directly in front of one of the slits, certain wavelengths are missing. Some of these missing wavelengths are :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The distance of nth bright fringe to the (n + 1) dark fringe in Young’s experiment is equal to :
A light of frequency 5 x 1014 Hz enters a medium of refractive index 1.5. In this medium, the velocity of light wave is.
Ratio of intensities of two light waves is given by 4 :1. The ratio of the amplitudes of the waves is :
In a Fresnel biprism experiment, the two positions of lens given separation between the slits as 16 cm and 9 cm respectively. What is the actual distance of separation?
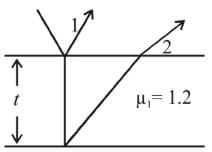
A thin oil film of refractive index 1.2 floats on the surface of water  When a light of wavelength λ = 9.6 x 10-7 m falls normally on the film from air, then it appears dark when seen normally. The minimum change in its thickness for which it will appear bright in normally reflected light by the same light is :
When a light of wavelength λ = 9.6 x 10-7 m falls normally on the film from air, then it appears dark when seen normally. The minimum change in its thickness for which it will appear bright in normally reflected light by the same light is :
A parallel beam of monochromatic light is used in a Young’s double slit experiment. The slits are separated by a distance d and the screen is placed parallel to the plane of the slits. If the incident beam makes an angle 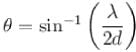 with the normal to the plane of the slits, find the intensity of the geometrical centre p0.
with the normal to the plane of the slits, find the intensity of the geometrical centre p0.
If one of the slits of a standard Young’s double slit experiment is covered by a thin parallel sided glass slab so that it transmits only one half the light intensity of the other, then :
A young’s double slit experiment is performed with white light:


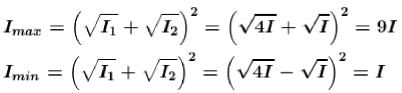
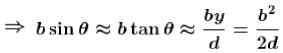

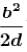 will be odd multiple of
will be odd multiple of 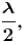 ,
,