Ionic Equilibrium MCQ - 1 (Advance) - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Ionic Equilibrium MCQ - 1 (Advance)
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
A 2.5 gm impure sample containing weak monoacidic base (Mol. wt. = 45) is dissolved in 100 ml water and titrated with 0.5 M HCl when 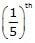 of the base was neutralised the pH was found to be 9 and at equivalent point pH of solution is 4.5. Given : All data at 25º C & log 2 = 0.3.
of the base was neutralised the pH was found to be 9 and at equivalent point pH of solution is 4.5. Given : All data at 25º C & log 2 = 0.3.
Select correct statement(s).
Which of the following is true for alkaline aqueous solution?
Ionisation constant of formic acid is 1.8 * 1.8*10−4 at 298 K. In 0.1 NHCOOH the percentage ionisation of HCOOH acid is
A solution contains HCl, Cl2HC COOH & CH3COOH at concentation 0.09 M in HCl, 0.09 M in Cl2HC COOH & 0.1 M in CH3COOH. pH for the solution is 1. Ionization constant of CH3COOH = 105. What is the magnitude of K for dichloroacetic acid ?
A solution of chloroacetic acid, ClCH2COOH containing 9.45 grams in 500 ml of the solution has a pH of 2.0. What is the degree of ionization the acid.
The Kw of water at two different temperature is :
Assuming that ΔH of any reaction is independent of temperature, calculate the enthalpy of neutralization of strong acid and strong base.
The equilibrium constant of the reaction.
2Ag(s) + 2I- + 2H2O 2Agl(s) + H2(g) + 2OH-
is 1.2 × 10-23 at 25°C. Calculate the pH of a solution at equilibrium with the iodine ion concentation = 0.10 and the pressure of H2 gas = 0.60 atm.
When a 40 mL of a 0.1 M weak base in titrated with 0.16 M HCl, the pH of the solution at the end point is 5.23. What will be the pH if 15 mL of 0.12 M NaOH is added to the resulting solution.
How many moles of sodium hydroxide can be added to 1.00 L of a solution 0.1 M in NH3 & 0.1 M in NH4Cl without changing the pOH by mor than 1.00 unit ? Assume no change in volume. Kb(NH3) = 1.8 × 10-5.
20 ml of a solution of 0.1 M CH3COOH solution is being titrated against 0.1 M NaOH solution. The pH vaues after the addition of 1 ml & 19 ml of NaOH are (pH)1 & (pH)2, what is ΔpH ?
Calculate the OH- concentration and the H3PO4 concentration of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.1 mol f Na3PO4 in sufficient water to make 1 l of solution. K1 = 7.1 × 10-3, K2 = 6.3 × 10-8, K3 = 4.5 × 10-13.
Solubility product of AgCl is 2.8 × 10-10 at 25ºC. Calculate solubility of the salt in 0.1 M AgNO3 solution -
Equilibrium constant for the acid ionization of Fe3+ to Fe(OH)+2 and H+ is 6.5 × 10-3. What is the max. pH, which could be used so that at least 95% of the total Fe3+ in a dilute solution. exists are Fe3+.
A solution of weak acid HA was titrated with base NaOH. The equivalence point was reaced when 36.12 ml of 0.1 M NaOH has been added. Now 18.06 ml of 0.1 M HCl were added to titration solution, the pH was found to be 4.92. What will be the pH of the solution obtained by mixing 10 ml 0.2 M NaOH and 10 ml of 0.2 M HA.
A weak base BOH was titrated against a strong acid. The pH at 1/4 the equivalence point was 9.24. Enough strong base was now added (6m eq.) to completely convert the salt. The total volume was 50 ml. Find the pH at this point.
At 25°C, will a precipitate of Mg(OH)2 form in a 10-4 M solution of Mg(NO3)2 if pH of the solution is adjusted to 9.0. Ksp [Mg(OH)2] = 10-11 M3. At what min value of pH will precipitation start.
What is the solubility of AgCl in 0.20 M NH3 ?
Given : Ksp(AgCl) = 1.7 × 10-10 M2, K1 = [Ag(NH3)+] / [Ag+] [NH3] = 2.33 × 103M-1 and
K2 = [Ag(NH3)2+] / [Ag (NH3)+ [NH3] = 7.14 × 103 M-1
Equal volumes of 0.02 M AgNO3 and 0.02 M HCN were mixed. Calculate [Ag+] at equilibrium. Take Ka(HCN) = 9 × 10-10, Ksp (AgCN) =4 × 10-6.



















