JEE Advanced 2017 Paper - 2 with Solutions - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced 2017 Paper - 2 with Solutions
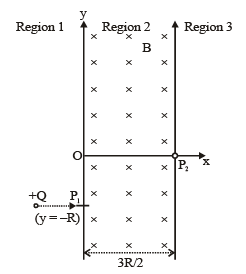
A uniform magnetic field B exists in the region between x = 0 and x = 3R/2 (region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge +Q and momentum p directed along x-axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1(y = –R). Which of the following options(s) is/are correct ?
A rocket is launched normal to the surface of the Earth, away from the Sun, along the line joining the sun and the Earth. The Sun is 3 × 105 times heavier than the Earth and is at a distance 2.5 ×104 times larger than the radius of the Earth. The escape velocity from Earth's gravitational field is ve = 11.2 km s–1. The minimum initial velocity (vs) required for the rocket to be able to leave the SunEarth system is closest to (Ignore the rotation and revolution of the Earth and the presence of any other planet)
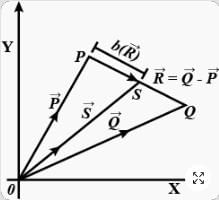
Three vectors  and
and  are shown in the figure. Let S be any point on the vector
are shown in the figure. Let S be any point on the vector  The distance between the points P and S is
The distance between the points P and S is 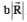 The general relation among vectors
The general relation among vectors 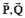 and
and 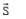 is :
is :

A symmetric star shaped conducting wire loop is carrying a steady state current I as shown in the figure. The distance between the diametrically opposite vertices of the star is 4a. The magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the loop is :
A photoelectric material having work-function φ0 is illuminated with light of wavelength The fastest photoelectron has a de-Broglie wavelength λd. A change in wavelength of the incident light by Δλ results in a change Δλd in λd. Then the ratio Δλd / Δλ is proportional to
A person measures the depth of a well by measuring the time interval between dropping a stone and receiving the sound of impact with the bottom of the well. The error in his measurement of time is δT = 0.01 second and he measures the depth of the well to be L = 20 meters. Take the acceleration due to gravity g = 10 ms–2and the velocity of sound is 300 ms–1. Then the fractional error in the measurement, δL/L, is closest to
Consider an expanding sphere of instantaneous radius R whose total mass remains constant. The expansion is such that the instantaneous density r remains uniform throughout the volume. The rate of fractional change in density is constant. The velocity v of any point on the surface of the expanding sphere is proportional to :
Consider regular polygons with number of sides n = 3, 4, 5 ..... as shown in the figure. The center of mass of all the polygons is at height h from the ground. They roll on a horizontal surface about the leading vertex without slipping and sliding as depicted. The maximum increase in height of the locus of the center of mass for each polygon is Δ. Then Δ depends on n and h as :
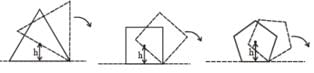
A rigid uniform bar AB of length L is slipping from its vertical position on a frictionless floor (as shown in the figure). At some instant of time, the angle made by the bar with the vertical is q. Which of the following statements about its motion is/are correct ?
Two coherent monochromatic point sources S1 and S2 of wavelength λ = 600 nm are placed symmetrically on either side of the center of the circle as shown. The sources are separated by a distance d = 1.8mm. This arrangement produces interference fringes visible as alternate bright and dark spots on the circumference of the circle. The angular separation between two consecutive bright spots is Δθ. Which of the following options is/are correct ?
A source of constant voltage V is connected to a resistance R and two ideal inductors L1 and L2 through a switch S as shown. There is no mutual inductance between the two inductors. The switch S is initially open. At t = 0, the switch is closed and current begins to flow. Which of the following options is/ are correct?
A wheel of radius R and mass M is placed at the bottom of a fixed step of height R as shown in the figure. A constant force is continuously applied on the surface of the wheel so that it just climbs the step without slipping. Consider the torque τ about an axis normal to the plane of the paper passing through the point
Q. Which of the following options is/are correct ?
The instantaneous voltages at three terminals marked X, Y and Z are given by
An ideal voltmeter is configured to read rms value of the potential difference between its terminals. It is connected between points X and Y and then between Y and Z. The reading(s) of the voltmeter will be:-
A point charge +Q is placed just outside an imaginary hemispherical surface of radius R as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is/are correct ?
PARAGRAPH–1
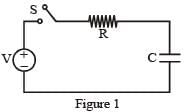
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.
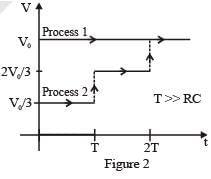
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to
without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.
Q. In Process 1, the energy stored in the capacitor EC and heat dissipated across resistance ED are related by :-
PARAGRAPH–1
Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e., charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then the voltage is raised to
without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1. These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.


Q. In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is :-
PARAGRAPH -2
One twirls a circular ring (of mass M and radius R) near the tip of one's finger as shown in Figure 1. In the process the finger never loses contact with the inner rim of the ring. The finger traces out the surface of a cone, shown by the dotted line. The radius of the path traced out by the point where the ring and the finger is in contact is r. The finger rotates with an angular velocity w0. The rotating ring rolls without slipping on the outside of a smaller circle described by the point where the ring and the finger is in contact (Figure 2). The coefficient of friction between the ring and the finger is µ and the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Q. The total kinetic energy of the ring is :-
PARAGRAPH -2
One twirls a circular ring (of mass M and radius R) near the tip of one's finger as shown in Figure 1. In the process the finger never loses contact with the inner rim of the ring. The finger traces out the surface of a cone, shown by the dotted line. The radius of the path traced out by the point where the ring and the finger is in contact is r. The finger rotates with an angular velocity w0. The rotating ring rolls without slipping on the outside of a smaller circle described by the point where the ring and the finger is in contact (Figure 2). The coefficient of friction between the ring and the finger is µ and the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Q.
The minimum value of w0 below which the ring will drop down is :-
Three randomly chosen non negative int egers x, y and z are found to satisfy the equat ion x + y + z = 10. Then the probability that z is even, is
Let S = {1, 2, 3,.....,9}. For k = 1,2, ....., 5, let Nk be the number of subsets of S, each containing five elements out of which exactly k are odd. Then N1 + N2 + N3 + N5 =
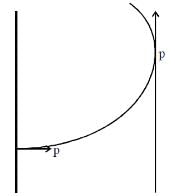
If ƒ :R → R is a twice differentiable function such that f''(x) > 0 for all x ∈ R, and then
If y = y(x) satisfies the differential equation 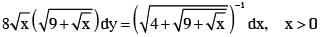 and y(0) =
and y(0) = 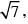 then y(256) =
then y(256) =
How many 3 × 3 matrices M with entries from {0,1,2} are there, for which the sum of the diagonal entries of MTM is 5 ?
Let O be the or igin and let PQR be an arbitrary triangl e. The point S issu ch that Then the triangle PQR has S as its
The equation of the plane passing through the point (1,1,1) and perpendicular to the planes 2x + y – 2z = 5 and 3x – 6y – 2z = 7, is
If ƒ : R → R is a differentiable function such that f"(x) > 2f(x) for all x ∈ R, and f(0) = 1, then
Let a and b be nonzero real numbers such that 2(cosβ - cosα) + cosα cosβ = 1. Then which of the following is/are true ?



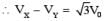
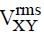
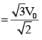
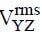
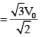

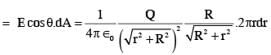
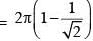
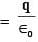
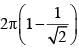 solid angle
solid angle 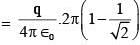
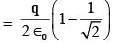
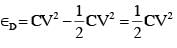 .........(ii)
.........(ii)
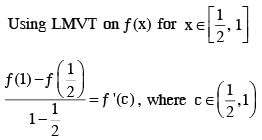
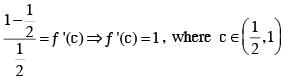
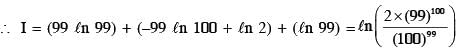 .... (1)
.... (1)










