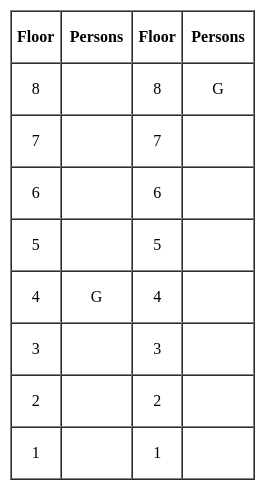
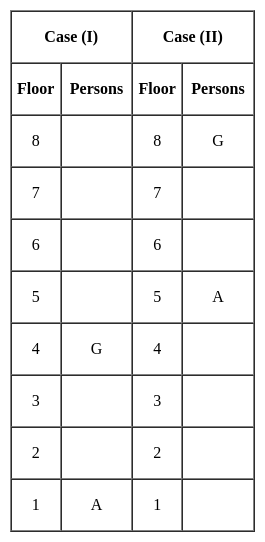
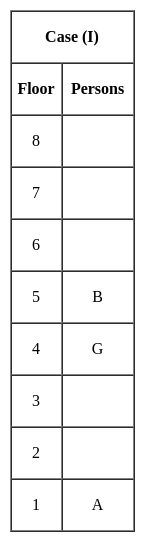
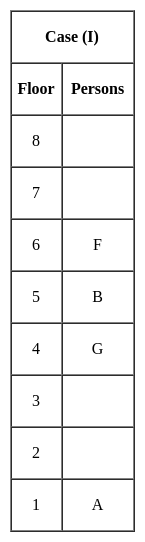
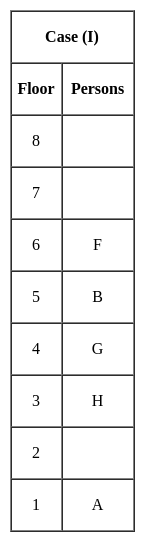
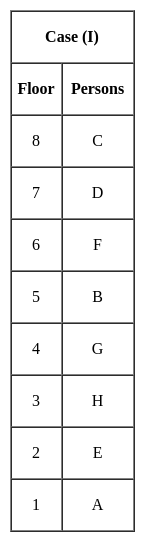
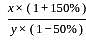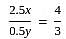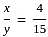Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 2 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2025 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 2
Which river originates near Ranchi, the capital of Jharkhand?
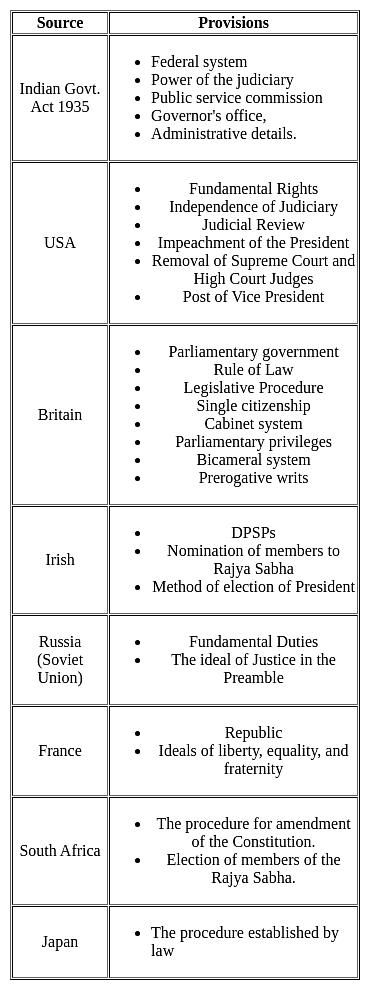
Which of the following provision is not borrowed by the Indian Constitution from the Canadian Constitution?
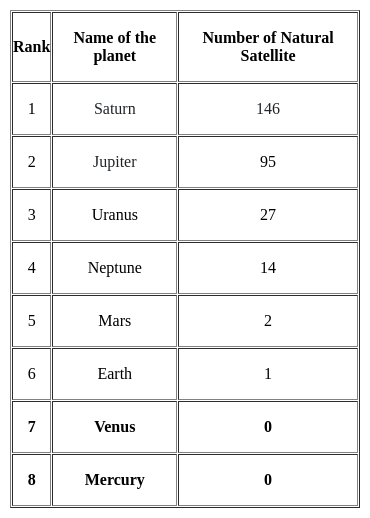
Which of the following planet/planets in the solar system have no satellite?
As per the 2011 census, which state has the highest literacy in India?
The Ganga-Brahmaputra delta is famous for _____________.
Consider the following pairs:
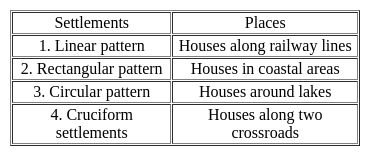
Which of the pairs above is/are correctly matched?
Which of the following contribute to pollution?
A. Thermal power plant
B. Automobiles
C. Hydroelectric power plant
D. Nuclear power plant
Which of the following statements are correct with respect to elections in the Parliament of India?
1. The minimum age of contesting in Lok sabha elections is 21 years.
2. In case a person is simultaneously elected to the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, he must intimate his choice to the ECI within 30 days.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Vaibhav can do a piece of work in 30 days. Pankaj can do the same work in 10 days. Both Vaibhav and Pankaj together finish the work and get Rs. 300. Calculate the share of both Vaibhav and Pankaj each.
When the numerator of a fraction is increased by 150% and the denominator is decreased by 50%, the fraction becomes 4/3. What is the original fraction?
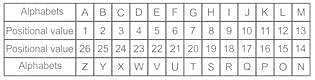
In a certain code language. 'AJDM' is written as 'JDMA'. How will 'SKWM' be written in that language?
What will come in the place of question mark (?) in each of the following number series?
45, 99, 62, 112, 81, ?, 102




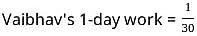
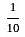
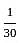 :
: 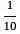 = 1 : 3
= 1 : 3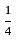 × 300 = Rs. 75
× 300 = Rs. 75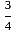 × 300 = Rs. 225
× 300 = Rs. 225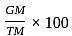 (Where, GM = Gain marks and TM = Total marks)
(Where, GM = Gain marks and TM = Total marks)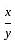 .
.