Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 3 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 3
Recently, which of the following states has approved the State sector 'Interest Subsidy-Subvention' scheme to give interest-free crop loans of up to Rs. 1 lakh to farmers?
Which lake of India is the result of tectonic activity?
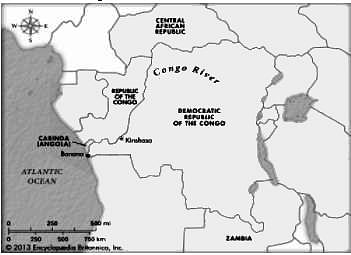
Which one of the following rivers crosses the Equator twice ?
The Guptas issued silver coins known as:
What was the real intention of British Government behind the partition of Bengal?
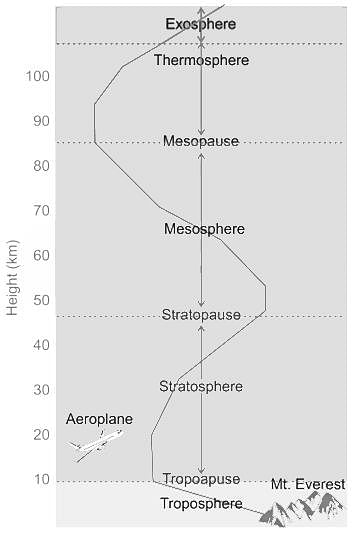
Which one of the following is correct order of layers in atmosphere?
Consider the following Islands:
1. Scarborough Shoal
2. Spratly Islands
3. Paracel Islands
4. Senkaku Islands
Which of the above-mentioned Islands are located in the South China Sea?
Consider the following statements with respect to the source of energy.
1. Coal, Natural Gas, and Firewood are examples of conventional sources of energy.
2. Wind, Solar, and Tidal are examples of non-conventional sources of energy.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
The ratio of present ages of Kajal and Ajay is 5:4. After 13 years the ratio of their ages will be 6:5. What is the present age of Kajal ?