Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT Exam > Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT Tests > Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 > Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT 2025 is part of Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 preparation. The Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT exam syllabus.The Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 MCQs are made for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 below.
Solutions of Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 questions in English are available as part of our Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT & Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 solutions in
Hindi for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 | 200 questions in 180 minutes | Mock test for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 1
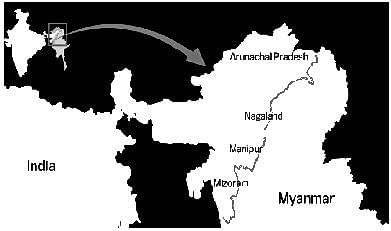
Which state does not share its boundary with Myanmar ?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 1
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 2
What is the 'quorum' required in the State Legislature to hold a meeting?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 2
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 3
First tribal leader who took arms in hand against Britishers was:
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 3
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 4
Who among the following was one of the founders of the Hindustan Republic Association?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 4
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 5
Recently, the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has informed that a cyclonic storm named "Cyclone Mocha" is developing over Bay of Bengal. Which of the following countries has named this cyclone?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 5
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 6
In 1775, who was appointed as a Civil Collector for Palamu, Ramgarh and Chhota Nagpur?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 6
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 7
Where has Jharkhand's first convention center been built recently?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 7
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 8
Who was handed over the conquered territories of Muhammad Ghori in India?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 8
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 9
Harsha was a distinguished patron of which university?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 9
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 10
Match the following with appropriate choices:
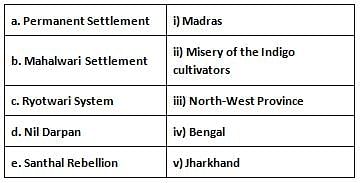
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 11
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 12
Which one of the following sea ports has natural harbour?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 12
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 13
Consider the following factors:
1. Rainfall
2. Topography
3. Soil
4. Temperature
5. Altitude
Which of the above influences natural vegetation of a given location?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 13
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 14
What is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake called?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 14
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 15
Which of the following is responsible for the formation of the Northeast Monsoon in India?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 15
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 16
Which of the following statements regarding the Deccan Plateau is NOT correct?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 16
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 17
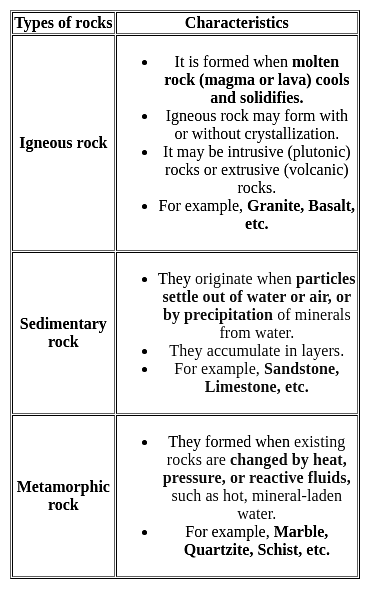
Which of the following is not a metamorphic rock?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 17
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 18
Which part of the Indian constitution has been described as the soul of the constitution?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 18
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 19
Where in the Constitution the provision for constitution of panchayats has been provided?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 19
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 20
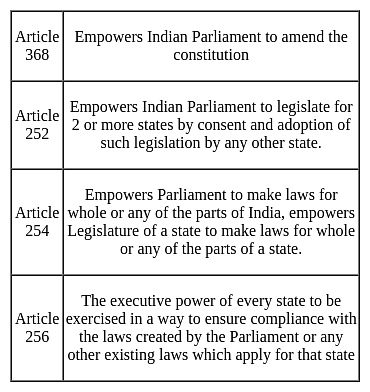
Which Article of Indian Constitution empowers Indian Parliament to amend the constitution?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 20
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 21
According to the constitution of India ______.
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 21
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 22
The Constitution of India was written in ___________.
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 22
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 23
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 24
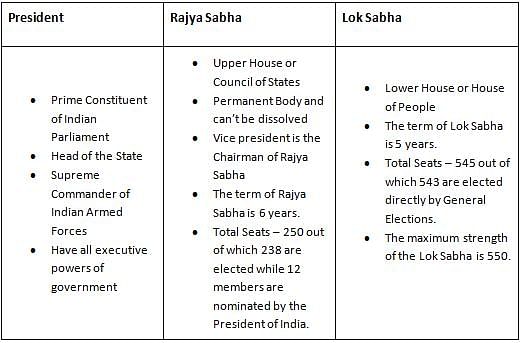
Which of the following is not a part of Parliament
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 24
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 25
Who presides over the Joint Session of Indian Parliament?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 25
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 26
10th schedule of the Constitution was added by which amendment of the constitution?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 26
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 27
Find P, if the average of 15, 26, 32, 41, P, 72 is 40 ?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 27
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 28
Ramu and Raju start running toward each other. Initially, the distance between each other is 234 m. The speed of Ramu and Raju is 52 m/s and 65 m/s respectively. So at what time will be meeting each other?
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 28
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 29
The second number in the given number performing certain mathematical operation(s) on the first number. The same operation(s) are followed in all the number pairs except one. Find that odd number pair.
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 29
Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 30
Which of the following answer figures will complete the pattern of the question figure?
Question figure:
Detailed Solution for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT Paper III Mock Test - 4, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice